- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
9th December 2020
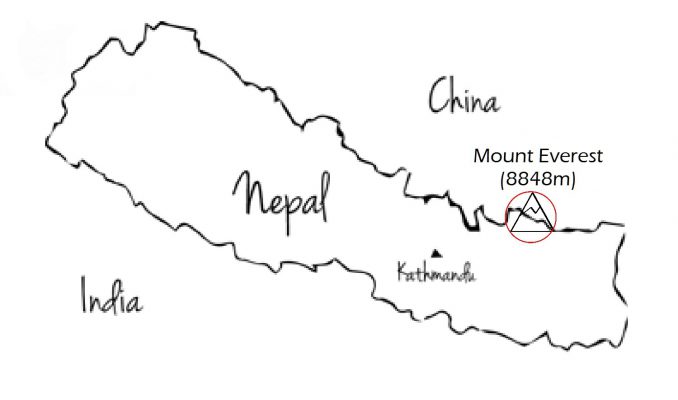
Mount Everest is 3 feet higher
Recently, the Foreign Ministers of Nepal and China jointly certified the elevation of Mount Everest at 8,848.86 metres above sea level i.e. 86 cm higher than what was recognised since 1954.
 Recently, the results of the research by scientists at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Georgia State University have shown that Molnupiravir can stop the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in 24 hours.
Recently, the results of the research by scientists at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Georgia State University have shown that Molnupiravir can stop the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in 24 hours.

- The current official height of Mount Everest has been widely accepted since 1956, when the figure was measured by the Survey of India.
- The height of the summit is known to change because of tectonic activity such as the 2015 Nepal earthquake.
- There is an ongoing debate on whether the height should be based on the highest rock point or the highest snow point.
- A team from Nepal completed its task of measuring the summit in 2019 and China carried out its expedition in May 2020.
- China using the Yellow sea and Nepal using a point close to the Bay of Bengal coast as reference for sea level.
- The mission to measure the world’s highest peak was taken up in 1847, and culminated with the finding of a team led by Andrew Waugh of the Royal Surveyor General of India.
- The team discovered that ‘Peak 15’ (Mt Everest was referred to then) was the highest mountain, contrary to the then prevailing belief that Mt Kanchenjunga (8,582 m) was the highest peak in the world.
- The IISF-2020 is organised by the Defence Institute of High Altitude Research (DIHAR) of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The theme for IISF-2020 is ‘Science for Self-Reliant India and Global Welfare’.
- The IISF is aimed at bringing people together from the remotest corners of the country in a single click and thereby helping in fulfilling the objectives of organising IISF.
- The IISF-2020 proposes to bring more than 10,000 researchers, scientists and experts from different subjects to discuss their research findings and exchange innovative ideas on the identified research themes.
- It was launched in 2015 as a celebration to promote Science and Technology and demonstrate how science could lead India towards a developed nation.
- The aim is to engage the public with science and celebrate the joy of science and show the ways how science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) provide us with the solutions to improve our lives.
- The Ministry of Science & Technology and Ministry of Earth Sciences in association with Vijnana Bharati (VIBHA) has created a unique platform of India International Science Festival which intends to inspire curiosity and make learning more rewarding
- It is the most coveted award for Investment Promotion Agencies given by United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
- It recognizes outstanding achievements and best practices of Investment Promotion Agencies (IPAs) across the globe.
- It is presented annually to make the investment community and general public aware of exceptional contributions by investment promotion agencies to the realization and advancement of national development strategies.
- It is a new digital platform for COVID 19 Vaccination Delivery.
- It is a user friendly mobile app for recording vaccine data which is working as a beneficiary management platform having various modules.
- The app will have separate modules for administrator, registration, vaccination, beneficiary acknowledgement and reports.
- The administrator module is for the administrators who will be conducting these vaccination sessions.
- The registration module is for people to get registered for vaccination.
- The vaccination module will verify beneficiary details and update vaccination status.
- The beneficiary acknowledgement module will send SMS to beneficiaries and also generate QR-based certificates after one gets vaccination.
- The report module will prepare reports of how many vaccine sessions have been conducted, how many people have attended those, and on how many people have dropped out.
- The CO-WIN platform will also be used to send real time temperature details of storage facilities to the main servers.
- In 1971, Bhutan was the first country in the world, followed by India as the second, to recognise Bangladesh as an independent country.
- The trade volume between the two countries is approximately 50 million dollars with 7.56 million of export and 42.09 million import into Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh is expected to sign 11 more PTAs and Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with countries like Indonesia and Nepal by June 2021.
- Bangladesh has signed its first Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) with Bhutan.
- The PTA will allow duty free access to a range of goods between the two countries.
- The agreement was signed on the occasion marking the 50 years of diplomatic ties between the two countries.
- Under the PTA 100 Bangladeshi products will get duty free access to Bhutan and 34 items from Bhutan will get duty free access into Bangladesh.
- A free trade agreement is a preferential arrangement in which members reduce tariffs on trade among themselves while maintaining their own tariff rates for trade with non-members.
- The PTAs or Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) is a special status given in trade by various countries.
- India has signed bilateral FTAs with Sri Lanka (1998), Afghanistan (2003), Thailand (2004), Singapore (2005), Bhutan (2006), Nepal (2009), Korea (2009), Malaysia (2011) and Japan (2011).
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) is an agency of the United Nations.
- It aims at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, and culture.
- The UNESCO seeks to encourage the identification, protection and preservation of cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity.
- It is embodied in an international treaty called the Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO in 1972.
- Encourage countries to sign the World Heritage Convention and to ensure the protection of their natural and cultural heritage;
- Encourage States Parties to the Convention to nominate sites within their national territory for inclusion on the World Heritage List;
- Encourage States Parties to establish management plans and set up reporting systems on the state of conservation of their World Heritage sites;
- Help States Parties safeguard World Heritage properties by providing technical assistance and professional training;
- Provide emergency assistance for World Heritage sites in immediate danger; and
- Support States Parties' public awareness-building activities for World Heritage conservation.
- The criteria are explained in the Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention.
- With the adoption of the revised Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention, one set of ten criteria exists:
- to represent a masterpiece of human creative genius;
- to exhibit an important interchange of human values, over a span of time or within a cultural area of the world, on developments in architecture or technology, monumental arts, town-planning or landscape design;
- to bear a unique or at least exceptional testimony to a cultural tradition or to a civilization which is living or which has disappeared;
- to be an outstanding example of a type of building, architectural or technological ensemble or landscape which illustrates (a) significant stage(s) in human history;
- to be an outstanding example of a traditional human settlement, land-use, or sea-use which is representative of a culture (or cultures), or human interaction with the environment especially when it has become vulnerable under the impact of irreversible change;
- to be directly or tangibly associated with events or living traditions, with ideas, or with beliefs, with artistic and literary works of outstanding universal significance.
- to contain superlative natural phenomena or areas of exceptional natural beauty and aesthetic importance;
- to be outstanding examples representing major stages of earth's history, including the record of life, significant on-going geological processes in the development of landforms, or significant geomorphic or physiographic features;
- to be outstanding examples representing significant on-going ecological and biological processes in the evolution and development of terrestrial, fresh water, coastal and marine ecosystems and communities of plants and animals; and
- to contain the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity.
 Recently, the results of the research by scientists at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Georgia State University have shown that Molnupiravir can stop the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in 24 hours.
Recently, the results of the research by scientists at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Georgia State University have shown that Molnupiravir can stop the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in 24 hours.
- It is an antiviral drug also known as MK-4482/EIDD-2801.
- It is being developed by the biotechnology firm Ridgeback Biotherapeutics in collaboration with pharmaceutical firm Merck.
- It is the first demonstration of an orally available drug to rapidly block SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
- It is a pro-drug of the synthetic nucleoside derivative N4-hydroxycytidine, and exerts its antiviral action through introduction of copying errors during viral RNA replication.
Ferrets
- Ferrets are a popular model for influenza and other respiratory infections because their lung physiology is similar to humans and researchers hope they will mimic aspects of Covid-19 in people such as its spread.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies