- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
9th July 2021
BUILDING RESILIENT HEALTH SYSTEMS
In the recently-concluded G-7 meeting, the wealthiest democracies reaffirmed their commitment to end the current pandemic and strengthen future health resilience.
Health policy and systems research is a complex field: Understanding the relationships between health policies and health systems, as well as the broader determinants of health, requires the best minds from economics, sociology, anthropology, political science, medicine and public health.
Health is a priority of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): It is reflected by the comprehensive health goal of SDG 3: “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages”.
Bridge disparate health and development agendas: The concept of resilience helps in coordinating health and development agendas such as universal health coverage, the Global Health Security Agenda, and the Sustainable Development Goals by lending fresh impetus to the need to invest in health systems.
 Exploring the concept of resilient health systems: The resilience emphasises the functions health systems need to respond and adapt to health shocks.
Exploring the concept of resilient health systems: The resilience emphasises the functions health systems need to respond and adapt to health shocks.


- It identifies the immediate and longer term payoffs of well-functioning, responsive, and adaptable health systems and highlights the unacceptable costs of inaction.
 Exploring the concept of resilient health systems: The resilience emphasises the functions health systems need to respond and adapt to health shocks.
Exploring the concept of resilient health systems: The resilience emphasises the functions health systems need to respond and adapt to health shocks.
- It will aim at introducing a dynamic dimension into more static health system models which can help the system cope with surges in demand and adapt to changing epidemiology and population expectations of care.
- The involvement of people and communities in crafting a response depends on and is a potential means of strengthening government accountability to its citizens.
- It is a web-based system which processes pension claims and credits pension directly into the bank accounts of defence pensioners without relying on any external intermediary.
- It is an end to end Online System facilitating and easing every aspect of Defence Pensions from Initiation to Disbursement.
- It is being implemented for meeting the pension sanction and disbursement requirements for Armed Forces viz. Army, Navy, Air Force and Defence Civilians.
- It will be administered by the Defence Accounts Department through the Principal Controller of Defence Accounts (Pensions), Prayagraj.

- It is available for pensioners to view their pension related information, access services and register complaints for redressal of grievances, if any, relating to their pension matters.
- It envisages establishment of Service Centres to provide last mile connectivity to pensioners who may be unable to directly access the SPARSH portal for any reason.
- The two largest banks dealing with defence pensioners i.e. State Bank of India (SBI) and Punjab National Bank (PNB) have been co-opted as Service Centres.
- It will interface all the stakeholders and provide a single source of truth there by ensuring transparency, accountability and ease of doing business through information dissemination.
- It is a jasmine flower which is known for its powerful, mysteriously attractive and seductive
- It is called as Madurai Malli because of its place of origin namely Madurai which is a province of Tamil Nadu.
- It is a very old traditional flower and has a botanical name of Jasminium.
- The Jasmine City or Madurai is also known as Malligai Managar.
- The ideal season for growth of Madurai Malli is warm summer and bright sunny
- The soil requirement for Madurai Malli varies from sandy loamy soil to even clayey
- It was granted the status of Geographical Indications (GI) under GI Act 1999 in 2013.
- It is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- A sign must identify a product as originating in a given place in order to function as a GI.
- The TRIPS prescribes minimum standards of protection of GIs and additional protection for wines and spirits.
- India has taken legislative measures by enacting the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- It defines Geographical Indications as an indication which identifies such goods as agricultural goods, natural goods or manufactured goods as originating, or manufactured in the territory of a country, or a region or locality in that territory.
- An application for the registration of a GI is to be made to the Registrar of Geographical Indications in the form prescribed under the Gi Act, 1999.
- A Geographical Indication is registered for a period of 10 years and the registration may be renewed from time to time for a period of 10 years at a time.
- Eligibility has now been extended to State Agencies/APMCs, National & State Federations of Cooperatives, Federations of Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs) and Federations of Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- At present Interest subvention for a loan upto Rs. 2 crore in one location is eligible under the scheme but in case, one eligible entity puts up projects in different locations then all such projects will be now be eligible for interest subvention for loan upto Rs. 2 crore.
- For a private sector entity there will be a limit of a maximum of 25 such projects.
- The limitation of 25 projects will not be applicable to state agencies, national and state federations of cooperatives, federations of FPOs and federation of SHGs.
- The location will mean physical boundary of a village or town having a distinct LGD (Local Government Directory) code.
- For APMCs, interest subvention for a loan upto 2 crore will be provided for each project of different infrastructure types e.g. cold storage, sorting, grading and assaying units, silos, etc. within the same market yard.
- The power has been delegated to the Minister of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare to make necessary changes with regard to addition or deletion of beneficiary.
- The period of financial facility has been extended from 4 to 6 years upto 2025-26 and overall period of the scheme has been extended from 10 to 13 years upto 2032-33.

- It aims to provide a medium-long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets.
- Under the scheme, Rs One Lakh Crore will be provided by banks and financial institutions as loans to the following:
- Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS),
- Marketing Cooperative Societies,
- Farmer Producers Organizations (FPOs),
- Farmers, Self Help Group (SHG) & Joint Liability Groups (JLG),
- Multipurpose Cooperative Societies,
- Agri-entrepreneurs & Startups,
- Aggregation Infrastructure Providers and
- Central/State agency or Local Body sponsored Public Private Partnership Project
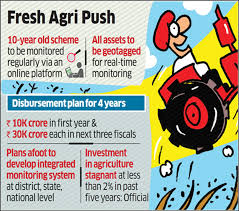
- The loans will be disbursed in four years starting with sanction of 10,000 crore in the current financial year and Rs. 30,000 crore each in next three financial years.
- All loans under this financing facility will have interest subvention of 3% per annum up to a limit of 2 crore for a maximum period of seven years.
- The credit guarantee coverage will be available for eligible borrowers from this financing facility under Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) scheme for a loan up to Rs. 2 crore.
- The National, State and District level Monitoring Committees will be set up to ensure real-time monitoring and effective feed-back.
- The MoC is aimed at promoting and strengthening cooperation in the matter of Competition Law and Policy.
- It will enable CCI to emulate and learn from the experiences and lessons of its counterpart competition agency in Japan which would enhance efficiency.
- It will help improve enforcement of the Competition Act, 2002 by CCI.
- It will benefit consumers at large and will promote equity and inclusiveness.
- It was established in March 2009 by Government of India under the Competition Act, 2002 for the administration, implementation, and enforcement of the Act.
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It is required to give opinion on competition issues on a reference received from a statutory authority established under any law.
- It aims to undertake competition advocacy, create public awareness and impart training on competition issues.
- Section 18 of the Competition Act, 2002 permits CCI to enter into any arrangement with any agency of any foreign country for the purpose of discharging its duties or performing its functions under the Act.

- Eliminate practices having adverse effect on competition
- Promote and sustain competition
- Protect the interests of consumers
- Ensure freedom of trade in the markets of India
- Establish a robust competitive environment through:
- Proactive engagement with all stakeholders, including consumers, industry, government and international jurisdictions;
- Being a knowledge intensive organization with high competence level; and
- Professionalism, transparency, resolve and wisdom in enforcement
- It will provide mutual advanced entry to the Members of both the Institutes through exemptions from appearing in majority of papers to acquire the qualification of the other Professional Body.
- It will lead to a focus attention towards exchange of knowledge and exchange of research and publications which will strengthen good governance
- Both parties will initiate joint research relevant to Cost Accountancy profession which could involve collaborative research in technical areas.
- It will facilitate the movement of professionals in both jurisdictions and will enhance the employability of Cost Accountants in India and abroad.
- It will provide a pathway to enable members of one Institute to seek full membership status of other Institute by successfully passing the minimum number of subjects of professional level.
- It was first established in 1944 as a registered company under the Companies Act.
- The erstwhile objectives of ICoAl were promoting, regulating and developing the profession of cost accountancy.
- In 1959, the Institute was established by a special act of Parliament, namely, the Cost and Works Accountants Act, 1959 as a statutory professional
- It was established for the regulation of the profession of cost and works
- It is the only recognised statutory professional organisation and licensing body in India specializing exclusively in cost and works accountancy.
- To develop the Cost and Management Accountancy function as a powerful tool of management control in all spheres of economic activities;
- To promote and develop the adoption of scientific methods in cost and management accountancy;
- To develop the professional body of members and equip them fully to discharge their functions and fulfill the objectives of the Institute in the context of the developing economy;
- To keep abreast of the latest developments in the cost and management accounting principles and practices, to incorporate such changes are essential for sustained vitality of the industry and other economic activities;
- To exercise supervision for the entrants to the profession and to ensure strict adherence to the best ethical standards by the profession;
- To organise seminars and conferences on subjects of professional interest in different parts of the country for cross-fertilisation of ideas for professional growth; and
- To carry out research and publication activities covering various economic spheres and the publishing of books and booklets for spreading information of professional interest
- It was founded in 1904 and incorporated by Royal Charter in 1947 under the laws of England and Wales.
- It is the global body for professional accountants, with more than 2,27,000 fully qualified members and 5,44,000 future members worldwide.
- The idea of opening up the profession, doing things differently and better, and never losing sight of our public interest remit are concepts that lie at the very heart of ACCA’s DNA.
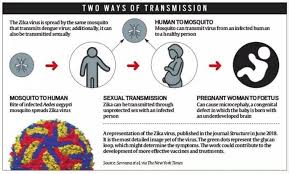
- It is a viral infection which is spread by mosquitoes.
 It is a mosquito-borne Flavivirus.
It is a mosquito-borne Flavivirus.- The vector of Zika virus is the Aedes aegypti mosquito, which also spreads dengue and chikungunya.
- It was first identified in Uganda in 1947 in monkeysand it was later identified in humans in 1952 in Uganda and the United Republic of Tanzania.
- In 2015, a major outbreak in Brazil led to the revelation that Zika can be associated with microcephaly, a condition in which babies are born with small and underdeveloped brains.
- The infected people cantransmit Zika sexually.
- The virus can be passed from a pregnant woman to her fetus and can cause infants to be born with microcephaly and other congenital malformations.
- The fears around Zika primarily involve microcephaly, especially when pregnant women are infected.
- The countries that have had a Zika outbreak, including Brazil, have reported a steep increase in Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- It is a neurological disorderthat could lead to paralysis and death.
- In 2017, following a study on Brazil’s confirmed cases, the US National Institutes of Health study estimated the fatality rate at 8.3 per cent.

- The symptoms are similar to those of flu, including fever body ache, headache etc.
- The additional symptoms can include the occasional rash like in dengue, while some patients also have conjunctivitis.
- The incubation period (the time from exposure to symptoms) of Zika virus disease is estimated to be 3-14 days.
- It has no treatment or vaccine.
- The symptoms of Zika virus are mild and usually require rest, consumption of plenty of fluids, and common pain and fever medicines.
- The governments take mosquito control measures such as spraying of pesticides, use of repellents etc. when Zika cases are reported.
- There is focus on contraceptives because of the possibility of congenital abnormalities and sexual transmission.
- The WHO requires countries to counsel sexually active men and women on the matter to minimise chances of conception at the time of an outbreak.
- In India, Zika virus was first recorded in 1952-53.
- The latest major outbreak was in 2018, when 80 cases were reported in Rajasthan.
- India’s comments came in response to the OIC secretary-general proposing to send a delegation to Jammu and Kashmirin line with relevant resolutions by the grouping’s council of foreign ministers.
- The OIC secretary-general Yousef Al-Othaimeen also asked about the possibility of a meeting between India and Pakista
- The Indian ambassador had used the meeting with the OIC official to convey theneed to correct some of the misperceptions about India that are perpetrated by vested interests in the OIC.
- Pakistan has repeatedly sought to raise the Kashmir issue at the OICagainst the backdrop of India’s dramatically improved relations with several key players in West Asia and in the Islamic Organisation.
- It is the second largest inter-governmental organisationafter the United Nations.
- It has a membership of 57 states, covering four continents.
- Its 57 members include Pakistan, Turkey, the UAE, Afghanistan and Bangladesh.
- It is the collective voice of the Muslim worldto ensure and safeguard their interest on economic socio and political areas.
- Its Headquarters is in Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- It was established upon a decision of the historical summit which took place in Rabat, Kingdom of Morocco in 1969following the criminal arson of Al-Aqsa Mosque in occupied Jerusalem.
- India is not a member of the OIC, but was invited as a ‘Guest of Honour’ at its plenary in 2019.
- India-Maldives relationsdeteriorated during the Progressive Party’s (PPM) five-year rule and the anti-India sentiment was apparent back then.
- The anti-India rhetoric was used during that time because the Maldivian government was pro-China.
- It started in 2020 as on-ground protests in the Maldives, and later widely spread across social media platforms using the phrase with a related hashtag.
- The main reasons behind the ‘India Out’ campaign was rooted in the controversy surrounding the ALF choppers and India’s reported refusal to take them back.
- It was launched by the opposition coalition PPM and PNC both on the street as well as on social media demanding the expulsion of Indian military personnel present in the country.
- Its aim is to garner people’s support to its demand for the release of President Yameenby putting the ruling Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) and India in a bad light.
- The first is the long-standing controversy over the two Dhruv Advanced Light Helicopters (ALF) that were given by India to the Maldives in 2010 and in 2015.
- These helicopters were for humanitarian purposes onlybut some in the anti-India constituency were trying to portray that by gifting these helicopters, India was creating military presence in the country because they were military choppers.
- In 2016, the Yameen government asked India to take back these gifted helicoptersand refused to extend the term of the agreement that would extend their stay and use in the country.
- A recurring complaint in social media posts by prominent members of ‘India Out’ campaign is the lack of transparency in agreementsbeing signed between the Solih government and India.
- The agreements signed by India and the Maldives are allegedly harmful to the Maldives including the agreement on the hydrographic survey, and the agreement on setting up of Coast Guard dockyard at Uthuru Thila Falhu (UTF) funded by India.
- It is argued that the Solih administration is “selling off Maldives”by entering into these agreements with India in the field of defence and security, and infrastructure development.
- India has made heavy investments in the Maldivesand an unfriendly party in power in case of defeat of the MDP in the future elections would go against India’s interests.
- It is important for India to sensitise the people of Maldives about the hateful campaignsgoing against it on baseless assumptions.
- The long silence on such campaigns, even though not supported and encouraged by the incumbent government, might facilitate the anti-India constituency an opportunity to validate their assumptions.
- The anti-India propaganda is getting traction because people don’t have any information about the contents of various deals signed between the two countries.
- The giant water plumes erupting from Enceladushave inspired research and speculation about the vast ocean that is believed to be sandwiched between the moon's rocky core and its icy shell.
- The Cassini spacecraft has found that Titan has methane in its atmosphereand Enceladus has a liquid ocean with erupting plumes of gas and water.
- An international research team has used new statistical methods to understand if methanogenesis or methane production by microbescould explain the molecular hydrogen and methane.
- Microorganisms called methanogens are capable of generating methaneas a metabolic byproduct.
- Methanogens do not require oxygento live and are widely distributed in nature.
- They are found inswamps, dead organic matter, and even in the human gut.
- They are known to survive in high temperaturesand simulation studies have shown that they can live in Martian conditions.
- On Earth, hydrothermal activity occurs when cold seawater seeps into the ocean floor, circulates through the underlying rock and passes close by a heat source.
- The team using the newly developed model gave a set of conditions, including dihydrogen concentration and different temperaturesto understand if microbes would grow.
- The team writes that methane could be formed by the chemical breakdown of organic matterpresent in Enceladus’ core.
- Hydrothermal processes could help the formation of carbon dioxide and methane.
- The results suggest that methane production from hydrothermal vents is not sufficientto explain the high methane concentration detected by Cassini in the plumes.
- It was launched on October 15, 1997 on a seven-year journey toinvestigate Saturn, its rings, and its moons.
- The spacecraft consists of an orbiterand the European Space Agency's Huygens Titan probe.
- Cassini arrived at the planet in 2004 and continues to study the Saturn system with 12 different instruments.
- The Huygens probe was deployed from the Cassini spacecraft and landed on the moon Titan in January of 2005.
- The probe entered the clouds of Titan and gathered atmospheric dataand images as it parachuted to the surface.
- Cassini-Huygens was a mission of firsts because it was first to orbit Saturn, first landing in the outer solar systemand first to sample an extraterrestrial ocean.
- It revealed Titan to be one of the most Earth-like worldswe have encountered and shed light on the history of our home planet.
- Christiaan Huygens(1629-1695) was a Dutch scientist who discovered Saturn's rings and, in 1655, its largest moon, Titan.
- Italian Jean-Dominique Cassini(1625-1712) discovered the Saturnian satellites Iapetus, Rhea, Tethys and Dione.
- In 1675 he discovered what is known today as the 'Cassini Division', the narrow gap separating Saturn's rings.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies