- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
April 08, 2024 Current Affairs
Union Environment Ministry announced the rules for its Green Credit Programme (GCP)
Green Credits:
It is an innovative market-based mechanism whereby voluntary environmental actions will be incentivized by participation from various stakeholders like individuals, communities, private sector industries, and companies.
The Green Credits are Categorised into Eight key Areas:
- Tree plantation; Water management; Sustainable agriculture; Waste management; Air pollution reduction; Mangrove conservation and restoration; Eco-mark labelling; Sustainable building and architecture
The Green Credit Programme (GCP):
- Green Credit Programme Launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in line with the Lifestyle for Environment (LiFe) movement at the recent COP28 in Dubai.
- Administered by the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE).
- Aim: To Generate Green Credits through plantation on degraded wasteland with its initial phase focusing on water conservation and afforestation.
Green Credit Programme Features:
- Creation of a land bank: Registered and approved entities ( individuals, groups, public and private sector units) can pay to finance afforestation projects in specific tracts of degraded forest and wasteland.
- State forest departments will carry out the actual afforestation.
- Each planted tree would be worth one ‘green credit’ after two years of planting and an evaluation by the International Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE).
- Offsetting mechanism: Companies can then use these green credits to offset some of their obligations under India’s compensatory afforestation laws.
- A Market-based Approach: The Green Credit Programme creates a market-based incentive for environment-positive actions like water conservation or soil improvements, apart from just carbon emission reductions.
Concerns:
- Increased Risk of more forest land diversion: The Green Credit Programme facilitates the creation of land banks by linking them to compensatory afforestation activities, which could enable more diversion of forest land to commercial entities.
- No economies of scale: The Indian market being undeveloped with a restricted number of participants could lead to inefficient transactions due to an unbalance in the number of buyers and sellers.
- Market volatility: Green Credit Programme would cause the value of green credits to fluctuate in value and result in businesses facing uncertainties related to their environmental investments.
- It would slow down the programme’s efficiency, with delays in receiving credit and receiving revenues from trades, and affect its success.
- Risk of Greenwashing: For efficient administration of the scheme, stronger regulations are needed to guarantee ongoing monitoring and validation of claims, which would otherwise risk mere greenwashing.
- No standard unit of measurement: The green credit system does not yet have a standard unit of measurement, unlike the carbon market (prices a standard unit per tonne of carbon emitted), as it is complicated to determine as they are accrued from various activities and across different sectors.
Compensatory Afforestation Law:
- Administered under The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, based on the Polluter’s Pay Principle.
- Purpose: The law obliges any industry or institution that has razed forest for non-forestry purposes, to provide an equivalent amount of non-forest land to forest authorities and pay for its afforestation.
Provisions:
- The compensatory land needs to be as near as possible to the forest tracts which have been razed.
- In case of unavailability, twice the amount of ‘degraded’ forest land (usually land with very low tree density but officially marked as forest) may also be made available for compensatory afforestation.
- Net Present Value Rule: Companies also need to compensate for the value of the forest ecosystem, called the ‘net present value’, which is lost due to the diversion of the forest land.
UNHRC adopts first resolution to protect rights of intersex people.
- UN Human Rights Council Adopts Landmark Resolution For Intersex Rights titled “Combating Discrimination, Violence, and Harmful Practices against Intersex Persons”.
- Key Objectives: To combat discrimination, violence, and harmful practices against intersex individuals and to address the underlying causes of such mistreatment.
- It urges states to address the root causes of these issues and ensure the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health for intersex people.
- The resolution requests the U.N. High Commissioner for Human Rights to publish a report examining discriminatory laws, violence, and harmful practices against individuals with innate variations in sex characteristics worldwide.
Intersex Individuals:
Intersex is when someone is born with reproductive or sexual parts that don’t fit typical definitions of male or female.
Intersex can be divided into four categories:
- 46, XX intersex
- 46, XY intersex
- True gonadal intersex
- Complex or undetermined intersex
- Intersex individuals are born with sex characteristics that do not conform to traditional binary notions of male or female.
- These characteristics may include variations in sexual anatomy, reproductive organs, hormonal patterns, and chromosomal patterns.
- Intersex individuals may identify with any gender identity or sexual orientation.
- Intersex people are distinct from transgender individuals.
- Transgender individuals are born with a body that possesses clear sexual characteristics (either male or female), but these characteristics do not align with their gender identity.
Example:
- Penis with Female Hormone Levels
- Absence of Penis but Male Traits
- Outwardly Female, Male-Typical Anatomy Inside: Some individuals may have a female appearance externally but predominantly male-typical internal anatomy.
- Blend of Male and Female Genital Characteristics.
- Mosaic Genetics: In some cases, individuals may have mosaic genetics, where certain cells contain XX chromosomes (typically female) while others contain XY chromosomes (typically male).
Statistics and Demographics:
- Experts estimate that up to 1.7% of the population is born with intersex traits, highlighting the significance of addressing their rights.
Causes of Intersex Traits:
- Intersex traits are estimated to occur in 1% to 2% of the population, making it more common than having red hair or being an identical twin.
- Underlying Factors:
- Genetic conditions that disrupt hormone levels during fetal development.
- Exposure to hormones from medications or other sources during early stages of development.
- Random variations in chromosomes occurring at conception.
UNHRC:
- The Human Rights Council, an intergovernmental body within the United Nations system, is tasked with enhancing the promotion and safeguarding of human rights worldwide.
- Established in 2006 by the General Assembly, it succeeded the United Nations Commission on Human Rights.
- It addresses instances of human rights violations and provides recommendations to address them.
- It is responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the globe.
- The Council is made of 47 Member States, which are elected by the majority of members of the General Assembly of the United Nations through direct and secret ballot.
- India was re-elected to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for the 2022-2024 term in 2021.
Key Mandate:
- Reviews the human rights records of all UN Member States through the Universal Periodic Review.
- Authorizes commissions of inquiry and fact-finding missions to investigate war crimes and crimes against humanity, among other issues.
Challenges faced by Intersex Individuals:
- Prejudice and Discrimination: These people face discrimination in the society due to non-alignment of their body with societal norms of sex and gender.
- Violence, and even infanticide: In various nations, people having visible intersex traits, such as ambiguous genitalia, face abandonment and violence.
- Intersex infanticide is prevalent in the southern and eastern Africa, South Asia, Brazil, and China.
- Unnecessary medical intervention: These people have to go through medical treatment due to People’ belief that intersex people need to be “fixed.”
- In this process, many young children get traumatized due to the experiences in medical procedures.
- Legal Identity: These people face problems in getting identity as society segregates intersex babies and people based on gender.
- Many a time, organizations prohibit them to issue identification which prevent them from doing jobs, opening bank accounts and getting higher education.
Impact of Resolution:
- Increased awareness and recognition: The resolution brings greater visibility to the issue of intersex people and their human rights. This can help to combat stigma and discrimination.
- Protection from harmful practices: The resolution calls on states to address violence and harmful practices against intersex people, such as medically unnecessary surgeries on infants.
- This can help to protect intersex people from physical and psychological harm.
- Improved access to healthcare: The resolution emphasizes the right of intersex people to the highest attainable standard of health.
- This could lead to better access to healthcare services that are sensitive to the needs of intersex people.
- Empowerment and self-determination: The resolution calls on states to respect the autonomy and bodily integrity of intersex people.
- This can empower intersex people to make their own decisions about their bodies and their lives.
- Foundation for further progress: This resolution is a significant step forward, but it’s just the beginning.
- It can pave the way for further legal and policy changes that protect the rights of intersex people around the world.
IMD raises alert for extreme heat wave weather.
Climate Change and Heatwaves:
- The warning from IMD aligns with the findings of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report in 2023.
- The IPCC''s 2023 report highlights the urgent need for action against climate change.
- Current carbon emission rates indicate a limited time frame of 10 years to offset emissions equivalent to a decade''s worth.
- Scientists warn that without immediate and strong measures, the world could face dire consequences, including heatwaves, droughts, food insecurity, and the spread of infectious diseases.
- The damage caused by global warming, even at just one degree above pre-industrial temperatures, has been more severe than anticipated, leading to disruptions in ecosystems and communities.
IMD''s Criteria for Heatwaves:
- IMD declares a heatwave when temperatures exceed 40°C in plains, 37°C in coastal areas, and 30°C in hills.
- Heatwaves are categorized based on departures from normal temperatures and actual maximum temperatures, with severe heatwaves occurring at higher thresholds.
- Heat Wave: 4.5°C to 6.4°C above normal temperature.
- Severe Heat Wave: Above 6.4°C above normal temperature.
- Heat Wave (Plains): Temperature ≥ 40°C.
- Severe Heat Wave (Plains): Temperature ≥ 45°C.
- If these conditions persist for two consecutive days, a heat wave is declared.
Favorable conditions include:
- Transportation of hot, dry air across the region.
- Lack of moisture in the upper atmosphere.
- Clear skies, allowing maximum insulation.
- Presence of large amplitude anti-cyclonic flow over the area.
Impact and Mitigation:
- Heatwaves pose significant health hazards, including heat strokes, and strain water and energy resources.
- Agriculture also suffers, with potential effects on crop yield and food security due to wilting and early ripening.
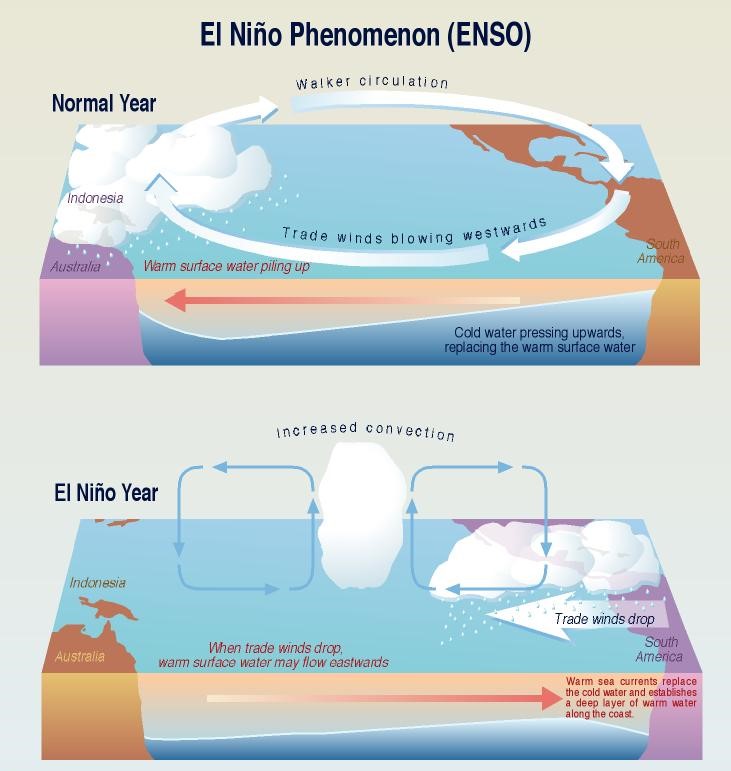
US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has predicted an 83% probability of the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) transitioning to a neutral range by April-June 2024.
Oceanic Niño Index:
- It is the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) primary indicator for monitoring the ocean part of the seasonal climate pattern called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or “ENSO”.
- The ONI tracks the running 3-month average sea surface temperatures in the east-central tropical Pacific between 120°-170°W, near the International Dateline, and whether they are warmer or cooler than average.
- Index values of +0.5 or higher indicate El Niño and values of -0.5 or lower indicate La Niña.
El Nino and La Nina:
- El Nino and La Nina are two opposing climate trends that deviate from the normal conditions and normally run nine to twelve months, but can often extend.
- These events occur every two to seven years on average (El Nino is more frequent than La Nina), but not on a regular basis and together are referred to as the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle by scientists.
- El Nino is typically known as the warm phase (a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean) and La Nina is identified as the cold phase (a band of cooler water spreads east-west) of ENSO.
- Both El Nino and La Nina can have global effects on weather, wildfires, ecosystems and economics.
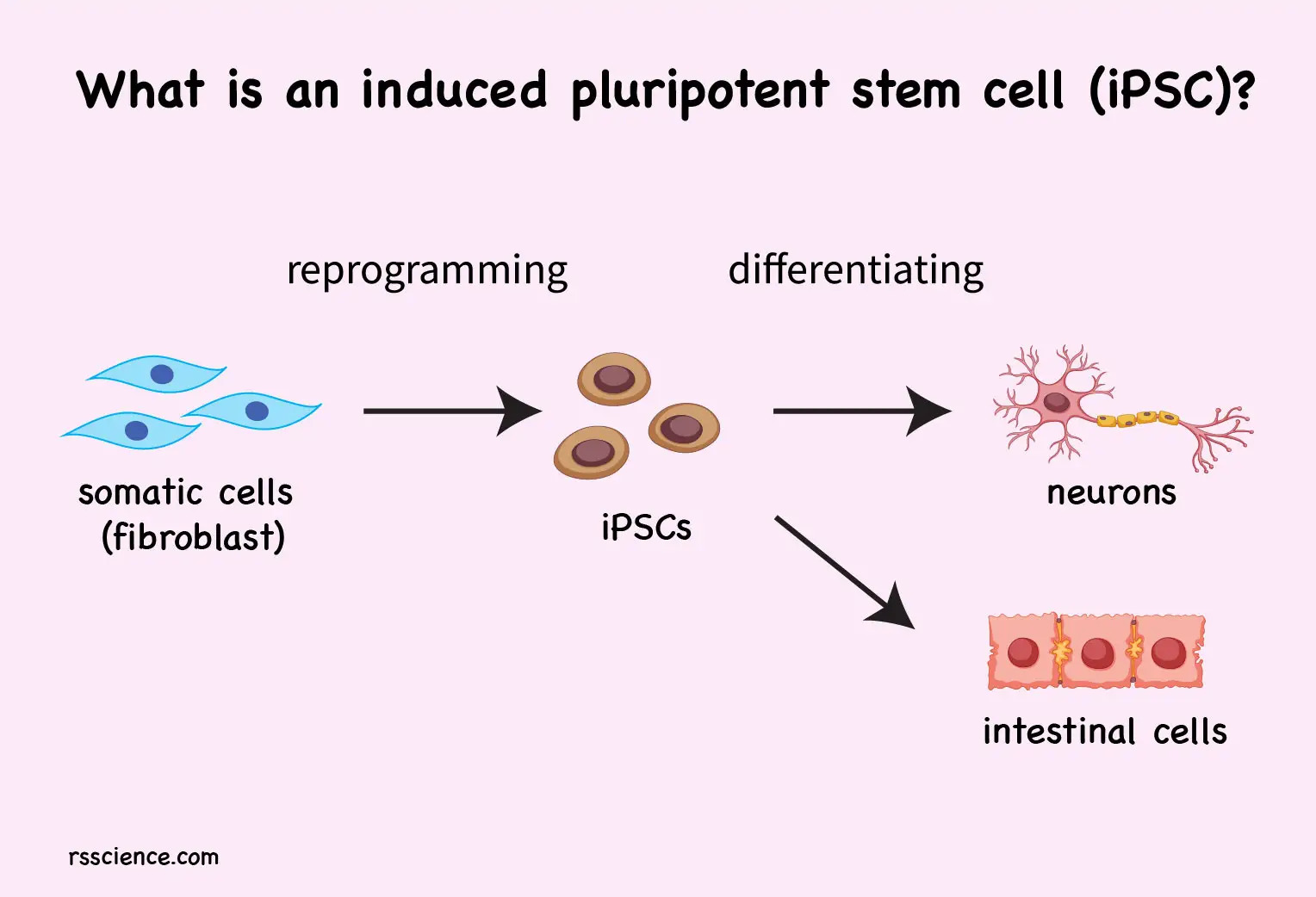
Lab-grown 'minibrains' help reveal why traumatic brain injury raises dementia risk.
Lab-grown Minibrains:
- These are scientifically known as brain organoids, but often called "minibrains" and serve as miniature, simplified models of full-size human brains.
How are minibrains made?
- Scientists typically grow brain organoids from stem cells, a type of immature cell that can give rise to any cell type, whether blood, skin, bowel or brain.
- The stem cells used to grow organoids can either come from adult human cells, or more rarely, human embryonic tissue.
- Scientists collect adult cells and then expose them to chemicals in order to revert them into a stem cell-like state. The resulting stem cells are called "induced pluripotent stem cells" (iPSC), which can be made to grow into any kind of tissue.
- To give rise to a minibrain, scientists embed these stem cells in a protein-rich matrix, a substance that supports the cells as they divide and form a 3D shape. Alternatively, the cells may be grown atop a physical, 3D scaffold.
- Application: These organoids can potentially be useful in basic research, drug development and even computer science.
Russia Declares Federal Emergency As Ural River Floods Orsk, Thousands Evacuated.
Ural River:
It is a 2,428 km long river that flows through Russia and Kazakhstan along the continental boundary between Europe and Asia.
It is also referred to as the Zhayyq River in the native Kazakh language.
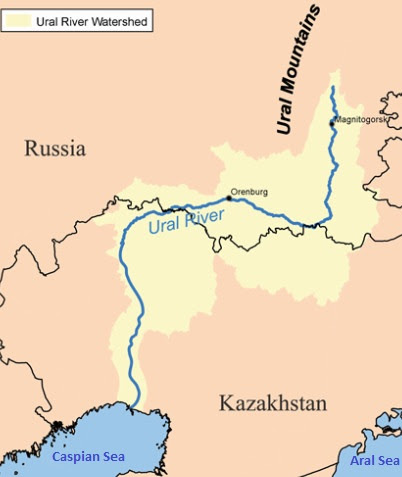
Course:
The river originates in the Ural Mountains, close to Mount Kruglaya in Russia.
It empties into the Caspian Sea; the world’s largest inland sea that lies between Europe and Asia.
It is Europe's third-longest river, after the Volga and the Danube rivers, and Asia's 19th longest river.
Melting snow constitutes about 60% to 70% of the river’s water source, while precipitation is a minor source.
A prominent feature of the Ural River is its digitate delta, or tree-like structure, that can be seen as the river enters the Caspian Sea.
Tributaries:
It has a total of 58 tributaries, with the most prominent ones being Kushum, Derkul, Chagan, Irtek, Utva, Elek, Bolshaya Chobda, Kindel, Sakmara, Tanalyk, Salmys, Or, and Suunduk.
Tributaries from the right side are typical mountain rivers, while the left side tributaries have flatland characteristics.
Orsk City:
It is located in the Orenburg Oblast region, Russia.
It lies about 150 miles (240 km) south of Magnitogorsk at the confluence of the Ural and Or rivers.
It lies adjacent to the Kazakhstan–Russia border.
Orsk is now a major industrial centre, with a large oil refinery using petroleum piped from fields on the Caspian Sea.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies