- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
April 28th, 2024 Current Affairs
IMD Study warns of ‘decreasing trend’ in solar radiation for electricity in India
Solar photovoltaic (SPV) potential:
- SPV potential refers to the maximum amount of solar radiation that can be converted into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) technology in a particular area.
- It is measured as kilowatt-hours per installed kilowatt of capacity (kWh/kWp).
- It depends on factors like sunlight availability, weather, and geographical location.
- Assessing this potential helps determine the feasibility of installing solar panels for electricity generation.
Global solar radiation:
- Global solar radiation is the total amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth''''s surface, made up of direct and diffuse radiation.
- It is important for the climate system because it affects air temperature, evaporation, biological growth, and how much solar energy is available.
- Global solar radiation exhibited a decreasing trend from 1981 to 2006, with greater dimming observed from 1971 to 2000 compared to 1981 to 2006.
- However, a reversal in trends occurred after 2001, with unclear causes for this shift.
Decreasing Solar Radiation Trends:
Study Findings:
- Analysis by IMD scientists shows a decreasing trend in solar radiation suitable for conversion to electricity by solar panels.
- Analysis conducted at 45 IMD stations revealed declining trends in SPV potential.
Locations Affected:
- SPV potential showed a general decline in all stations which included Ahmedabad, Chennai, Goa, Jodhpur, Kolkata, Mumbai, Nagpur, New Delhi, Pune, Shillong, Thiruvananthapuram, and Vishakhapatnam.
- India''''s largest solar parks, mainly in Gujarat and Rajasthan, are also experiencing a decrease in solar photovoltaic (SPV) potential.
Factors Contributing to Decline:
- Increased Aerosol Load: Emissions from carbon, fossil fuel burning, and dust contribute to higher aerosol presence.
- Impact of Aerosols and Clouds: Aerosols absorb the sunlight and deflect it away from the ground and they can also aid the formation of dense clouds,that again block sunlight.
Implications for Solar Energy:
- The efficiency of solar panels are significantly influenced by the amount of sunlight incident on them.
India’s Solar Power Capacity:
- As of now, India''''s installed solar capacity stands at approximately 81 GW, about 17% of the total electricity capacity.
- The country''''s solar energy potential, estimated by the National Institute of Solar Energy, is 748 GW.
- India ranks 5th globally in Solar Power Capacity.
- India plans to obtain around 500 GW, almost half of its electricity needs, from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- This includes achieving at least 280 GW from solar power by that year, requiring an annual addition of at least 40 GW of solar capacity until 2030.
Government Initiatives:
- Rooftop Solar Initiative: A major initiative to fund rooftop solar installations in at least one crore houses across the country, announced earlier this year.
- National Solar Mission (NSM): Launched in 2010, this initiative promotes solar energy use for grid-connected and off-grid applications through financial incentives, subsidies, and policy support.
- Solar Park Scheme: It aims to create 50 solar parks, each with a capacity of 500 MW or more, totaling approximately 38 GW by 2025-26.
- These parks serve as key hubs for solar energy generation, attracting investments and facilitating solar power development.
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for High-Efficiency Solar Photovoltaic Modules: It aims to incentivize the production of such modules as part of the national program.
- PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: Offers subsidies for rooftop solar panel installations.
INCOIS scientists map Indian Ocean floor to study currents
- Recently, a study titled ''''Impact of bathymetry on Indian Ocean circulation in a nested regional ocean model'''' was undertaken by scientists from the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS).
- Bathymetry involves mapping the depths of various water bodies, including rivers, seas, and oceans.
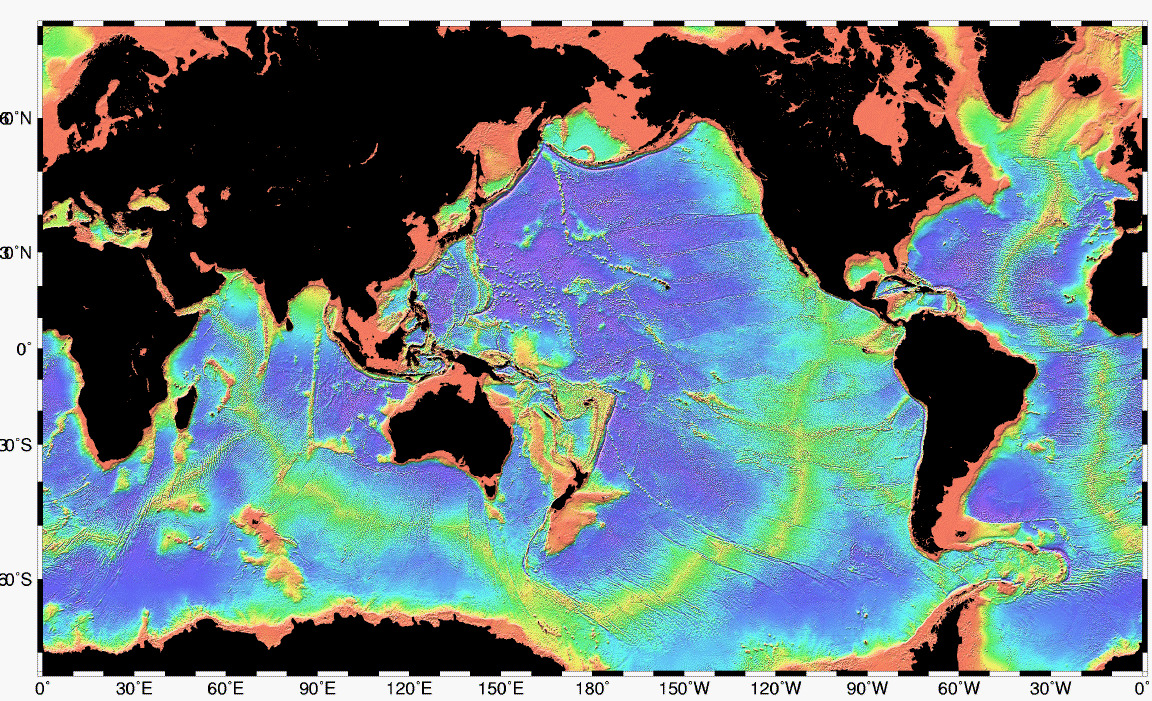
Findings in the Study:
- East India Coastal Current (EICC): At depths of 1,000 meters and 2,000 meters, the EICC flows in the opposite direction to surface currents. This finding contradicts previous models and highlights a more accurate representation of the EICC''''s behavior at depth.
- Equatorial Under Current (EUC): The EUC, influenced by the presence of the Maldives Islands, extends westward and displays significant seasonal variations. During the northeast monsoon, it''''s centered on the equator and can be found as deep as 150 meters.
- Currents along Andaman and Nicobar Islands: A significant boundary current was identified at a depth of 2,000 meters along the coast of these islands, indicating complex deep-sea dynamics not previously recognized.
- Salinity and temperature: The study confirmed that salinity and temperature measurements of the upper ocean are very close to observed values near the coast, validating the improvements in ocean modeling.
- The study''''s insights are crucial for improving weather and climate forecasts, which affect not only environmental understanding but also maritime and economic activities.
Biohacking is picking up in India especially in metro cities like Delhi and Mumbai and also slowly making inroads into Tier II and III cities too.
Biohacking:
- It is a term used to describe various tips and tricks for enhancing the body’s ability to function at peak performance—and maybe even extend one’s lifespan.
- It includes the practice of employing methods drawn from fields like biology, genetics, neuroscience and nutrition to enhance physical or mental performance, improve overall health and well-being, or achieve a specific health outcome.
- The term was coined by Dave Asprey, an entrepreneur and author, back in 2011.
- For Asprey, biohacking meant “changing the environment outside of you and inside of you so you have full control of your biology”.
Most types of biohacking generally fall into one of the following categories below:
- Lifestyle: This category focuses on making positive health and behavior choices. It is probably the most accessible way most people can start experiencing biohacking, as it includes factors like dietary shifts, breathwork, meditation and exercise.
- Molecular: It involves the use of natural and synthetic molecules that can help shift one’s biology. Taking supplements would fall into this biohacking category.
- Biologics: These are biological products that are meant to improve or enhance biology. They could be cells, or they could be small little information packets like exosomes, which are basically biological bundles of DNA, mRNA proteins and growth factors. Biologics typically need to be ingested, injected (such as stem cells) or delivered intravenously (i.e. by IV transfusion).
- Technology: This category includes devices like wearables (such as smartwatches) and diagnostics (such as blood sugar monitors). In such cases, biohacking uses technology to gather data about the body and its functioning so an individual can use that information to adjust their health as they strive for improved performance.
- There are currently no laws in India that specifically address biohacking.
Research conducted on using drugs to target H3 and H4 receptors for the potential treatment of neurological and immunological disorders.
Histamine:
- Histamine is a critical compound in the body, involved in various physiological processes such as allergies, inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and the regulation of gastric acid secretion.
- Histamine consists of two main components: ethylamine (CH3CH2NH2) and imidazole (C2N2H4), which have a ring-like structure.
- It is primarily stored in the secretory granules of mast cells and basophils.
Release Triggers:
- Immune-related triggers include allergens and snake venom.
- Non-immune triggers involve physical injuries.
Roles of Histamine:
- H1 receptors are found in blood vessels, neurons, and smooth muscles.
- H2 receptors enhance gastric acid secretion in the stomach.
- H3 receptors are present in the central nervous system and play a role in regulating neurotransmitters.
- H4 receptors are involved in controlling inflammatory and allergic responses.
Antihistamines:
- Antihistamines are drugs designed to counteract the effects of histamine by blocking its receptors.
- These medications are widely used and can be purchased over-the-counter for treating common allergic symptoms such as sneezing and itching.
- They effectively mitigate the actions of histamine, providing relief from minor allergic reactions.
Supreme Court Rejects Plea For 100% EVM-VVPAT Verification
Supreme Court’s directions:
- The Symbol Loading Units (SLUs) used in VVPATs must be sealed, secured, and stored for 45 days following the election results.
- The SLUs are to be stored alongside the EVMs and undergo examination akin to the EVMs.
- Candidates can request verification of 5% of the EVMs, including ballot units, control units, and VVPATs, in any given constituency by engineers of the manufacturers.
- This request must be made in writing within seven days of the declaration of the election results.
Electronic Voting Machine(EVM):
- An EVM is a portable instrument for the purpose of conducting elections to the parliament, legislature and local bodies like panchayats and municipalities.
- In 1989, the Election Commission (EC) developed India's indigenous EVMs in alliance with two central government undertakings - the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL) and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- It is a microcontroller-based instrument designed to modernise the election procedure and there is no scope for invalid votes and total secrecy of voting data is maintained and it also facilitates quick and accurate counting.
- The voting data recorded in EVMs can be retained for years and can be extracted if necessary.
- It was first time used in the general election in Kerala in 1982.
Working Module of EVM:
- An EVM consists of a control unit and a balloting unit.
- The control unit belongs to a polling officer while the balloting unit is kept in a compartment to cast votes.
- The balloting unit presents the voter with blue buttons horizontally labelled with corresponding party symbols and candidate names.
- The Control Unit, on the contrary, provides the officer-in-charge with a 'Ballot' marked button to proceed to the next voter, instead of issuing a ballot paper to them.
- EVMs can even be used in areas with no electricity, as they can be operated on alkaline batteries.
Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT):
- Initially introduced during the 2014 Lok Sabha elections in India, the VVPAT is essentially a system for verifying votes without traditional paper ballots, directly linked with the EVM.
- VVPAT generates a paper slip post-vote, displayed for seven seconds, showing the party's name and symbol chosen by the voter.
- Voters can see the slip through a transparent window on the EVM to verify their selection.
- After viewing, the slip drops into a secure compartment within the EVM, which can be accessed in case of any disputes.
- In 2019, the Supreme Court of India required cross-verification of VVPAT slips with EVM results for 5 machines per assembly segment in each parliamentary constituency.
- Ensures voter confidence and transparency by providing a physical proof of electronically cast votes.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies