- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Daily Current Affairs | 20th April 2020
Sufiana music of Kashmir, turbans of Rajasthan, Kumbh mela on India’s 'intangible cultural heritage’ list release by culture minister Prahlad Patel
The Ministry of Culture has launched the draft National List of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of India .
Key Points
- The National ICH List is an attempt to recognize the diversity of Indian culture embedded in its intangible heritage.
- It aims to raise awareness about the various intangible cultural heritage elements from different states of India at national and international level and ensure their protection.
- This initiative is also a part of the Vision 2024 of the Ministry of Culture.
- The list has more than 100 elements which also include 13 elements recognized by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) as Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- Following UNESCO’s 2003 Convention for Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, this list has been classified into five broad domains in which intangible cultural heritage is manifested.
- The 2003 Convention is a part of the Convention Concerning the Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage which was adopted by the General Conference of UNESCO in 1972 in order to promote the identification, protection and safeguarding of natural cultural heritage.
- The five domains are:
- Oral traditions and expressions, including language as a vehicle of the intangible cultural heritage.
- Performing arts.
- Social practices, rituals and festive events.
- Knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe.
- Traditional craftsmanship.
- Kerala’s martial art form, Kalaripayuttu, and the practice of making designs at the entrance of homes and temples called kolam in Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh are included in the draft list.
- The present items in the list have been collated from the projects sanctioned under the scheme for ‘Safeguarding the Intangible Cultural Heritage and Diverse Cultural Traditions of India’ formulated by the Ministry of Culture in 2013.
Scheme for Safeguarding the Intangible Heritage and Diverse Cultural Traditions of India
- The scheme was set up under the Ministry of Culture (MoC) during 2013-14.
- The objective of the Scheme is to support and strengthen the efforts of various stakeholders vis-a-vis wider recognition and acceptance, dissemination, preservation and promotion of the rich, diverse and vast ICH of India including recognition of the same by UNESCO.
- The Scheme aims to support
- Institutions/ Universities/ State Govts/ UT Administrations/ non-MoC Institutions/ Societies/ Non-government organisations, involved in the preservation and propagation of intangible cultural heritage, cultural expressions etc.
- Individuals, researchers, scholars, professionals who are involved in the research, training, preservation, perpetuation, dissemination, and propagation of intangible cultural heritage, cultural expressions etc.
How reverse repo rate became benchmark interest rate in the economy?.
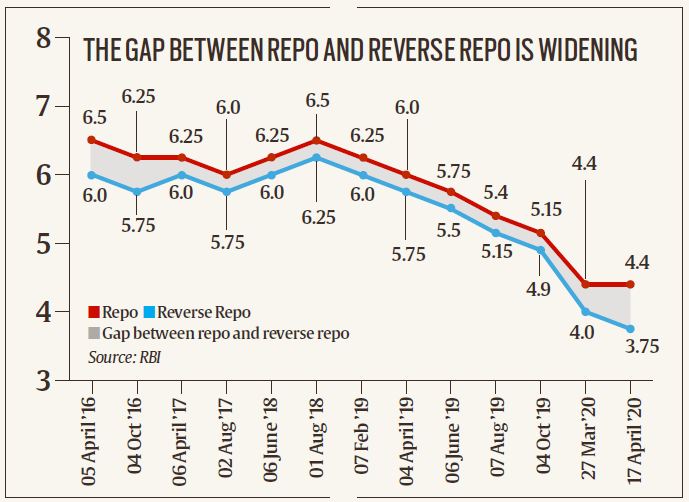
Coronavirus (COVID-19): The Indian economy’s slowdown during 2018 and 2019 is becoming much worse in 2020 with the spread of COVID-19 and the stalling of almost all economic activity. Like most other central banks in the world, the Reserve Bank of India, too, has tried to cut interest rates to boost the economy. However, unlike in the past, when the RBI used its repo rate as the main instrument to tweak the interest rates, today, it is the reverse repo rate that is effectively setting the benchmark.
What are repo and reverse repo rates?
The repo rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to the banking system (or banks) for short durations. The reverse repo rate is the rate at which banks can park their money with the RBI.
With both kinds of repo, which is short for repurchase agreement, transactions happen via bonds — one party sells bonds to the other with the promise to buy them back (or repurchase them) at a later specified date.
In a growing economy, commercial banks need funds to lend to businesses. One source of funds for such lending is the money they receive from common people who maintain savings deposits with the banks. Repo is another option.
Under normal circumstances, that is when the economy is growing, the repo rate is the benchmark interest rate in the economy because it is the lowest rate of interest at which funds can be borrowed and, as such, it forms the floor rate for all other interest rates in the economy — for instance, the interest rate consumers would have to pay on a car loan or the interest rate they will earn from a fixed deposit etc.
What has changed now?
Over the last couple of years, India’s economic growth has decelerated sharply. This has happened for a variety of reasons and has essentially manifested in lower consumer demand. In response, businesses have held back from making fresh investments and, as such, do not ask for as many new loans. Add to this, the pre-existing incidence of high non-performing assets (NPAs) within the banking system. Thus, the banks’ demand for fresh funds from the RBI has also diminished. This whole cycle has acutely intensified with the ongoing lockdown.
As such, the banking system is now flush with liquidity for two broad reasons: on the one hand, the RBI is cutting repo rates and other policy variables like the Cash Reserve Ratio to release additional and cheaper funds into the banking system so that banks could lend and yet, on the other, banks are not lending to businesses, partly because banks are too risk-averse to lend and partly because the overall demand from the businesses has also come down.
So, how has reverse repo become the benchmark rate?
The excess liquidity in the banking system has meant that during March and the first half of April, banks have been using only the reverse repo (to park funds with the RBI) instead of the repo (to borrow funds). As of April 15, RBI had close to Rs 7 lakh crore of banks’ money parked with it. In other words, the reverse repo rate has become the most influential rate in the economy.
What has the RBI done?
Recognising this, the central bank has cut the reverse repo rate more than the repo (see graph) twice in the spate of the last three weeks. The idea is to make it less attractive for banks to do nothing with their funds because their doing so hurts the economy and starves the businesses that genuinely need funds.
Will the move to cut reverse repo work?
It all depends on the revival of consumer demand in India. If the disruptions induced by the outbreak of novel coronavirus disease continue for a long time, consumer demand, which was already quite weak, is likely to stay muted and businesses would feel no need to borrow heavily to make fresh investments. If consumer demand revives quickly, the demand for credit will build up as well.
From the banks’ perspective, it is also important for them to be confident about new loans not turning into NPAs, and adding to their already high levels of bad loans. Until banks feel confident about the prospects of an economic turnaround, cuts in reverse repo rates may have little impact.
What are India's new FDI rules and why is China furious over it?
The Government of India has made its approval for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) by neighbouring countries mandatory.
- This revised FDI policy aims to curb opportunistic takeovers/acquisitions of Indian companies due to the current Covid-19 pandemic.
| Foreign Direct Investment FDI is an investment from a party in one country into a business or corporation in another country with the intention of establishing a lasting interest.Lasting interest differentiates FDI from foreign portfolio investments, where investors passively hold securities from a foreign country.Foreign direct investment can be made by expanding one’s business into a foreign country or by becoming the owner of a company in another country. |
- FDI in India: FDI is allowed under two modes - either through the automatic route, for which companies don't need government approval, or through the government route, for which companies need a go-ahead from the centre.
- According to the new FDI policy:
- An entity of a country, which shares a land border with India or where the beneficial owner of an investment into India is situated in or is a citizen of any such country, can invest only under the Government route.
- A transfer of ownership in an FDI deal that benefits any country that shares a border with India will also need government approval.
- India shares land borders with Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
- Investors from countries not covered by the new policy only have to inform the RBI after a transaction rather than asking for prior permission from the relevant government department.
- Impact
- The earlier FDI policy was limited to allowing only Bangladesh and Pakistan via the government route in all sectors. The revised rule has now brought companies from China under the government route filter.
- China's footprint in the Indian business space has been expanding rapidly, especially since 2014.
- Chinese investment in India
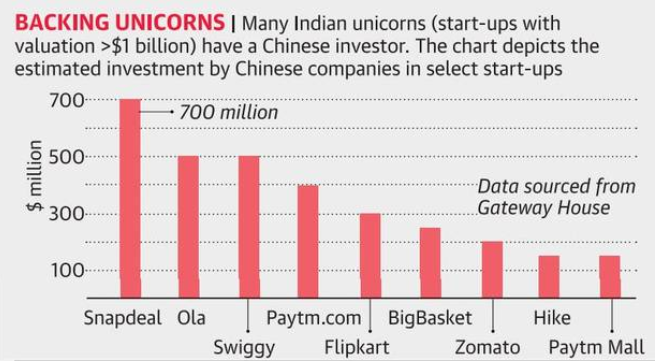
- The net Chinese investment in India, which was $1.6 billion in 2014, shot up five-folds to at least $8 billion (Rs 60,800 crore) in the next three years — with a noticeable shift from state-driven to market-driven investment from the Chinese private sector.
- Official figures underestimate the amount of investment: They neither account for all Chinese companies’ acquisitions of stakes in the technology sector nor investments from China routed through third-party countries, such as Singapore.
- For instance, a $ 504-million investment from the Singapore arm of the mobile firm Xiaomi would not figure in official statistics because of how investments are measured.
- It has been seen that the Chinese firms have escaped the kind of scrutiny in India that their investments have attracted in the West despite several high-profile investments and acquisitions.
- Another concern is that there is no clear separation between the Chinese state and private business. They work closely in pursuing many goals.
Gamma-ray flux variability of luminous and high energy blazars: clues to blazar emission mechanisms
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bangalore have conducted the first systematic study on the gamma-ray flux variability nature of different types of blazars.
- The research work based on characterizing the flux variability nature on month-like time scales in the high energy gamma-ray (100 MeV to 300 GeV) band for different types of blazars has been published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
- IIA is an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India.
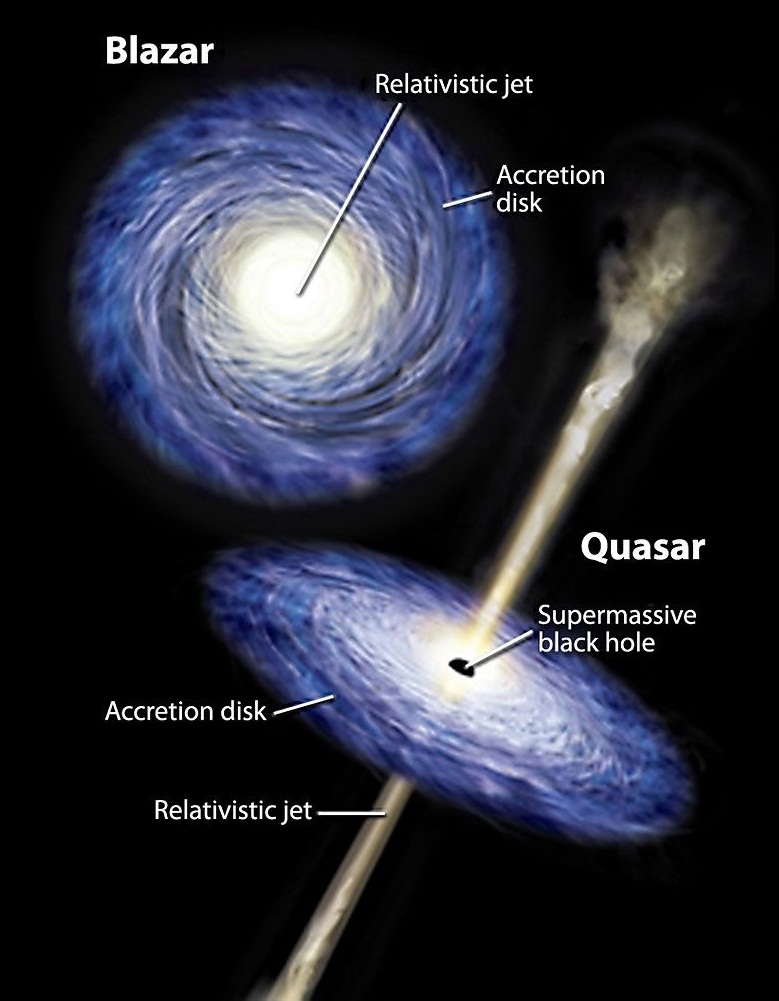
Blazars
- Blazars are active galactic
nuclei (AGN), whose jets are aligned with the observer’s line
of sight. Some blazars are thought to host binary black holes in them
and could be potential targets for future gravitational-wave searches.
- Active Galactic Nuclei:
- At the center of most galaxies, there’s a massive black hole with a huge mass accumulating gas, dust, and stellar debris around it. AGN is formed when the gravitational energy of these materials, being pulled towards the black hole, is converted into light.
- A minority of AGN (~15%) emits collimated charged particles called jets travelling at speeds close to the speed of light.
- Quasar and Radio-Galaxies are
also AGN.
- The difference between Quasar, radio galaxy and a Blazar is the angle of the stream/jet. If the stream is straight up, it is a radio galaxy and the observer is not in the firing line. If the stream is angled slightly towards the observer, then it is a Quasar and if the stream is angled directly towards the observer, it is a Blazar.
- Active Galactic Nuclei:
- Blazars are the most luminous and energetic objects in the known universe and they were found to be emitters of gamma-rays in the 1990s.
- The flux variability characteristics of blazars on a range of time scales was found out with the help of Fermi Gamma-ray space telescope (launched in 2008) which is capable of scanning the entire sky once in three hours.
- Study by Indian Institute of
Astrophysics:
- The research characterised the
amplitude and time scale of flux variations and then looked
for similarity and/or differences in the amplitude and time scale
between different types of blazars.
- With the availability of near-simultaneous data covering the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultra-violet, optical, and infrared bands, the existing notion on high energy emission in blazars is challenged.
- The reduction of large volumes of data for a large number of sources was accomplished by the use of the High-Performance Computing facility of the IIA.
- The research characterised the
amplitude and time scale of flux variations and then looked
for similarity and/or differences in the amplitude and time scale
between different types of blazars.
| Major Atmospheric Cerenkov Experiment Telescope It is the India's largest and the world's highest gamma-ray telescope being established at Hanle, Ladakh.It is being built by the Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL), Hyderabad for the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).It is remotely operated and runs on Solar Power.It will help to explore the exciting energy range of the gamma-ray energy region in between satellites and the traditional Atmospheric Cerenkov experiments.The telescope is named after the Russian scientist Cerenkov who predicted that charged particles moving at high speeds in a medium, emit light. |
Significance of the Study
- The study can provide clues to the processes happening close to the black hole which are not visible through direct imaging. It will also enhance the knowledge of blazars.
- Exploring the Gamma-ray band of the electromagnetic spectrum will provide key inputs to constrain the high energy production site as well as the high energy emission processes.
- The results of this work will fill the gap on the knowledge of the high energy flux variability nature of blazars.
- Gamma-ray band is one of the bands of the electromagnetic spectrum on which there is limited knowledge on the flux variability of blazars.
- Localizing the site for the production of gamma-rays is one of the major problems in high energy astrophysics.
- The expertise of handling high energy data from celestial sources gained in this work will build capacity to interpret the gamma-ray data that will emerge from India's upcoming facility, the Major Atmospheric Cerenkov Experiment (MACE) Telescope as well as from any X-ray missions by India in the future.
IIA scientists connect Lithium abundance in interstellar space to new Lithium rich red giants
Recently, the researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have discovered hundreds of Lithium (Li) rich giant stars which indicate that lithium is being produced in the stars and accounts for its abundance in the interstellar (between stars) medium.
- The study was published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters and Monthly Notices of Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
Key Points
- The scientists have discovered a number of super Li-rich giants with the Li quantity equal to or in some cases, more than 10 times the present value, A(Li) = 3.2 dex (measured in logarithmic scale relative to hydrogen).
- Scientists followed a two-fold
strategy of systematically searching for high Li among low
mass evolved stars in the Galaxy and determining the exact
evolutionary phase of these high Li abundance stars.
- Hundreds of Li-rich giants were discovered by employing data from large scale ground and space missions.
- However, Li-rich giants still account for only about 1 in 100 in the Galaxy.
- The evolutionary phase of
these giants was determined by analyzing relative positions of
thousands of stars using their temperature and luminosity and
also subjecting their independent data set to atmospheric oscillations
analysis using data from Kepler Space Telescope.
- For
the first time, it was shown that the Li enhancement in giants is
associated only with central He-burning stars (also known as the Red
Clump Giants)
- This discovery will help to eliminate or validate many proposed theories such as planet engulfment or Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN) during the red giant evolution in which helium at the center is not burning.
- For
the first time, it was shown that the Li enhancement in giants is
associated only with central He-burning stars (also known as the Red
Clump Giants)
- Lithium (Li), is one of the three
primordial elements, apart from Hydrogen (H) and Helium
(He), produced in the BBN.
- This model predicts primordial Li abundance [A(Li) ~2.7~dex].
- Stars are also proposed as a likely
Li source in the Galaxy and are considered as Li sinks.
- The original Li, with which stars are born, only gets depleted over stars’ life-time as Li burns at relatively very low temperatures of about 2.5x106 Kelvin (a range which is easily encountered in stars).
| Planetary Engulfment In the universe, planets accompany host stars (like the Sun is the host star for the planets of the Solar system).As the host star evolves off the main sequence to become a white dwarf, the planets with sufficiently close orbits can be engulfed during the giant phase.Planetary engulfment events involve the chemical assimilation of a planet into a star's external layer.This can cause a change in the chemical pattern of the stellar atmosphere in a way that mirrors the composition of the rocky object engulfed. Big Bang Nucleosynthesis It is the leading explanation about how the universe began. At its simplest, it says that the universe started with a small singularity and then inflated over the next 13.8 billion years to the cosmos currently observed.The Universe's light-element abundance is another important criterion by which this theory is verified.It is now known that the elements observed in the Universe were created in either of two ways.Light elements (namely deuterium, helium, and lithium) were produced in the first few minutes of the Big Bang, while elements heavier than helium are thought to have their origins in the interiors of stars which formed much later in the history of the Universe.The theory predicts that roughly 25% the mass of the Universe consists of Helium. It also predicts about 0.01% deuterium, and even smaller quantities of lithium. |









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies