- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
DECEMBER 15, 2025
Fourth National Lok Adalat of 2025 successfully resolved 2.59 crore disputes
- From 2022-23 to 2024-25, more than 23.5 crore cases have been resolved in various Lok Adalats across India.
Lok Adalat Framework
- Established: under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 to provide speedy and cost-effective justice as an Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanism.
- Objective: Reduce pendency (e.g. more than 4.7 crore pendency as per NJDG), promote consensual settlements, and strengthen access to justice.
- Authority: Organised by the NALSA with the CJI as Patron-in-Chief.
- Enforcement: Awards are final, binding, equivalent to a civil court decree, with no appeal provision.
- Scope: Covers pre-litigation and pending cases, excluding non-compoundable offences and divorce matters.
Types of Lok Adalats
- National Lok Adalat (NLA): Involve simultaneous, nationwide sittings on a single day at all levels of the judiciary, from the Supreme Court down to the Taluk Levels, aiming to clear a large volume of cases.
- Permanent Lok Adalat (PLA): Organized for cases related to Public Utility Services (e.g., transport, postal, telegraph, electricity, water supply) up to ₹ 1 Crore.
E-Lok Adalats and Mobile Lok Adalats:
- E-Lok Adalats allow for remote participation and bring justice through digital platforms.
- Mobile Lok Adalats are organized to travel from one location to another to resolve disputes.
NCAER Report on Employment
The National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) released a report titled “India’s Employment Prospects: Pathways to Jobs.”
- It highlights skilling and small enterprises as key drivers of job creation to sustain the 8% GDP growth.
- The report underlines the role of skilling and small enterprises as key drivers of job creation in the country.
- The NCAER is India’s oldest and largest independent, non-profit think tank. Established in New Delhi in 1956, it conducts evidence-based economic research to guide public policy.
Key Findings of the Report
- Employment Pattern: India’s recent employment growth is driven mainly by necessity-based self-employment in low-technology, subsistence household enterprises.
- Income Level: Despite economic growth, India’s per capita GDP is relatively low, ranking 128th globally.
- Skill Deficit: Transition to skilled labour has been slow; only 4.1% workers had vocational training in 2024, much less than in countries like Germany, Singapore, and Canada.
- Job Potential: A 9% rise in skilled workers could generate about 9.3 million jobs by 2030.
- Multiplier Effects: Moderate growth of labour-intensive sub-sectors could increase employment in manufacturing by 53% and in services by 79%.
Policy Recommendations for Job Creation
- PLI Reorientation: Redirect Production-Linked Incentives toward labour-intensive sectors like textiles, garments, footwear, and food processing.
- Service Sectors: Increase support for tourism, education, and healthcare to generate large-scale, employment-intensive job opportunities.
- Digital Adoption: Improve access to digital technologies and credit, as enterprises using digital technologies hire 78% more workers than non-digital firms.
Empanel Heritage Conservation Architects
- The Ministry of Culture has initiated a process to empanel heritage conservation architects for the upkeep, conservation, and restoration of ASI-protected monuments.
About Empanel Heritage Conservation Architects:
- A heritage (conservation) architect is a specialised professional trained in the restoration, conservation, and management of historic structures, ensuring preservation of architectural integrity, materials, and cultural value in line with established conservation norms.
The Initiative
- The Ministry of Culture has begun empanelling qualified conservation architects to form a national pool approved by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- This allows donors, corporates, and private entities to directly engage ASI-approved professionals for conservation works funded through the National Cultural Fund (NCF).
- Key Features of the Initiative
- Donor flexibility: Donors can choose architects from the ASI-approved panel for monuments of their choice.
- ASI oversight mandatory: ASI will continue to monitor all projects to ensure compliance with scientific conservation standards.
- Defined responsibilities: Empanelled architects will prepare Detailed Project Reports (DPRs), design conservation methods, provide project management support, and supervise execution.
- Execution mechanism: Actual restoration work will be carried out by agencies selected by donors, subject to ASI approval.
- Eligibility criteria: Architects must have prior experience in conserving or restoring heritage structures over 100 years old.
- Tenure: Empanelment valid for three years, with annual performance review.
Emperor Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II
- Prime Minister of India has welcomed the release of a commemorative postage-stamp honouring Emperor Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II (Suvaran Maran), recognising his administrative excellence and patronage of Tamil culture.
About Emperor Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II:
- Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II, also known as Suvaran Maran or Shatrubhayankar, was a prominent ruler of the Mutharaiyar lineage who ruled during c. 705–745 CE.
- Belonged to the Mutharaiyar dynasty, a powerful Tamil ruling lineage.
- Functioned as feudatories of the Pallavas, particularly under Pallava king Nandivarman II.
- Controlled the central Cauvery region, including Thanjavur, Tiruchirappalli, Pudukkottai, Perambalur, and surrounding areas.
- Ruled primarily from Tiruchirappalli, exercising authority for nearly four decades.
Key Contributions
Administrative & Military Achievements:
- Known as a formidable administrator with strategic foresight and governance stability.
- Fought several battles alongside Pallava forces, helping maintain regional order during Pallava decline.
Temple Building & Architecture:
- The Mutharaiyars were among the early temple builders of Tamil Nadu, contributing to rock-cut and structural temples.
- Their architectural innovations influenced the early Chola temple tradition, even before the rise of Vijayalaya Chola.
Cultural & Religious Patronage:
- Patronised Shaivism, while also hosting philosophical debates involving Jain scholars such as Acharya Vimalachandra, reflecting religious pluralism.
- Supported Tamil language, literature, and religious institutions, as evidenced by inscriptions.
Public Works:
- Inscriptions attest to his contributions to temple endowments, irrigation systems, and agrarian infrastructure, strengthening the Cauvery delta economy.
Significance
- Historical significance: Represents the rise of powerful regional chieftains during the weakening of imperial Pallava authority.
- Cultural legacy: Acts as a bridge between Pallava and Chola traditions, especially in temple architecture and governance.
- Social relevance: Revered as an icon by the Mutharaiyar community, classified among Most Backward Classes (MBCs) in Tamil Nadu.
|
About Pallava Dynasty
|
Dandami Maria Tribe
- The Bison Horn Maria dance of the Dandami Madia (Maria) tribe of Bastar, Chhattisgarh, has drawn attention for its enduring cultural vitality despite modern influences.
Dandami Maria Tribe:
- The Dandami Maria, also known as Bison Horn Maria or Khalpati Maria, are a tribal community belonging to the broader Gond (Koytorias) ethnic group.
- They are recognised for their distinctive ceremonial dance and headgear resembling bison horns, which has become a cultural marker of their identity.
Origin:
- The Dandami Maria trace their lineage to the ancient Gondwana region, once spread across central India.
- They identify as part of the Gond tribal tradition, one of the oldest indigenous groups of the Deccan plateau.
- Linguistically, they speak Dandami Maria, with many also using Gondi dialects, an oral language of Dravidian origin.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Predominantly inhabit the Bastar region of southern Chhattisgarh, especially in Darbha, Tokapal, Lohandiguda, Dantewada, and surrounding forested tracts.
- Their settlements are closely integrated with dense forests, shaping their subsistence patterns, rituals, and worldview.
- They practice agriculture, supplemented by hunting and fishing.
Key Cultural Characteristics
Bison Horn Maria Dance:
- Performed by both men and women during festivals, rituals, and communal gatherings.
- Men wear horn-shaped bamboo headgear decorated with bison or cattle horns, feathers, cowries, and cloth strips, along with bead necklaces and ankle bells.
- Women wear handwoven saris, heavy silver and brass jewellery, coin ornaments, and ceremonial crowns.
Social and Cultural Life:
- The ghotul (youth dormitory) plays a vital role in socialisation, cultural transmission, and community cohesion.
- Distinct hairstyles, traditional ornaments, and ceremonial objects such as tobacco boxes and combs are culturally significant.
- They permit divorce and widow remarriage, reflecting flexible social norms.
Significance
- Represents a living tribal heritage that preserves Gond identity and pre-Aryan cultural traditions.
- Embodies a nature-centric worldview, celebrating hunting traditions, seasonal cycles, and forest deities like Budhadev and Danteshwari Mai.
Bondi Beach attack
- Australia was shaken by a deadly terror-linked mass shooting at Sydney’s Bondi Beach during a Jewish festival, prompting the government to consider tougher gun laws.
About Bondi Beach:
- Bondi Beach is a world-famous ocean beach and adjoining suburb in Sydney, known for its surf culture, tourism, and public recreation. It is among the most visited beaches in Australia and a major symbol of the country’s coastal lifestyle.
Location:
- Situated 7 km east of Sydney’s Central Business District (CBD).
- Lies in the Eastern Suburbs of Sydney within the Waverley Council local government area.
- Neighbouring suburbs include North Bondi, Bondi Junction, Rose Bay, and Bellevue Hill.
Key features
- Natural setting: Crescent-shaped sandy beach facing the Tasman Sea, popular for surfing and swimming.
- Cultural prominence: Featured in global TV series such as Bondi Rescue and Bondi Vet.
- Demographics: Historically multicultural, with a strong Jewish community and migrant heritage.
- Indigenous heritage: Traditionally inhabited by Bidjigal, Birrabirragal, and Gadigal Aboriginal peoples.
- Name origin: Derived from the Dharawal word “Bondi”, meaning a loud thud, like waves crashing on rocks.
Significance
- Tourism & economy: A key contributor to Sydney’s tourism-driven economy and international image.
- Cultural history: Site of major social movements, including early 20th-century debates on public decency and beach culture.
- Public safety relevance: The recent attack highlights challenges of urban security, counter-terrorism, and public space safety.
National Energy Conservation Awards
- The President of India felicitated the winners of the National Energy Conservation Awards (NECA) 2025 on National Energy Conservation Day at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
About National Energy Conservation Awards:
- The National Energy Conservation Awards (NECA) are annual national-level awards that recognise industries, institutions, establishments, and innovators for outstanding achievements in energy efficiency and reduction of energy consumption while maintaining or improving productivity.
Launched in:
- Instituted in 1991 (under the Energy Conservation framework)
- Presented annually on 14 December, observed as National Energy Conservation Day
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Power
- Implementing Agency: Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- BEE was established under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001
Aim:
- Promote energy conservation and efficiency across sectors of the economy.
- Encourage adoption of energy-efficient technologies and practices.
Key Features of NECA 2025
- Wide sectoral coverage: Industry, Buildings, Transport, Institutions, Appliances, Innovation, and Professionals
- High participation: 558 applications received across categories
- New category introduced: Social Media Influencers & Digital Content Creators to promote behavioural change through digital outreach
Transparent selection process:
- Technical Committee (headed by Member–Thermal, CEA)
- Award Committee chaired by Secretary (Power)
Significance of NECA
- Energy security: Promotes “energy saved = energy produced” approach without resource depletion.
- Climate action: Supports India’s decoupling of GDP growth from GHG emissions.
- Policy alignment: Complements schemes like PAT, Standards & Labelling, RCO, and ADEETIE.
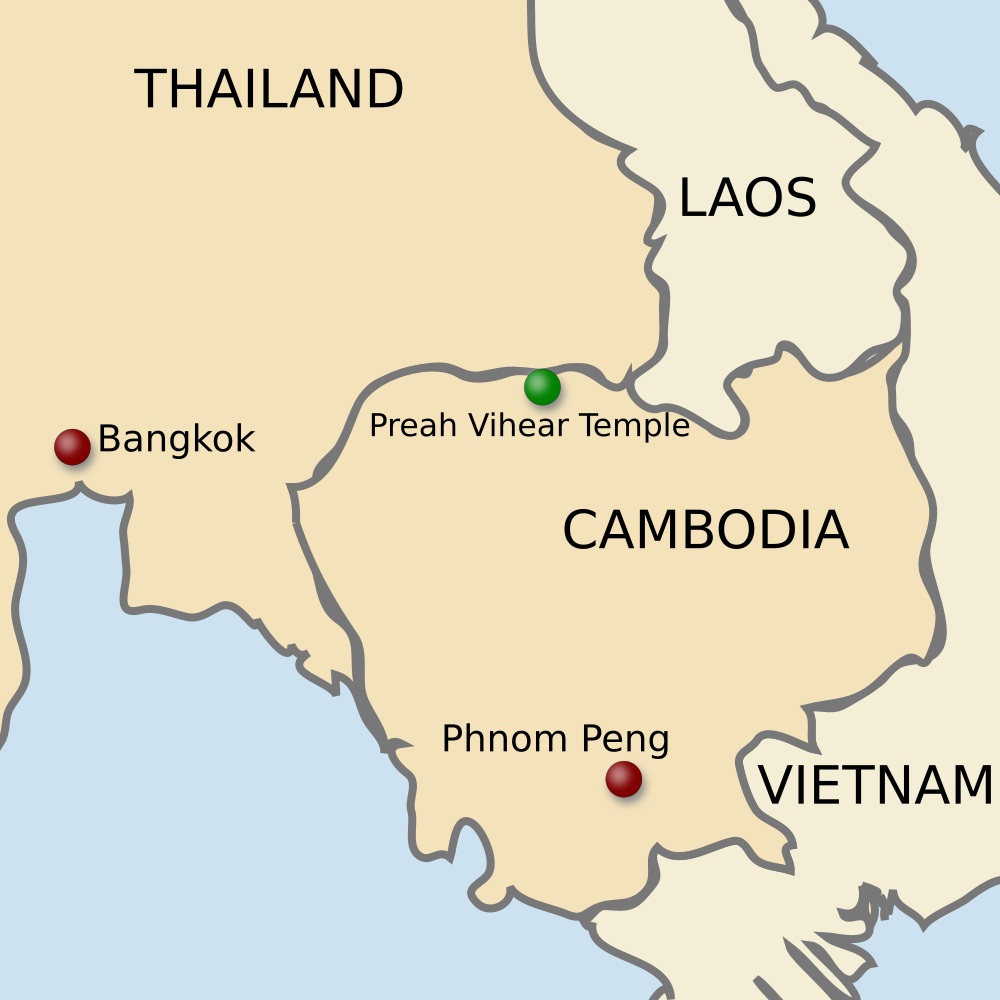
Preah Vihear Temple
- India expressed concern over reported damage to conservation facilities at the Preah Vihear temple amid ongoing Thailand-Cambodia border clashes.
About Preah Vihear Temple
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, located in Preah Vihear province, northern Cambodia, situated atop a cliff in the Dangrek Mountains along the Cambodia-Thailand border.
- It was constructed during the Khmer Empire in the 11th-12th centuries CE, initially built under Suryavarman I (1002-1050 CE) and later expanded by Suryavarman II (1113-1150 CE).
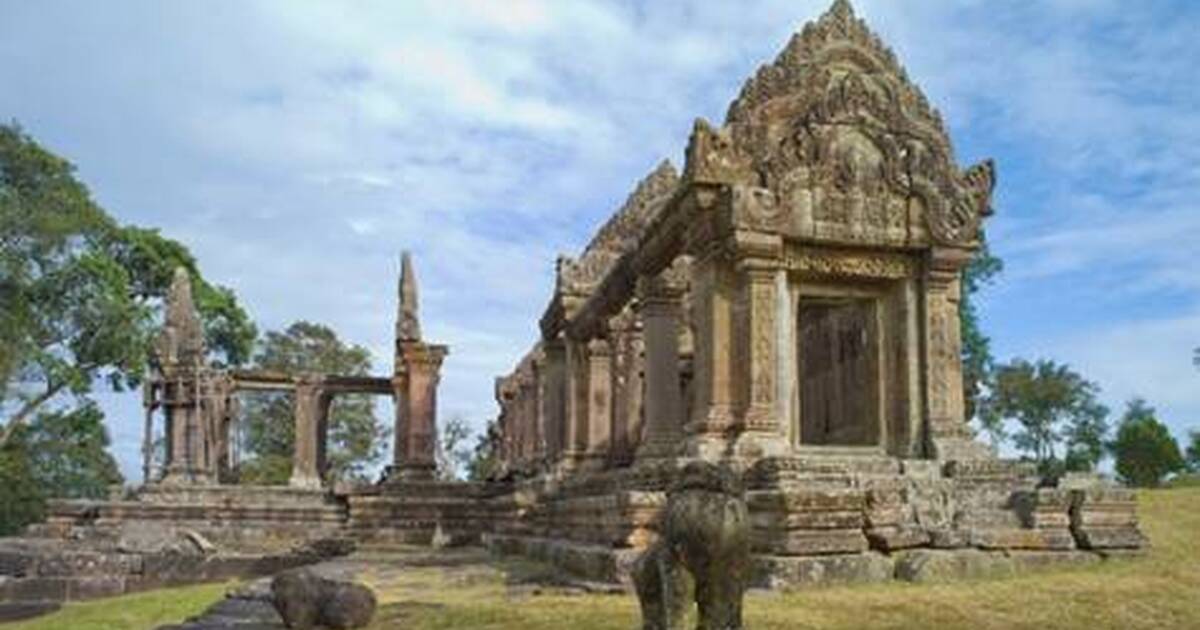

- It embodies the Khmer temple architecture, aligned along an ~800-metre axial processional path with a sequence of five gopuras connected by stairways and pavements.
- It was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2008) for its architectural significance and outstanding testimony to the Khmer civilisation.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies