- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
25th Oct 2021
WEB-BASED PROJECT MONITORING PORTAL FOR MILITARY ENGINEER SERVICES
 RakshaMantri has launched Web Based Project Monitoring Portal (WBPMP) for Military Engineer Services (MES) at New Delhi recently.
RakshaMantri has launched Web Based Project Monitoring Portal (WBPMP) for Military Engineer Services (MES) at New Delhi recently.
 External Affairs Minister has visited Israel's Ovda Airbase to meet the Indian contingent participating in the biennial Blue Flag exercise involving Air Force missions from eight countries.
External Affairs Minister has visited Israel's Ovda Airbase to meet the Indian contingent participating in the biennial Blue Flag exercise involving Air Force missions from eight countries.
 Jailed Russian Opposition leader Alexei Navalny wins the top EU human rights prize.
Jailed Russian Opposition leader Alexei Navalny wins the top EU human rights prize.
 The University Grants Commission has issued a notification recognizing Bachelor of Sowa Rigpa Medicine and Surgery (BSRMS) under the specified Degrees.
Highlights:
The University Grants Commission has issued a notification recognizing Bachelor of Sowa Rigpa Medicine and Surgery (BSRMS) under the specified Degrees.
Highlights:

 First Survey:
First Survey:

 RakshaMantri has launched Web Based Project Monitoring Portal (WBPMP) for Military Engineer Services (MES) at New Delhi recently.
RakshaMantri has launched Web Based Project Monitoring Portal (WBPMP) for Military Engineer Services (MES) at New Delhi recently.
- The portal conceptualized in accordance with the Digital India Mission of the Union Government.
- It has been developed by Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-G).
- The unified portal is the first project management e-Governance to be implemented by the MES.
- It will enable real time monitoring of projects from its inception to completion.
- All stakeholders not only from MES but also Armed Forces users can gain access to the project information.

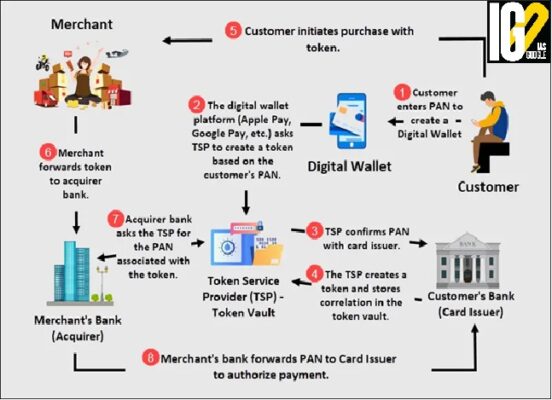
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) on Wednesday launched NPCI Tokenization System (NTS) to support tokenization of RuPay cards.
- Acquiring banks, aggregators and merchants can get themselves certified with NPCI as token requestors and save the token reference number against all card numbers saved.
- It refers to a process that replaces details of a card, such as its number and CVV, used for making a transaction with an encrypted algorithmically generated token.
- The token is generated either by the card issuer or payments network.
- The purpose of tokenization is to protect sensitive data while preserving its business utility.
- The tokens can be:
- Single-use (low-value) for operations such as one-time debit card transactions that don't need to be retained.
- Persistent (high-value) for items such as a repeat customer's credit card number that needs to be stored in a database for recurring transactions.
- They retain certain elements of the original data—commonly length or format—so they can be used for uninterrupted business operations.
- The original sensitive data is then safely stored outside of the organization's internal systems.
- Unlike encrypted data, tokenized data is undecipherable and irreversible.
- There is no mathematical relationship between the token and its original number, tokens cannot be returned to their original form without the presence of additional, separately stored data.
- As a result, a breach of a tokenized environment will not compromise the original sensitive data.
- Tokens are not susceptible to personally identifiable information fraud.
- Builds confidence among the investors as it secures the money with ease.
- Sales can take a boost as customers can utilize the token information to pay without using credit card or personal details.
- Acquirers, merchants, and processors experience a lower risk of accessible, sensitive cardholder data if compromised by cyber-attacks.
- Customers do not need to enter payment details for every purchase.
- Merchants no longer deal with sensitive payment information.
- Well-suited for in-app and mobile transactions.
- A single PAN can be used to create an unlimited number of tokens. This means that customers can have one credit card and multiple tokens for different devices or various payment gateways.
- If a token is compromised, the customer does not need to change their credit card.
- Merchants can create a powerful mechanism that lets them innovate better retail experiences. This is because they now do not have to worry about storing and handling sensitive data.
 External Affairs Minister has visited Israel's Ovda Airbase to meet the Indian contingent participating in the biennial Blue Flag exercise involving Air Force missions from eight countries.
External Affairs Minister has visited Israel's Ovda Airbase to meet the Indian contingent participating in the biennial Blue Flag exercise involving Air Force missions from eight countries.
- The Blue Flag drill is a bi-annual exercise designed to strengthen Israel’s military cooperation internationally.
- It aims to share knowledge and combat experience to improve operational capabilities.
- US, UK, Germany, France, India, Italy, Greece and Israel are the participating nations of the exercise.
- India had also participated in this event in 2017.

- Action was needed by littoral states of the Black Sea amid Russia “militarization” of the region.
- The security and stability of the Black Sea are in the U.S.’s national interest and critical for the security of NATO’s eastern flank.
- The region is vulnerable to Russian aggression like the ongoing actions in eastern Ukraine the occupations of parts of Georgia.
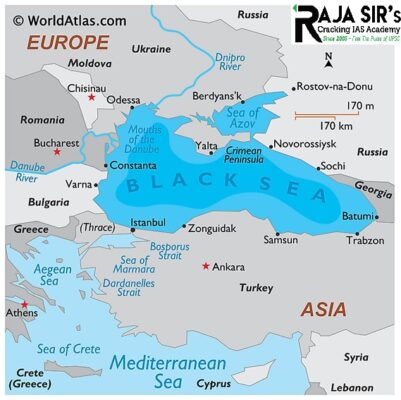
- The Black Sea is in Eurasia surrounded by Europe, Caucasus, and Anatolia.
- The countries that share a border with the Black Sea include Romania, Turkey, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Russia, and Georgia.
- The inland sea is a meeting point of several rivers like the Danube, Southern Bug, Dnieper, and Dniester.
- The Black Sea connects with the Mediterranean Sea through the Bosporus Strait, and then through the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles Strait.
- It has a unique anoxic water, there is a significant absence of oxygen in the water.
- It is home to many small islands. These islands also include Snake Island, which is located near the Danube Delta.
- St. Thomas Island in Bulgaria is infamous for the presence of fish-eating Grey Water Snakes.
- The Black Sea holds a special significance for Russia for several reasons.
- It is an important crossroads and strategic intersection for the entire region.
- Access to the Black Sea is vital for all littoral and neighboring states, and enhances the projection of power into several adjacent regions.
- The region is an important transit corridor for goods and energy.
- It is rich in cultural and ethnic diversity, and due to geographical proximity, share close historical ties with Russia.
 Jailed Russian Opposition leader Alexei Navalny wins the top EU human rights prize.
Jailed Russian Opposition leader Alexei Navalny wins the top EU human rights prize.
- He had campaigned consistently against the corruption of Russian President’s regime, and through his social media accounts and political campaigns.
- The Sakharov Prize for Freedom of Thought is the highest tribute paid by the European Union to human rights work.
- It gives recognition to individuals, groups and organisations that have made an outstanding contribution to protecting freedom of thought.
- The European Parliament awards the Sakharov Prize, with its EUR 50 000 endowment, at a formal plenary sitting in Strasbourg towards the end of each year.
- Policies for water and climate action developed within the sustainable development agenda will be integrated to yield maximum benefit for people.
- The agenda will be achieved through partnerships for capacity development, knowledge exchange, and information sharing, formulating policies, institutional and regulatory frameworks.
- The Water and Climate Coalition will promote sharing and access to the integrated hydrological, cryosphere, meteorological, and climate information.
- The formation of the Coalition is significant at a time when just 40 percent of countries globally have operational early flood and drought warning systems.
- The Coalition is thus aimed at accelerating the progress of water-related United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, especially SDG 6.
- The new Sustainability Strategy for strengthening the Flash Flood Guidance System with Global Coverage (FFGS/WGC) was approved at the World Meteorological Congress.
- 60 percent of WMO member countries lack hydrological monitoring capabilities.
- 107 countries are not on track to have sustainably managed water resources.
- Half of the world’s population is at risk due to a lack of information on the state of their water resources including rivers, lakes, groundwater.
- WMO is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 193 Member States and Territories.
- Aim: To provide world leadership and expertise in international cooperation in the delivery and use of high-quality, authoritative weather, climate, hydrological, and related environmental services by its members.
- It originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO). WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences.
- It facilitates the "free and unrestricted" exchange of data, information, and research between the respective meteorological and hydrological institutions of its members.
- Headquarters: Geneva
 The University Grants Commission has issued a notification recognizing Bachelor of Sowa Rigpa Medicine and Surgery (BSRMS) under the specified Degrees.
Highlights:
The University Grants Commission has issued a notification recognizing Bachelor of Sowa Rigpa Medicine and Surgery (BSRMS) under the specified Degrees.
Highlights:
- The UGC has recognized BSRMS as a new degree under Medicine & Surgery, Ayurveda, Unani, Homeopathy and Health & Allied Sciences, Pharmacy, Paramedical and Nursing.
- Duration: 5 years and (10+2) is fixed as entry qualification.
- Sowa Rigpa is a traditional and popular medicinal practice in the Himalayan region.
- Only Central Institute of Buddhist Studies (CIBS) in Leh and Central Institute of Higher Tibetan Studies (CIHTS) located in Saranath are offering the degree in Sowa Rigpa medicine.
- With UGC recognition, any university could offer BSRMS degree in their colleges.

- In case the constituency is comprised in State Capital/Metropolitan Cities/Municipal Corporations, then MCC instructions would be applicable in the area of concerned Constituency only.
- In all other cases, aforesaid instructions would be enforced in the entire district(s) covering the Constituency going for bye-election(s).
- The spirit of these instructions has been that developmental and administrative works should continue without the implications of MCC and the campaigning for the bye election should be restricted in the PC/AC concerned only.
- However, there exists a situation that political activities akin to ongoing bye election may be conducted outside the PC/AC but within the district.
- Such activities will be in contravention to the spirit of the aforesaid instructions.
- If any electioneering activities connected to ongoing bye election are organized anywhere within the district, then all instructions related to enforcement of MCC, COVID and expenditure monitoring shall apply as done in case of political activities.
- District Election Officer concerned shall exercise all necessary action in such cases and ensure strict compliance.
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) is a document from the Election Commission of India that lays down the minimum standards of behaviour for political parties and their candidates contesting elections.
- The guidelines are issued mainly with respect to speeches, polling day, polling booths, election manifestos, processions and general conduct.
- The Model Code of Conduct comes into force immediately on announcement of the election schedule by the commission.
- The Code remains in force till the end of the electoral process.
- MCC does not have any statutory backing but it gained strength in the past decade because of its strict enforcement by the EC.
- The MCC was first mooted by Kerala in its 1960 assembly elections.
- It was later adopted by the Election Commission (EC) during mid-term elections in 1968 and 1969.
- EC issued MCC for the first time in 1971 (5th general elections) and revised it from time to time.
- Researchers identified 13,604 smokers between 2013 and 2015 over two annual surveys to explore changes in use of 12 tobacco products.
 First Survey:
First Survey:
- 9.4% of the established smokers had quit. Among them, 62.9% remained tobacco-free, while 37.1% had switched to another form of tobacco use
- Including 22.8% who used e-cigarettes, with 17.6% of switchers using e-cigarettes daily.
- Individuals who switched to other form of tobacco use, including e-cigarettes, were more relapse compared to former smokers who had quit all tobacco, by a total of 8.5 percentage.
- Among recent former smokers who abstained from all tobacco product, 50% have successfully quit smoking compared to 41.5% of recent former smokers who switched to other form of tobacco use, including e-cigarettes.
- In September 2019, Government of India announced a complete ban on e-cigarettes, preventing health risks among India's youth.
- Production, manufacture, trade, transport, of e-cigarettes and other Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS) like vapes, e-hookahs and e-cigars will be a punishable offence.
- First-time offenders will face imprisonment of up to one year, a fine up to Rs 1 lakh, or both.
- Subsequent offenders will face three years’ imprisonment and Rs 5 lakh in fine,
- Those found storing e-cigarettes and other ENDS products will face up to six months in prison and up to Rs 55,000 in fines, or both.
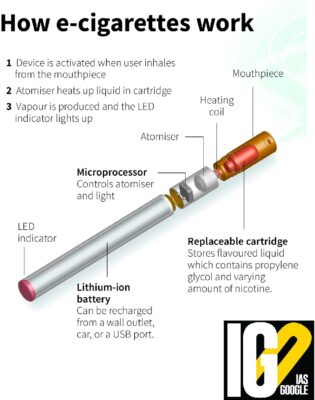
- E-cigarettes are battery-powered devices that heat a solution of nicotine to create aerosol, which is then inhaled.
- These devices belong to a category of vapour-based nicotine products called Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS).
- E-cigarettes and other ENDS products look like regular cigarettes or cigars, they also come in other shapes and sizes like pens and USB drives.
- India’s vapour products market was valued at over $57 million in 2018, and projected to grow nearly 60 per cent a year up to 2022.
- Imports of e-cigarettes, their accessories and other ENDS products grew around 119 per cent from 2016-17 to 2018-19.
- These products have neither been assessed for safety, nor been approved under provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940. Yet, they are widely available in market.
- Though some smokers have claimed to have cut down smoking while using ENDS, the total nicotine consumption seemed to remain unchanged.
- As per the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), uses of ENDS, or e-cigarettes, have adverse effects.
- Including DNA damage, cellular, and immunological toxicity, respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological disorders.
- Abstinence:
- It points out risky behavior and drastically changing incentives to make them stop.
- This can include bans with severe penalties for violations or imposing high sin taxes.
- The approach is a right move in many cases, where harm is clearly identified, like smoking or excessive drinking.
- Prohibition:
- Aim: To reduce the harm by providing less risky alternatives.
- For example: Regulating alcohol content in drinks, providing sex education to teenagers, mandating the use of helmets on motorbikes, instead of banning motorbikes altogether.
- India has taken a more stringent option than the US by completely banning the product.
- There are no extra restrictions on traditional cigarettes, which are proven to be more harmful
- The long-term harm of e-cigarettes is less than 5% compared to other tobacco products.
- There are thriving black markets for all these substances and it is no different with e-cigarettes.
- People can buy e-cigarettes online quite easily on various portals and markets.
- By selling these products in black, the government loses all forms of control over the product.
- The government should opt for a harm reduction approach, by developing a regulatory plan for e-cigarettes that maximizes smoking cessation among adults while limiting youth uptake.
- The regulatory plan can include:
- Levying appropriate taxes, issuing public use guidelines, providing information about the product.
- Enforcing a minimum age for sales, and individual product restrictions on nicotine concentration in e-cigarette products.

- As per the report, the governments across the world are planning to produce more than double the fossil fuels than it requires to limit the global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- The climate crisis has not been able to compel major emitters to improve action on the ground so far.
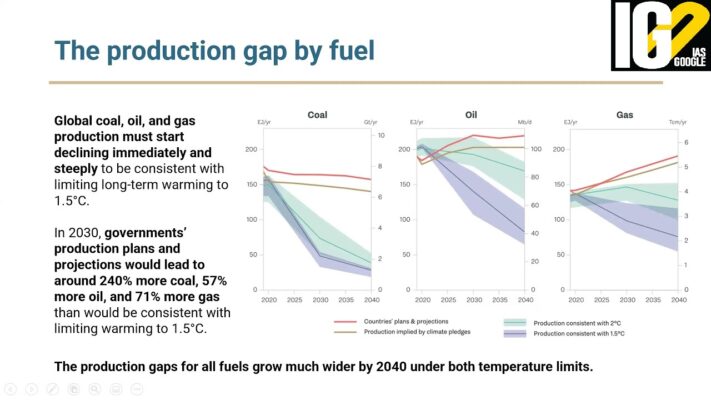
- Almost all major coal, oil and gas producers are planning to increase their production till at least 2030 or beyond, creating an ever-widening production gap.
- The production gap to achieve the climate goal is the widest for coal.
- Production plans and projections by governments would lead to around:
- 240 per cent more coal
- 57 per cent more oil
- 71 per cent more gas in 2030, than global levels consistent with limiting warming to 1.5°C.
- The international public finance for production of fossil fuels from G20 countries and major multilateral development banks (MDBs) has significantly decreased in recent years.
- One-third of MDBs and G20 development finance institutions (DFIs) by asset size have adopted policies that exclude fossil fuel production activities from future finance.
- There has been incremental capital flow towards fossil fuels in comparison to clean energy in the post novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) recovery phase.
- The Group of 20 countries has channelised $300 billion to fossil fuels since the beginning of the pandemic, and the sector is still enjoying significant fiscal incentives.
- Carbon dioxides removal (CDR) technologies should be deployed widely and methane emissions and leakages should be arrested.
- Massive gap between the pledges and actions of countries needs to be rectified with a real policy plan and finance.
- All public as well as private financers, including commercial banks and asset managers, should switch their funding from coal to renewables to promote full decarbonization of the power sector and access to renewable energy for all.
- The report was first launched in 2019.
- Issued by: United Nations Environment Programme
- It measures the gap between governments’ planned production of coal, oil, and gas and the global production levels consistent to limit global warming to 1.5°C and 2°C.
- The FATF also announced the ‘greylisting’ of Jordan, Mali and Turkey, following the conclusion of the Plenary session.

- FATF observed that it needed to further demonstrate that investigations and prosecutions were being pursued against the senior leadership of U.N.-designated terror groups, which include Lashkar-e-Taiba, Jaish-e-Mohammed, al-Qaeda and the Taliban.
- The Pakistan Government has two concurrent action plans with a total of 34 action plan items. It has addressed or largely addressed 30 of the items.
- Its most recent action plan focussed on money laundering deficiencies, was issued after the FATF’s regional partner- Asia Pacific Group, identified a number of serious issues.
- At the previous Plenary in June,2021; the FATF had kept Pakistan in the list of “jurisdictions under increased monitoring” owing to its failure in prosecuting the top operatives of the Security Council-designated terror groups.
- Pakistan has been in the greylist since June 2018.
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an inter-governmental body decision-making body.
- It was established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris to develop policies against money laundering.
- It is a “policy-making body” which works to generate the political will to bring about national legislative and regulatory reforms in money laundering.
- It has also started dealing with virtual currencies.
- Secretariat: Paris.
- India became an Observer at FATF in 2006.
- Since then, it had been working towards full-fledged membership.
- On June 25, 2010 India was taken in as the 34th country member of FATF.
- FATF sets standards and promotes effective implementation of:
- Legal, regulatory and operational measures for combating money laundering.
- The FATF works to identify national-level vulnerabilities with the aim of protecting the international financial system from misuse.
- Black List:
- Countries knowns as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) are put in the blacklist.
- These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities.
- The FATF revises the blacklist regularly, adding or deleting entries.
- Grey List:
- Countries that are considered safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put in the FATF grey list.
- This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies