- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Dec 5th, 2021 - Daily Quiz
1. Which of the following Statements regarding Rani Kamlapati is/are true?.

- She was the widow of Nizam Shah, whose Gond dynasty ruled the then Ginnorgarh, Bhopal.
- She did great work in the area of water management and set up parks and temples.
- Omicron, identified in southern Africa in November 2021.
- Delta, which emerged in India in late 2020 and spread around the world.
- Mu (B.1.621), which emerged in Colombia in early 2021.
- Lambda (C.37), which emerged in Peru in late 2020.
- Chairman is required to be a serving or retired Chief Justice of a High Court or a judge of the Supreme Court of India.
- It has a sanctioned strength of 30 members which includes 20 expert members and 10 judicial members.
- It is not bound by the procedure laid down under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908
- It was constructed during the reign of the Kakatiya Empire.
- It was named after the king who patronized the work in the temple.
- The lower part of the temple is red sandstone while the white gopuram is built with light bricks that reportedly float on water.
- (c)
- Rani Kamlapati was the widow of Nizam Shah, whose Gond dynasty ruled the then Ginnorgarh, 55 km from Bhopal, in the 18th century.
- Kampalati is known to have shown great bravery in facing aggressors during her reign after her husband was killed.
- Kamlapati was the “last Hindu queen of Bhopal”, who did great work in the area of water management and set up parks and temples.
- Implementation of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, which allows self-governance through traditional gram sabhas for people living in scheduled areas.
- Bhopal’s Habibganj station renamed after Gond queen- Rani Kamlapati.
- Legalising mohua, a staple drink of the tribals, which will be sold as ‘heritage liquor’.
- The chief minister has also announced that petty cases registered against tribals will also be withdrawn, most of which are for production and sale of mahua-based liquor.
- Home delivery of foodgrains distributed under public distribution across all 89 tribal blocks has also been announced.
- University in Chhindwara to be named after Shankar Shah. Shankar Shah, son of Sumer Shah, was the last ruler of Garha Kingdom under Gond rule.
- Railway station, bus stop to be renamed after Tantya Bhil, a memorial in his name in Khandwa.
- A medical college in Mandla will be named after Raja Hirde Shah Lodhi, who had come from Kashi and settled in MP’s Bundelkhand region. His ancestors had established their kingdom in the present-day Damoh which was then under Gond rulers.
- Raja Sangram Shah award for best work in tribal art and culture. He was the 48th Gond ruler of Garha kingdom.
- (a)
- The WHO currently lists 5 variants of concern:
- 1 is correct: Omicron (B.1.1.529), identified in southern Africa in November 2021.
- 2 is correct: Delta (B.1.617.2), which emerged in India in late 2020 and spread around the world.
- Gamma (P.1), which emerged in Brazil in late 2020.
- 3 is correct: Beta (B.1.351), which emerged in South Africa in early 2020.
- 5 is correct: Alpha (B.1.1.7), which merged in Britain in late 2020.
- 4 is incorrect: Lambda is Variants of Interest
- VARIANTS OF INTEREST– There are currently two:
- Mu (B.1.621), which emerged in Colombia in early 2021.
- Lambda (C.37), which emerged in Peru in late 2020.
- How different it is from the original virus?
- The B1.1.529 has more than 2 times the number of bad spike mutations than the Delta variant. The new variant has an extremely high 32 worrisome mutations in the spike protein, which is a real concern than the Delta variant.
- Variant of Interest (VOI) and Variant of Concern (VOC): A SARS-CoV-2 VOI is a SARS-CoV-2 variant:
- with genetic changes that are predicted or known to affect virus characteristics such as transmissibility, disease severity, immune escape, diagnostic or therapeutic escape; AND
- that has been identified as causing significant community transmission or multiple COVID-19 clusters, in multiple countries with increasing relative prevalence alongside increasing number of cases over time, or other apparent epidemiological impacts to suggest an emerging risk to global public health.
- A SARS-CoV-2 VOC is a SARS-CoV-2 variant that meets the definition of a VOI and, through a comparative assessment, has been demonstrated to be associated with one or more of the following changes at a degree of global public health significance:
- increase in transmissibility or detrimental change in COVID-19 epidemiology; OR
- increase in virulence or change in clinical disease presentation; OR
- decrease in effectiveness of public health and social measures or available diagnostics, vaccines, therapeutics.
- How do variants of a virus emerge and why?
- Variants of a virus have one or more mutations that differentiate it from the other variants that are in circulation.
- Essentially, the goal of the virus is to reach a stage where it can cohabitate with humans because it needs a host to survive.
- Errors in the viral RNA are called mutations, and viruses with these mutations are called variants. Variants could differ by a single or many mutations.
- (c)
- The Tribunal is not bound by the procedure laid down under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, but shall be guided by principles of natural justice.
- NGT is mandated to make disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing of the same.
- With the establishment of the NGT, India became the third country in the world to set up a specialised environmental tribunal, only after Australia and New Zealand, and the first developing country to do so.
- Established on 18th October, 2010 under the National Green Tribunal Act 2010.
- Established for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources.
- New Delhi is the Principal Place of Sitting of the Tribunal and Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata and Chennai shall be the other four places of sitting of the Tribunal.
- Composition:
- Sanctioned strength: The act allows for up to 40 members (20 expert members and 20 judicial members).
- Chairman: Is the administrative head of the tribunal, also serves as a judicial member and is required to be a serving or retired Chief Justice of a High Court or a judge of the Supreme Court of India.
- Selection:
- Members are chosen by a selection committee (headed by a sitting judge of the Supreme Court of India) that reviews their applications and conducts interviews.
- The Judicial members are chosen from applicants who are serving or retired judges of High Courts.
- Expert members are chosen from applicants who are either serving or retired bureaucrats not below the rank of an Additional Secretary to the Government of India (not below the rank of Principal Secretary if serving under a state government) with a minimum administrative experience of five years in dealing with environmental matters. Or, the expert members must have a doctorate in a related field.
- (a)
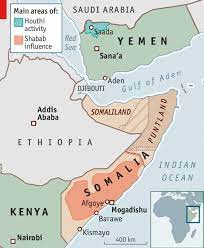
- Gulf of Aden, also known as the Gulf of Berbera, is a deepwater gulf between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, Socotra (Yemen), and Somalia to the south.
- In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east. To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti.

- (c)
- The Rudreswara temple was constructed in 1213 AD during the reign of the Kakatiya Empire by Recherla Rudra, a general of Kakatiya king Ganapati Deva.
- The presiding deity here is Ramalingeswara Swamy.
- It is also known as the Ramappa temple, after the sculptor who executed the work in the temple for 40 years.
- The temple stands on a 6 feet high star-shaped platform with walls, pillars and ceilings adorned with intricate carvings that attest to the unique skill of the Kakatiya sculptors.
- The foundation is built with the “sandbox technique”, the flooring is granite and the pillars are basalt.
- The lower part of the temple is red sandstone while the white gopuram is built with light bricks that reportedly float on water.
- An inscription dates the temple to 1135 Samvat-Saka on the eight-day of Magha (12th January, 1214).
- The distinct style of Kakatiyas for the gateways to temple complexes, unique only to this region, confirm the highly evolved proportions of aesthetics in temple and town gateways in South India.
- European merchants and travellers were mesmerized by the beauty of the temple and one such traveller had remarked that the temple was the "brightest star in the galaxy of medieval temples of the Deccan".
- Rudreswara Temple, (also known as the Ramappa Temple) at Mulugu district, Telangana has been inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage list.










 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies