- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
23rd December 2020
Legion of Merit Award
Recently, the US government has awarded the ‘Legion of Merit Award’ to Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi.The Legion of Merit was instituted in 1942 by former US president Franklin D Roosevelt.
 Recently, the Winter Solstice was observed on December 21.
Recently, the Winter Solstice was observed on December 21.
 What happens on the Winter Solstice?
What happens on the Winter Solstice?
 Recently, the two giant planets i.e. Jupiter and Saturn brought closest in the night sky by an astronomical event called the “great conjunction”.
What is Great Conjunction?
Recently, the two giant planets i.e. Jupiter and Saturn brought closest in the night sky by an astronomical event called the “great conjunction”.
What is Great Conjunction?
- It is the only US military decoration that has distinct ranks, and the first US medal to be awarded to citizens of other nations.
- The Legion of Merit, in the highest degree of the Chief Commander, is a prestigious award conferred by the President of the United States.
- The award is conferred to members of the US military and foreign military members and political figures who have displayed exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements.
- It is awarded for outstanding service, fidelity, and loyalty in either combat or non-combat positions.
- The previous Indian recipients of the award include Field Marshal KM Cariappa (1950) and Satyawant Mallana Srinagesh (1955).
- Under the criteria outlined in Army Regulation 672-7, this award is awarded to the degrees of Chief Commander, Commander, Officer, and Legionnaire of armed forces of foreign nations and is based on the relative rank or position:
-
- Chief Commander: Some Allied World War II theater commanders, usually for joint amphibious landings or invasions, are awarded this degree.
- Commander: Equal of a US military head of staff or higher position, but not to a chief of state.
- Officer: General below the equal of a US military chief of staff; colonel or equal rank for service in assignments equal to those held by a general or flag officer in US military service; or military attaches.
- Legionnaire: All recipients not included above.
- It seeks to recognize and reward outstanding startups and ecosystem enablers that are contributing to economic dynamism by spurring innovation and injecting competition.
- The first-ever National Startup Awards (NSA) were concluded in October 2020.
- It aims to cover flagship schemes launched by the Government of India through innovations in corresponding areas, thereby solving community problems at large.
- The entity should be a DPIIT-recognized startup.
- The entity must have hardware or software product or a process solution that is present in the market.
- The entity must have all applicable trade-specific registrations.
- There should not have been any default in the last three years (FY17-18, 18-19, 19-20) by the entity or any of its promoters or any of their group entities.
- The entity must submit Audited Financial Statements (Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss Account) for the last three financial years.
- Participation in the National Startup Awards is voluntary
- Startups/Incubators/Accelerators who have won in their respective category in National Startup Awards 2020 will not be eligible to apply for National Startup Awards 2021.
- One startup can nominate itself in a maximum of two categories.
- The application form is to be filled in English only.
- DPIIT reserves the right at its sole discretion to cancel, terminate, modify, or suspend the National Startup Awards or not award any entity in any sector or sub-sector.
- It is a flagship initiative that aims to build a strong eco-system for nurturing innovation.
- It was launched in 2016 with the objective of supporting entrepreneurs, building a robust startup ecosystem and transforming India into a country of job creators instead of job seekers.
- Startups in the country will drive sustainable economic growth and generate large-scale employment opportunities.
- The National Highways of India carry about 40 percent of road traffic and several sections of these highways have inadequate capacity, weak drainage structures and black spots prone to accidents.
- The $500 million loan from the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) has a maturity of 18.5 years including a grace period of five years.
- It aims to build safe and green national highway corridors in the states of Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
- The ultimate objective of transport infrastructure is to provide seamless connectivity and reduce logistics costs.
- The project will support analytics to map the freight volume and movement pattern on the National Highway network, identify constraints, and provide innovative logistics solutions.
- The project has three components:
- The Green Highway Corridor Improvement and Maintenance includes upgradation and maintenance for five years of about 783 kilometers of selected existing National Highways.
- The Institutional Capacity Enhancement has the following subcomponents:
- Development and implementation of a Climate Adaptation Policy and guidelines and mainstreaming climate resilience in National Highways design and construction processes;
- Development and implementation of policy for reducing emissions from transport services;
- Research and Development and mainstreaming green technologies in National Highways design and construction processes;
- Development and implementation of guidelines and model documents for mainstreaming safety and green technologies;
- Mainstreaming safety and green technologies in the development of highways; and
- Implementing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution in Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) and its implementing agencies.
- The Road Safety has the following subcomponents:
- Support to improve road safety data analytics and highway safety monitoring and implementation;
- Support for operationalization of the National Road Safety Board; and
- Strengthening highway patrol and emergency response along the project highway
- It will support Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) construct 783 km of highways in various geographies by integrating safe and green technology designs.
- The project will help reduce GHG emissions in the construction and maintenance of highways.
- The project will also enhance the capacity of the MoRTH in mainstreaming safety and green technologies.
- The project will support the ministry with an in-depth analysis of gender-related issues in the transport sector along with help in creating jobs for women.
- The project will strengthen and widen existing structures; construct new pavements, drainage facilities and bypasses; improve junctions; and introduce road safety features.
- The Prime Minister has announced for setting up of Rs. 15000 crore Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund under AtmaNirbhar Bharat Abhiyan stimulus package.
- It has been approved for incentivizing investments by individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSME, Farmers Producers Organization (FPOs) and Section 8 companies to establish:
-
- Dairy processing and value addition infrastructure,
- Meat processing and value addition infrastructure and
- Animal Feed Plant.
- The interest subvention is provided @ 3% to all eligible entities.
- The Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme for 20,000 bovines per district for 600 districts in the country was launched by the Government in September, 2019.
- It is one of the largest such programmes with 100% central assistance for undertaking breed improvement.
- Under “Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme” Phase I, 76 lakh bovines have been covered, 90 lakh AIs performed and more than 32 lakh farmers have been benefitted.
- The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying has introduced a new component “interest subvention on Working capital loans for Dairy sector”.
- It is one of the components under its scheme “Supporting Dairy Cooperatives and Farmer Producer organizations engaged in dairy activities” (SDC&FPO).
- The modified scheme envisages a budgetary provision of Rs 100 Crore earmarked for the component “Interest Subvention on Working Capital Loans for Dairy sector” during 2020-21.
- It is a special drive which has been undertaken to provide concessional credit to PM-KISAN beneficiaries.
- The Animal Husbandry & Dairying farmers have been included in this drive.
- It will enable such farmers to gain access to institutional credit at concessional interest rate. 2.5 crore farmers will be covered and will benefit from credit flow of about Rs 2 lakh crores.
- The commission observed that the disclosure of names of donors and the donees may be in contravention of provisions contained in section 8 (1) of the RTI Act itself.
- The section 8 (1) of the RTI Act exempt a public authority to give a citizen information available to a person in his fiduciary relationship, unless the competent authority is satisfied that the larger public interest warrant the disclosure of such information.
- In January 2020, the commission had directed the Centre to reveal the names of electoral bond scheme donors who wanted their identities to remain confidential.
- It is similar to promissory note (PN) because it can be bought by any Indian citizen or company incorporated in India from select branches of State Bank of India.
- The citizen or corporate can then donate the same to any eligible political party of his/her choice.
- It is an interest free banking instrument issued on a non-refundable basis and is not available for trading i.e. no loan would be provided against these bonds.
- The bonds are similar to bank notes that are payable to the bearer on demand and are free of interest.
- An individual or party will be allowed to purchase these bonds digitally or through cheques.
- The electoral bonds were introduced with the Finance Bill (2017).
- The bonds will be issued in multiples of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 100,000 and Rs 1 crore.
- Any party that is registered under section 29A of the Representation of the Peoples Act, 1951 (43 of 1951) and has secured at least one per cent of the votes polled in the most recent General elections or Assembly elections is eligible to receive electoral bonds.
- The party will be allotted a verified account by the Election Commission of India (ECI) and the electoral bond transactions can be made only through this account.
- The electoral bonds will not bear the name of the donor and the political party might not be aware of the donor's identity.
- The Electoral Bond shall be redeemable in the designated account of a registered political party within the prescribed time limit from issuance of bond.
- The Electoral Bonds would have a life of only 15 days during which it can be used for making donation only to the political parties registered under section 29A.
- The political party needs to disclose the details of non-governmental corporations and persons who donate more than Rs. 20,000 to it in a financial year.
- A donor will get a deduction under section 80GGB and the recipient or the political party, will get tax exemption, provided returns are filed by the political party.
- Every political party would have to file its return within the time prescribed in accordance with the provision of the Income-tax Act.
- It has been constituted with effect from 2005 under the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- The jurisdiction of the Commission extends over all Central Public Authorities.
- It shall consist of the Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and such number of Information Commissioners not exceeding 10 as may be deemed necessary.
- The Chief Information Commissioner shall hold office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office and shall not be eligible for reappointment.
- The members of the committee to appoint Chief Information Commissioner consists of:
- Prime Minister, who shall be the Chairperson of the committee;
- Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha; and
- A Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister.
- The report documents the trends in health loss due to air pollution and its economic impact in every state of India, using the latest improved methods and data.
- The findings in the paper highlight that while the disease burden due to household air pollution is reducing in India, the same has increased due to ambient outdoor air pollution.
- The percentage of fatalities attributable to air pollution was highest in Rajasthan, followed by West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Bihar, Gujarat, Uttarakhand and Delhi.
- The report highlighted that if air pollution is eliminated, then 18 per cent deaths could be avoided.
- The findings show that while 40 per cent of the disease burden due to air pollution is from lung diseases, the remaining 60 per cent is from ischemic heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and neonatal deaths related to preterm birth.
- It stated that the household air pollution is decreasing in India, resulting in 64 per cent reduction in the death rate attributable to it from 1990 to 2019.
- The death rate from outdoor ambient air pollution has increased during this period by 115 per cent.
- The economic loss due to air pollution as a percentage of the state GDP was higher in the northern and central India states, with the highest in Uttar Pradesh (2.2 per cent) and Bihar (2 per cent).
- The report highlighted that the estimated expenditure of 0.4 per cent of the GDP is done on the treatment of air pollution-related diseases.
- The high burden of death and disease due to air pollution and its adverse economic impact from loss of output could impede India’s aspiration to be a $5-trillion economy by 2024.
India State-level Disease Burden Initiative
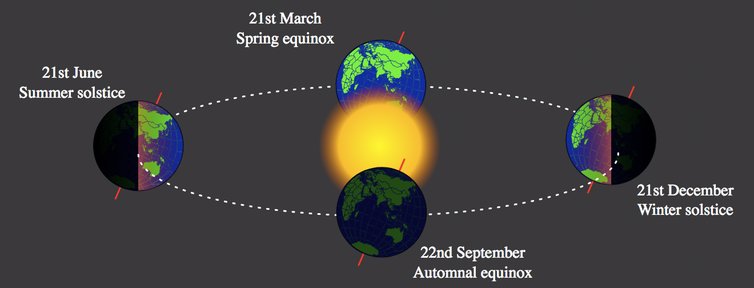
Winter Solstice
- It was launched in 2015 as collaboration between the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI), Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), and senior experts and stakeholders.
- It reported an unprecedented comprehensive assessment of the diseases causing the most premature deaths and ill-health in each state of the country.
 Recently, the Winter Solstice was observed on December 21.
Recently, the Winter Solstice was observed on December 21.
- It is the shortest day in the Northern Hemisphere.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, December 21st is the summer solstice i.e. the longest day in in places like Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
- The winter solstice marks the official beginning of astronomical winter (as opposed to meteorological winter, which starts about three weeks prior to the solstice).
- The reason for difference in hours of daylight lies in the tilting of Earth.
- The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5° to its orbital plane and combined with factors such as Earth’s spin and orbit, leads to variations in the duration of sunlight that any location on the planet receives on different days of the year.
- The Northern Hemisphere spends half the year tilted in the direction of the Sun, getting direct sunlight during long summer days.
- The tilt is also responsible for the different seasons that we see on Earth as the side facing the Sun experiences day, which changes to night as Earth continues to spin on its axis.
- During summer, in either hemisphere, that pole is tilted towards the Sun and the polar region receives 24 hours of daylight for months.
- The Earth’s tilt helps define some familiar imaginary lines, which are also key to determining when a Solstice occurs.
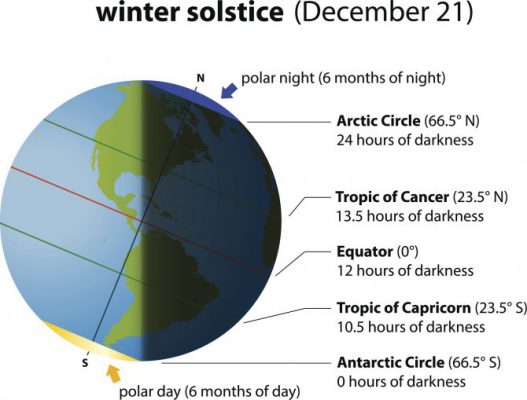
 What happens on the Winter Solstice?
What happens on the Winter Solstice?
- The Sun’s path reaches its most southerly point in the sky on the day of solstice.
- The Sun’s path will be high in the sky on the winter solstice directly overhead at noon at the latitude called the Tropic of Capricorn.
- The day after the winter solstice, the Sun’s path begins to advance northward again, eventually reaching its most northerly point on the day of the summer solstice.
 Recently, the two giant planets i.e. Jupiter and Saturn brought closest in the night sky by an astronomical event called the “great conjunction”.
What is Great Conjunction?
Recently, the two giant planets i.e. Jupiter and Saturn brought closest in the night sky by an astronomical event called the “great conjunction”.
What is Great Conjunction?
- It is popularly referred to as the “Christmas Star”.
- The conjunction is not unique to Saturn and Jupiter but it is the name given to any event where planets or asteroids appear to be very close together in the sky when viewed from the Earth.
- The “spectacular” conjunction in 2005 when Mercury, Venus and Saturn appeared so close together in the sky that the patch of sky where the three planets were could be covered by a thumb.
- The “Great Conjunction” happens once in about 20 years because of the time each of the planets take to orbit around the Sun.
- The planets in a conjunction are typically above or below each other, because their orbits are slightly tilted with respect to each other.
- The sudden imposition of lockdown resulted in "unprecedented disruptions" in the country but acknowledged that the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has shown signs of recovery in Q2.
- The panel said the sudden imposition of lockdown caused stoppage of intra-state and inter-state movement of people, goods, shutdown of factories, hotels, eateries, tourism, etc.
- The National Health Policy 2017 has set a target of government expenditure on healthcare up to 2.5% of GDP by 2025 from just 1.15% in 2017.
- It has recommended the government to set up a database of the migrant workers and prepare a comprehensive healthcare legal framework to tackle any future pandemic.
- It called for seeking to update the Epidemic Act and reducing reliance on the National Disaster Management Act to deal with a pandemic-like situation.
- The panel called for a "national plan" for coordination between the Centre and states and a public health safety law that keeps a control on private hospitals that looks at commercial opportunity during a pandemic.
- The panel emphasised the need for having proper data on migrant labourers because the task of identifying the location and disbursing relief measures to them became "very difficult".
- The panel said more funds should be allocated for public hospitals to strengthen the public health infrastructure to equip them appropriately to handle such pandemics in future.
- It recommended that good quality and affordable medicines should be provided to everyone at a cheaper or subsidised rate to the marginalised sections of the society.
- It strongly recommends the government to increase its investments in the public healthcare system and make consistent efforts to achieve the National Health Policy targets of expenditure up to 2.5% of GDP.
- Choudhary Charan Singh, who briefly served as prime minister between 1979 and 1980, is widely regarded as one of the country’s most famous peasant leaders.
- He was known for his pioneering work to promote the welfare of farmers and the agricultural sector.
- While serving as agriculture minister in 1952, he led UP in its efforts to abolish the zamindari system.
- On 23 December, 1978, he founded the Kisan Trust as a non-political, non-profit making body with the aim of educating India’s rural masses against injustice, and fostering solidarity among them.
- It is celebrated to honour India’s farmers and mark the birth anniversary of the nation’s fifth Prime Minister, Choudhary Charan Singh.
- In 2001, the government decided to recognise Choudhary Charan Singh’s contribution to the agriculture sector and welfare of farmers by celebrating his birth anniversary as Kisan Diwas.
- It is aimed at organising awareness campaigns and drives across the country to educate people on the role of farmers and their contribution to the economy.
- The Army version of MRSAM is a Surface to Air Missile.
- It is developed by India's Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for use of the Indian Army.
- The MRSAM Army weapon system comprises of Command post, Multi-Function Radar and Mobile Launcher system.
- It is a 4.5m long nuclear-capable ballistic missile which weighs around 2.7 tonne and can carry a payload of 60 kg.
- The launching platform includes a Multi-Functional Surveillance and Threat Alert Radar (MFSTAR) for detection, tracking, and guidance of the missile.
- The new generation MRSAM has been developed to neutralise airborne threats like jets, missiles and rockets, including projectiles launched simultaneously.
- MRSAM is a land-based configuration of the long-range surface-to-air missile (LRSAM) or Barak-8 naval air defence system, which is designed to operate from naval vessels.
Barak 8 Missile
- Barak 8, also known as LR-SAM or as MR-SAM, is an Indo-Israeli surface-to-air missile (SAM).
- It is designed to defend against any type of airborne threat including aircraft, helicopters, anti-ship missiles, and unmanned aircraft as well as ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and combat jets.
- Both maritime and land-based variants of the system exist.
- It was jointly developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), Israel’s Administration for the Development of Weapons and Technological Infrastructure, Elta Systems, Rafael and other companies.
- India’s Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) produces the missiles.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies