- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
January 30, 2024 Current Affairs
GenAI Predicted To Become A $100 Billion Industry By 2026
- Generative AI, or generative artificial intelligence, is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) in which algorithms automatically produce content in the form of text, images, audio, and video.
- Unlike traditional AI systems that are designed to recognize patterns and make predictions, generative AI creates new content.
- Generative AI is powered by foundation models (large AI models) that can multi-task and perform out-of-the-box tasks, including summarization, Q&A, classification, and more.
- These systems have been trained on massive amounts of data.
- It works by using a Machine Learning (ML) model to learn the patterns and relationships in a dataset of human-created content. It then uses the learned patterns to generate new content.
- Typically, it starts with a simple text input, called a prompt, in which the user describes the output they want. Then, various algorithms generate new content according to what the prompt is asking for.
Popular Generative AI Tools:
- ChatGPT: ChatGPT is an AI-powered chatbot developed by OpenAI, with a unique ability to not only generate written content but also converse with users fluently.
- Bard: Bard is a generative AI chatbot created by Google, based on LaMDA language model technology. It can answer questions asked by users or create new content from text or image prompts.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
- It is defined as a discipline of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides machines with the ability to automatically learn from data and past experiences to identify patterns and make predictions with minimal human intervention.
- Machine learning methods enable computers to operate autonomously without explicit programming.
- ML applications are fed with new data and they can independently learn, grow, develop, and adapt.
- ML algorithms use computation methods to learn directly from data instead of relying on any predetermined equation that may serve as a model.
Scientists Have Discovered a Previously Unknown Protein Capable of Keeping Human Cells Healthy.
- Researchers discovered a previously unidentified protein named mitochondrial coxiella effector F (MceF) with antioxidant properties produced by Coxiella burnetii, a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium.
- Mitochondrial coxiella effector F (MceF) is a bacterial protein capable of keeping human cells healthy even when the cells have a heavy bacterial burden.
- It is produced by Coxiella burnetii, a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium.
- After invading host cells, Coxiella burnetii releases MceF into cells.
- MceF interacts with glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), an antioxidant enzyme located in the mitochondria, to improve mitochondrial function by promoting an anti-oxidizing effect that averts cell damage and death, which may occur when pathogens replicate inside mammalian cells.
Key Facts about Coxiella burnetii:
- It is a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium.
- It is the causative agent of a serious infection called Q fever, a zoonotic disease that can affect humans and animals.
- The bacterium is primarily transmitted to humans through the inhalation of contaminated aerosols from infected animals, particularly through the air-borne particles from placental tissues, urine, faeces, and milk of infected domestic animals like cattle, sheep, and goats.
- It causes atypical pneumonia in humans and coxiellosis in some animals, such as cattle, sheep, and goats.
- It is highly adapted to invade and control macrophages and monocytes–white blood cells that are part of the organism’s front-line immune defence–inhibiting the host’s responses to the infection.
- Unlike other bacteria, which cause disease only when they multiply to reach large numbers, a single C. burnetii is enough to make a healthy person sick.
Delhi HC upholds validity of anti-profiteering provisions under GST
- The Delhi High Court upheld the constitutional validity of anti-profiteering provisions in the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Any reduction in the GST rate or benefit of input tax credit should be passed on to the end consumer and not retained by the business. This is the basis of the anti-profiteering provisions under GST.
- Under anti-profiteering provisions, it’s illegal for a business to not pass on the benefits of the GST rate benefits to the end consumer, and thereby indulging in illegal profiteering.
Who regulates anti-profiteering under the GST?
- The Anti-Profiteering Rules, 2017 (defined under Section 171 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act 2017), prevents entities from making excessive profits due to the lowering of GST.
- The Government has created the National Anti-Profiteering Authority (NAA) to find and take action against taxable registered persons indulging in illegal profiteering.
- NAA has the power to determine the methodology and procedure for determining whether a taxable person is engaging in illegal profiteering.
Reporting to the Anti-Profiteering Authority:
- Any interested party who has information to believe a taxable person is engaging in illegal profiteering from GST can refer the matter to the local screening committee.
- The State level Screening Committee shall examine the matter constituted by the State Governments consisting of officers of the State Government.
- If the screening committee determines that the information contains merit, the committee shall forward it with recommendations to the Standing Committee on Anti-Profiteering, which consists of officers of both the State Government and Central Government.
- If the Standing Committee contains enough proof to show that the taxable person engaged in illegal profiteering, then the committee shall refer to the Director General of Safeguards for a detailed investigation.
Investigation by the Director General of Safeguards:
- All matters referred by the Standing Committee will be investigated by the Director General of Safeguards.
- The Director General of Safeguards will collect evidence, conduct an investigation, and issue notices to the interested parties. The notice must contain the following details:
- The description of the goods or services in respect of which the proceedings have been initiated.
- Summary of the statement of facts on which the allegations are based.
- The time limit allowed to the interested parties and other persons who may have information related to the proceedings for furnishing their reply.
- Once all the information and hearings are complete, the Director General of Safeguards will provide a report of findings.
- A report of findings must be submitted by the Director General of Safeguards, normally within 3 months or within 6 months if an extension is provided.
- Order under Anti-Profiteering Provisions: Once all the proceedings are completed and a report is obtained from the Director General of Safeguards, the Members of Committee will pass an order. An order from the Authority could mandate:
- Reduction in prices.
- Return to the recipient, an amount equivalent to the amount not passed on by way of a commensurate reduction in prices along with interest.
- Imposition of penalty as specified under the Act.
- Cancellation of GST registration.
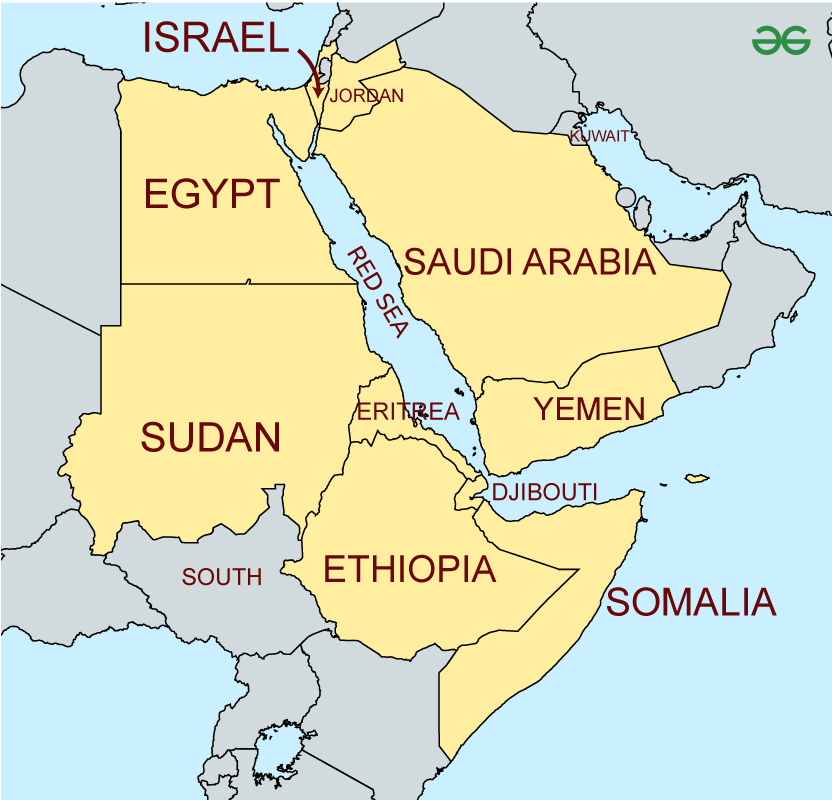
Red Sea trouble impacted India
- A spate of attacks on cargo ships in the Red Sea since November by the Houthi militia of Yemen has turned the quickest marine route linking Asia with Europe through the Suez Canal unsafe.
- It has forced freighters to take a longer transit around the Cape of Good Hope in Africa’s southern tip, making shipments both dearer and longer to deliver.
Attacks
- Yemen’s backed Houthi have been targeting vessels in the Red Sea since November to show their support for the Hamas in the war against Israel.
Significance Of Red Sea Trade Route
- Historical significance – red sea has been one of the most important route since ages that connected many civilizations and continents i.e. Asia, Africa, Europe.
- Economic significance – Suez Canal since its inception in 1869 has been the busiest trade route that reduced distance between Europe and Asia by 7000km.
- Geopolitical significance -because of its economic importance and strategic location (narrow width of Suez Canal) it has also become geopolitically significant.
Freight rates
- Ever since the attacks along the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait began earlier this month, global shipping firms have begun imposing war risk surcharges over and above the normal freight rates.
- Indian exporters said that freight rates for Indian shipments headed to Europe and Africa could surge as much as 25-30 per cent if the ongoing security concern along the Red Sea trade route continues.
- This is troubling, as the European Union is one of India’s second-largest export destinations. Slowing demand from the region has impacted India’s labour-intensive sectors, such as textiles, gems and jewellery exports.
Measures Taken by India
- The Indian Navy has substantially enhanced maritime surveillance efforts in the central/north Arabian Sea and augmented force levels.
- Task Groups comprising destroyers and frigates have been deployed to undertake maritime security operations and render assistance to merchant vessels in case of any incident
- Aerial surveillance by long-range maritime patrol aircraft and RPAs remotely piloted aircraft has been enhanced to have complete maritime domain awareness.
- Towards effective surveillance in economic exclusive zone , the Indian Navy is operating in close coordination with the Indian Coast Guard.
- The Indian navy is monitoring the overall situation in coordination with national maritime agencies.
- US Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin announced the creation of Operation Prosperity Guardian to protect Red Sea commerce but India is yet to decide on joining it.
|
Red Sea
Physical Characteristics
Salinity
Biodiversity
Economic factors
Climate
Significance of Red Sea
|
How to grow seafood outside the sea — and why a Govt lab in Kochi has taken up this project.
- ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has entered into a collaborative research agreement with a private-sector start-up offering cultivated meat technology solutions to grow fish meat in the laboratory.
- Lab-grown fish is merely a type of lab-grown — or cultivated/cultured — meat.
- Seafood without the sea is ‘grown’ in the same way as other cultivated meats are grown — without the need to raise and kill an animal.
- Process: Cultivated fish meat is produced by isolating specific cells from fish and growing them in a laboratory setting using media that is free of animal components.
- The final product is expected to replicate the flavour, texture, and nutritional qualities of ‘real’ fish meat.
Role of Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute:
- It will focus on the genetic, biochemical, and analytical work related to the project.
- In its cell culture lab, it will carry out research on early cell line development of high-value marine fish species — a process that involves isolating and cultivating fish cells for further research and development.
- It will initially focus on developing cell-based meat of fish such as pomfret, kingfish, and seerfish.
- Recently, a number of countries have made great strides in this pioneering technology.
- Israel is the frontrunner, followed by Singapore, the United States and China.









 Latest News
Latest News
 Red Sea is Red
Red Sea is Red General Studies
General Studies