- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
August 13 , 2024 Current Affairs
Australia, U.S. and U.K. sign nuclear transfer deal for AUKUS submarine
AUKUS
AUKUS is a new trilateral security partnership for the Indo-Pacific, between Australia, the UK and the US (AUKUS). Under the pact, the US and the UK will help Australia to acquire conventionally armed nuclear-powered submarines. The pact also includes cooperation on advanced cyber, artificial intelligence and autonomy, quantum technologies, undersea capabilities, hypersonic and counter-hypersonic, electronic warfare, innovation and information sharing.
Submarine Component:
- It is designed to equip Australia with nuclear-powered attack submarines(SSNs).
- In total, Australia will end up with eightof the new nuclear submarines, called SSN-AUKUS.
- These submarines will be based on a British design but have American technology or an American combat system.
- AUKUS will make Australia the seventh countryin the world to be armed with nuclear-powered submarines and the second, after the United Kingdom, with whom the United States has shared this technology.
- These countries, however, made it clear that their aim is not to arm the new submarines with nuclear weapons. This is because Australia is a signatory tothe Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT), which bans it from acquiring or deploying nuclear weapons.
Significance:
- AUKUS aims forfreedom and openness in the Indo-Pacific region, including the South China Sea.
- AUKUS partnership is signed to bolster Australia’s naval power in the Indo-Pacific region as a challenge to the regional hegemonic ambitions of China.
- The operationalisation of this security partnership will lead tocloser military coordination among the participating nations in the region.
- China’s encirclement of India can be partially mitigated by AUKUS.
- India may derive secondary benefitsfrom having top of the class military know-how in the region.
Challenges:
- Many of its regional partners such as Indonesia oppose Australian operating nuclear attack submarines.
- Virginia class submarines are world’s most potent in terms of capabilities many U.S. policymakers are sceptical about the sale.
- Integration of three different systems will prove difficult.
- The S.’s stringent export control and protocol regime could spoil the technology transfer agreement, particularly in areas related to undersea capabilities and electronic warfare.
AUKUS and India
- India takes a balanced approach toward AUKUS, considering its role as a vital Indo-Pacific and European partner.
- AUKUS scrutinises India''s ties with the U.S., France and Russia.
- It also allows India to strengthen relations with the European Union when NATO is facing issues.
- India is concerned that AUKUS will increase the number of nuclear submarines operating in the Indian Ocean region starting in the 2030s.
- India has an indigenous nuclear submarine program with two operational boats. It also has a long-term lease with Russia for a nuclear submarine.
- India would welcome the strengthening of Quad partner Australia, a critical ally sharing information on Chinese forces.
- AUKUS highlights some dilemmas for India in the Quad.
President Droupadi Murmu honoured with Timor-Leste’s highest civilian award; PM says, proud moment for country
East Timor
Timor-Leste is a Southeast Asian nation occupying half the island of Timor and is ringed by coral reefs teeming with marine life. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, of which the western half is administered by Indonesia, the exclave of Oecusse on the island’s north-western half, and the minor islands of Atauro and Jaco. Australia is the country’s southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea.
- Timor-Leste was a Portuguese colony until 1975,followed by Indonesian rule after the conflict.
- In a 1999 UN-supervised referendum, East Timorese voted for independence, which led to further violence until peace-keeping forces intervened, and the country was officially recognized by the UN in 2002.
- East Timor has applied for ASEAN membership and currently holds observer status
Challenges and Opportunities:
Timor-Leste plays a significant and evolving role in India''s Act East Policy, which is a strategic initiative aimed at strengthening India''s ties with countries in the Asia-Pacific region. Here''s a discussion on the role of Timor-Leste in India''s Act East Policy
Strategic Geopolitical Location:
- Timor-Leste''s geographical location in Southeast Asia makes it strategically important for India''s outreach in the region.
- It provides India with an entry point to engage with the ASEAN countries and reinforces India''s presence in the Indo-Pacific region.
Economic Engagement:
- Timor-Leste offers economic opportunities for India, particularly in sectors like oil and gas exploration.
- Strengthening economic ties aligns with the economic objectives of India''s Act East Policy, promoting trade, investment, and technology exchange.
Diplomatic Cooperation:
- Diplomatically, Timor-Leste adds to India''s network of friends in the region.
- By building diplomatic ties with Timor-Leste, India enhances its influence in international forums and reinforces its commitment to fostering peaceful and cooperative relations in the Indo-Pacific.
ASEAN Connectivity:
- Timor-Leste''s potential membership in ASEAN can further enhance India''s connectivity with the ASEAN community. This aligns with India''s efforts to deepen its engagement with regional organizations, a key pillar of the Act East Policy.
Philippines President condemns China’s actions in disputed South China Sea
South China Sea
It is one of the most strategically and economically important waterways in the world, extending from the Strait of Malacca in the southwest, to the Strait of Taiwan in the northeast. It is a crucial maritime gateway and junction for shipping between the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- It is surrounded by several nations, including China, Taiwan, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, Singapore, Cambodia, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and fisheries, and serves as a crucial trade route for various economies.
Importance:
- This sea holds tremendous strategic importance for its location as it is the connecting link between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, through Strait of Malacca.
- According to the United Nations Conference on Trade And Development (UNCTAD) one-third of the global shipping passes through it, carrying trillions of trade which makes it a significant geopolitical water body.
- According to the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Philippines, this sea has one-third of the entire world’s marine biodiversity and contains lucrative fisheries providing food security to the Southeast Asian nations.
- The SCS is believed to have huge oil and gas reserves beneath its seabed.
- It is one of the world’s most heavily trafficked waterways. An estimated USD 3.4 trillion in ship-borne commerce transits the sea each year, including energy supplies to U.S., Japan and South Korea.
Territorial Disputes
- The territorial disputes in the South China Sea primarily involve China and several Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries.
- China claims sovereigntyover virtually the entire South China Sea, putting it at odds with the Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Brunei, who all maintain claims over islands, reefs, and undersea resources in the region.
- The major island and reef formations in the South China Sea are the Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, Pratas, the Natuna Islands and Scarborough Shoal.
- As many as 70 disputed reefs and islets are under contention, with China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Taiwan all building more than 90 outposts on these disputed features.
- China claims up to 90% of the sea with its "nine-dash line" mapand has physically expanded islands and constructed military installations to assert control.
- China has been particularly active in theParacel and Spratly Islands, engaging in extensive dredging and artificial island-building, creating 3,200 acres of new land since 2013.
- China also controls the Scarborough Shoal through a constant Coast Guard presence.
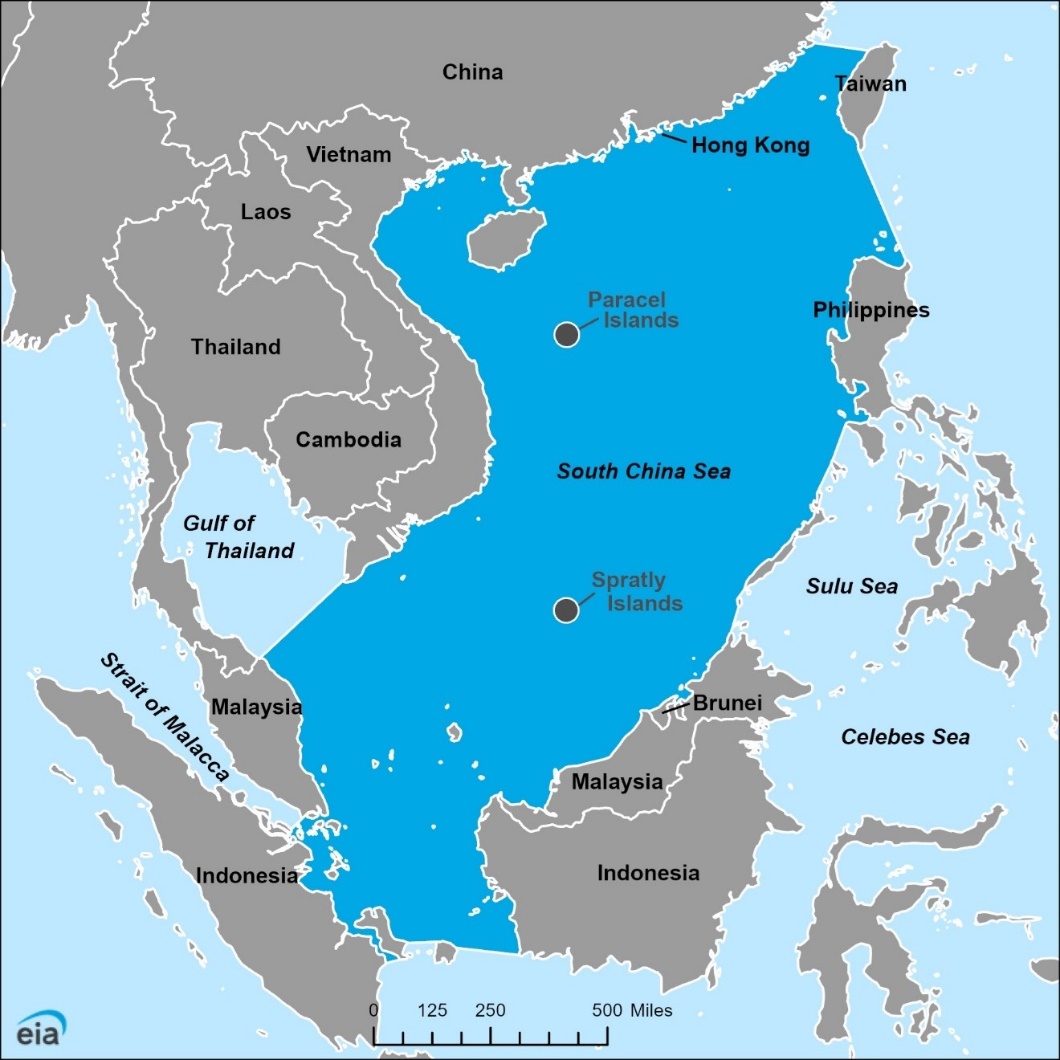
India and the South China Sea
- India remained acutely conscious of its official position of neither being party to the disputes nor taking sides for many years. But with increasing ties with East Asian countries (Act East Policy), India indirectly started raising concerns about Chinese illegitimate claims in the South China Sea. India believes that the disputes in the Southeast Asian littorals are a litmus test for the international maritime law.
- In the aftermath of the Hague Tribunal’s verdict on the South China Sea, India obligated to take a principled stand on the issue of freedom of navigation and commercial access enshrined in the UNCLOS.
- Despite China’s protests, India continues its oil exploration in Vietnam’s exclusive economic zone (EEZ) in the South China Sea from where ONGC Videsh Limited supplies oil to Vietnam.
- India also supports a negotiated settlement of Brunei’s maritime dispute with China and has inked defence cooperation agreement that would provide an institutional foundation for more collaborative work on maritime security and secure India’s energy lanes to Brunei.
Anti-diabetic herb Gurmar found on Gaya’s Brahmayoni Hill
- Researchers have identified a range of medicinal plants on Brahmayoni Hill in Gaya, Bihar, including Gymnema sylvestre (Gurmar).
- Gurmar is noted for its anti-diabetic properties and has been used in developing the anti-diabetic drug BGR-34 by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
Properties and Benefits of Gurmar
- Gymnema sylvestre contains gymnemic acid, which helps reduce blood sugar levels by blocking sugar absorption in the intestines.
- It includes flavonoids (antioxidants) and saponins (which help lower cholesterol and regulate lipid metabolism).
Development and Efficacy of BGR-34
- BGR-34 is an Ayurvedic formulation marketed by Aimil Pharma, incorporating Gurmar along with other phyto-ingredients such as Daruharidra, Giloy, Vijaysar, Manjishtha, and Fenugreek.
- A 2022 study by AIIMS Delhi confirmed BGR-34''s effectiveness in reducing obesity, managing blood sugar levels, and improving metabolic health.
- The study references that the first diabetes drug, Metformin, was derived from the medicinal plant Galega, emphasizing the potential of plant-based treatments.
- The researchers advocate for further exploration of Gurmar to develop new therapeutic options and enhance understanding of its benefits.
Sustainability and Community Involvement
- There is a call to involve local populations in cultivating commonly used medicinal herbs to prevent their extinction.
- This approach aims to ensure the sustainability and continued availability of these valuable resources for future generations.
From Gaming to Digital Assets: How Web 3.0 is transforming India''s tech industry through metaverse
Web 3.0
It is the decentralized form of internet run on blockchain technology. In this user can own stakes in platforms and applications which is now controlled by big Tec companies. The term ‘Web 3’ was first coined by Gavin Wood, founder of Ethereum in 2014, referring to a decentralized online ecosystem based on blockchain.
Significance of Web 3.0
- Web3 will deliver a decentralized and fair internetwhere users control their own data.
- With block chain, the time and place of the transaction are recorded permanently. Thus, Web3 enables peer to peer transactions by eliminating the role of the intermediary. This concept can be extended to
- The spirit of Web3 is Decentralized Autonomous Organization .
- DAO is all about the business rules and governing rules in any transaction are transparently available for anyone to see and software will be written conforming to these rules.
- With DAO, there is no need for a central authority to authenticate or validate.
Metaverse
It refers to a virtual or digital universe where people can interact with each other and digital objects in a shared online space. The term “metaverse” first appeared in author Neal Stephenson’s 1992 science-fiction novel Snowcrash, which describes a future where millions of people use virtual avatars to participate in a cyberspace realm. The metaverse is essentially an interconnected network of virtual worlds, augmented reality, and virtual reality environments accessible through the internet.
- In this digital realm, users can create avatars, socialize with others, engage in various activities, explore virtual landscapes, and even conduct business or trade virtual goods and services.
- Elements of the metaverse include virtual reality platforms, augmented reality experiences, online games, social media, virtual commerce, and virtual art galleries, among others.
- The metaverse aims to offer a seamless and immersive experience, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
- Companies such as Meta, Microsoft, and Roblox are all investing heavily in the metaverse, and it is seen as a potential major driver of growth in the technology industry in the coming years.
Applications of Metaverse
- Hardware Sales:Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg believes augmented reality glasses will eventually be as widespread as smartphones. If that is the case, this will be a very big market.
- Software Sales:Huge scope in the development of software applications to support the meta-verse ecosystem.
- Gaming:Facebook’s gaming platform Oculus VR is expected to be the gateway into the metaverse.
- Physical Sales:Sales of physical goods and services will be linked to the virtual ecosystem in the future.
- Immersive Learning: Immersive Learning is a training methodology that uses Virtual Reality (VR) to simulate real-world scenarios and train students in a safe and engaging immersive training environment.
- decentralized commerce: In-world transactions to happen peer-to-peer.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):NFTs – the claim of ownership for a unique, non-interchangeable digital asset that is stored on a blockchain – may be widely adopted.
Challenges Associated with Metaverse in India
- Privacy and Security:Online risks may be exacerbated in the metaverse, where unwanted contact could become more intrusive and pervasive.
- There are both benefits and drawbacks to social networking sites. The riseof social media has introduced pseudo social behaviour that has slightly delineated traditional social values of collectivism and brotherhood.
- Protecting the IPR (IP Rights) of content creators will also be a challenge considering thedifficulty in tracking copyright infringements in the virtual space.
- it will require a 5G connection to provide a safe and reliable experience.Most rural communities are still struggling with acquiring and maintaining a secure 4G connection.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies