- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
DECEMBER 15, 2025
Fourth National Lok Adalat of 2025 successfully resolved 2.59 crore disputes
- From 2022-23 to 2024-25, more than 23.5 crore cases have been resolved in various Lok Adalats across India.
Lok Adalat Framework
- Established: under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 to provide speedy and cost-effective justice as an Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanism.
- Objective: Reduce pendency (e.g. more than 4.7 crore pendency as per NJDG), promote consensual settlements, and strengthen access to justice.
- Authority: Organised by the NALSA with the CJI as Patron-in-Chief.
- Enforcement: Awards are final, binding, equivalent to a civil court decree, with no appeal provision.
- Scope: Covers pre-litigation and pending cases, excluding non-compoundable offences and divorce matters.
Types of Lok Adalats
- National Lok Adalat (NLA): Involve simultaneous, nationwide sittings on a single day at all levels of the judiciary, from the Supreme Court down to the Taluk Levels, aiming to clear a large volume of cases.
- Permanent Lok Adalat (PLA): Organized for cases related to Public Utility Services (e.g., transport, postal, telegraph, electricity, water supply) up to ₹ 1 Crore.
E-Lok Adalats and Mobile Lok Adalats:
- E-Lok Adalats allow for remote participation and bring justice through digital platforms.
- Mobile Lok Adalats are organized to travel from one location to another to resolve disputes.
NCAER Report on Employment
The National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) released a report titled “India’s Employment Prospects: Pathways to Jobs.”
- It highlights skilling and small enterprises as key drivers of job creation to sustain the 8% GDP growth.
- The report underlines the role of skilling and small enterprises as key drivers of job creation in the country.
- The NCAER is India’s oldest and largest independent, non-profit think tank. Established in New Delhi in 1956, it conducts evidence-based economic research to guide public policy.
Key Findings of the Report
- Employment Pattern: India’s recent employment growth is driven mainly by necessity-based self-employment in low-technology, subsistence household enterprises.
- Income Level: Despite economic growth, India’s per capita GDP is relatively low, ranking 128th globally.
- Skill Deficit: Transition to skilled labour has been slow; only 4.1% workers had vocational training in 2024, much less than in countries like Germany, Singapore, and Canada.
- Job Potential: A 9% rise in skilled workers could generate about 9.3 million jobs by 2030.
- Multiplier Effects: Moderate growth of labour-intensive sub-sectors could increase employment in manufacturing by 53% and in services by 79%.
Policy Recommendations for Job Creation
- PLI Reorientation: Redirect Production-Linked Incentives toward labour-intensive sectors like textiles, garments, footwear, and food processing.
- Service Sectors: Increase support for tourism, education, and healthcare to generate large-scale, employment-intensive job opportunities.
- Digital Adoption: Improve access to digital technologies and credit, as enterprises using digital technologies hire 78% more workers than non-digital firms.
Empanel Heritage Conservation Architects
- The Ministry of Culture has initiated a process to empanel heritage conservation architects for the upkeep, conservation, and restoration of ASI-protected monuments.
About Empanel Heritage Conservation Architects:
- A heritage (conservation) architect is a specialised professional trained in the restoration, conservation, and management of historic structures, ensuring preservation of architectural integrity, materials, and cultural value in line with established conservation norms.
The Initiative
- The Ministry of Culture has begun empanelling qualified conservation architects to form a national pool approved by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- This allows donors, corporates, and private entities to directly engage ASI-approved professionals for conservation works funded through the National Cultural Fund (NCF).
- Key Features of the Initiative
- Donor flexibility: Donors can choose architects from the ASI-approved panel for monuments of their choice.
- ASI oversight mandatory: ASI will continue to monitor all projects to ensure compliance with scientific conservation standards.
- Defined responsibilities: Empanelled architects will prepare Detailed Project Reports (DPRs), design conservation methods, provide project management support, and supervise execution.
- Execution mechanism: Actual restoration work will be carried out by agencies selected by donors, subject to ASI approval.
- Eligibility criteria: Architects must have prior experience in conserving or restoring heritage structures over 100 years old.
- Tenure: Empanelment valid for three years, with annual performance review.
New Insurance Bill, 2025
- The Sabka Bima Sabki Raksha (Amendment of Insurance Laws) Bill, 2025, aims to modernise India’s insurance framework in line with Insurance for All by 2047.
- It has amended the Insurance Act 1938, the LIC Act 1956, and the IRDAI Act 1999 to expand the insurance coverage.
Status of Insurance Sector in India
- Insurance Market (Global): India’s overall insurance market is ranked the 10th largest in the world in terms of total premium volume.
- Life Insurance Sector: India also ranks 10th globally in the life insurance business.
- LIC Global Ranking: The Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) is ranked among the 3rd strongest insurance brands globally according to Brand Finance’s 2025 report.
- Market Size: The Indian insurance market was valued at approximately USD 303.3 billion (₹25 lakh crore) in 2024 and is expected to grow substantially in the coming decade.
- Penetration: Insurance penetration in India stood at around 3.7% of GDP (latest for FY24), with life insurance accounting for ~2.8% and non-life for ~0.9%.
Need for the New Insurance Bill
- Low Insurance Penetration: Insurance penetration in India is only ~4% of GDP, compared to the global average of ~7%, leaving large populations uninsured.
- Capital & Investment Deficit: Long-term insurance requires deep capital, but restricted inflows limited expansion. E.g. Raising FDI to 100% can attract global insurers into a market with a 1.4 billion population.
- Reinsurance Concentration Risk: India’s reinsurance market is dominated by GIC Re (General Insurance Corporation of India Reinsurance), limiting risk diversification.
- Weak Consumer Protection: Earlier regulatory tools had limited deterrence against unfair practices.
Key Provisions of the Bill
- FDI Liberalisation: Raises insurance FDI cap from 74% to 100%, enabling global capital inflows.
- Reinsurance Entry: Cuts Net Owned Funds for foreign reinsurers from ₹5,000 crore to ₹1,000 crore.
- Equity Flexibility: Raises IRDAI approval threshold for share transfer from 1% to 5%.
- Autonomy: Allows LIC to open zonal offices and restructure overseas operations without prior approvals.
- IRDAI Empowerment: Grants powers for disgorgement, penalties and one-time registration.
- Disgorgement: A regulatory enforcement tool that requires entities to return unlawfully gained profits, preventing unjust enrichment and deterring violations.
Key Issues Within the Bill
- Composite Licensing: No provision allowing insurers to operate across life and non-life segments.
- Entry Barriers: ₹100 crore minimum paid-up capital for insurance companies (life and general insurers) and ₹200 crore for reinsurance companies, remaining unchanged under the Bill
- Limited Inclusion: Missed opportunity for niche, regional, health-only, or micro-insurers.
- Product Silos: No permission for bundled insurance or cross-financial product distribution.
- Risk Innovation: Absence of a framework for captive insurance for large corporations.
- Captive Insurance: A risk-management arrangement where a company creates its own subsidiary insurer to cover internal risks and reduce dependence on external insurance markets.
Way Forward
- Composite Licensing: Allow single insurers to operate across life, health and general insurance; E.g. global markets like the UK and Australia permit composite insurers.
- Capital Rationalisation: Reduce minimum paid-up capital to enable niche and regional players; E.g. micro-insurance models in ASEAN markets expanded coverage among low-income households.
- Inclusive Insurance: Promote health-only, micro and rural insurers to reach underserved groups; E.g. PMFBY and Ayushman Bharat show targeted schemes improve last-mile coverage.
- Regulatory Safeguards: Strengthen IRDAI’s supervision alongside liberalisation to protect policyholders; E.g. SEBI-style disgorgement powers ensure market discipline.
National Blood Transfusion Bill, 2025
- Thalassaemia patient groups welcomed the National Blood Transfusion Bill, 2025, introduced in Parliament.
- The Bill proposes a National Blood Transfusion Authority to enforce uniform statutory blood management standards, to consolidate the fragmented regulation framework.
- Blood regulation in India currently operates under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940; the National Blood Transfusion Council, created by a Supreme Court directive, issues non-statutory guidelines.
About Thalassaemia
- Thalassemia is an inherited genetic blood disorder in which defective haemoglobin production leads to chronic anaemia.
- Types: There are two main types based on the haemoglobin protein affected.
- Alpha thalassaemia: Insufficient production of the Alpha globin chain of haemoglobin; disease severity increases as more genes are affected.
- Beta thalassaemia: Insufficient production of the Beta globin chain; one affected gene causes beta-thalassaemia minor (mild), while two affected genes cause beta-thalassaemia major (severe).
- Globin chains are the protein building blocks of haemoglobin that enable red blood cells (RBCs) to carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Treatment: Severe cases need regular blood transfusions coupled with Iron Chelation Therapy; a Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) or Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) is the only cure.
- India’s Burden: India accounts for about 25% of the global beta-thalassaemia burden; it affects around 3–4% of the population.
Govt Initiatives for Thalassemia Control
- Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojana: A Coal India Limited CSR initiative providing up to ₹10 lakh for bone marrow transplants of underprivileged children with thalassaemia major or aplastic anaemia.
- NHM Support: The National Health Mission supports states with blood banks, transfusion day-care centres, free blood products, iron chelation drugs, diagnostics, and trained healthcare personnel.
- National Guidelines 2016: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare issued guidelines for the prevention and control of haemoglobinopathies, including thalassaemia.
- e-RaktKosh Platform: A national digital platform linking licensed blood banks to provide real-time blood availability for patients needing regular transfusions.
- Legal Recognition: Thalassaemia is recognised as a disability under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD Act), 2016, enabling access to welfare benefits.
Emperor Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II
- Prime Minister of India has welcomed the release of a commemorative postage-stamp honouring Emperor Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II (Suvaran Maran), recognising his administrative excellence and patronage of Tamil culture.
About Emperor Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II:
- Perumbidugu Mutharaiyar II, also known as Suvaran Maran or Shatrubhayankar, was a prominent ruler of the Mutharaiyar lineage who ruled during c. 705–745 CE.
- Belonged to the Mutharaiyar dynasty, a powerful Tamil ruling lineage.
- Functioned as feudatories of the Pallavas, particularly under Pallava king Nandivarman II.
- Controlled the central Cauvery region, including Thanjavur, Tiruchirappalli, Pudukkottai, Perambalur, and surrounding areas.
- Ruled primarily from Tiruchirappalli, exercising authority for nearly four decades.
Key Contributions
Administrative & Military Achievements:
- Known as a formidable administrator with strategic foresight and governance stability.
- Fought several battles alongside Pallava forces, helping maintain regional order during Pallava decline.
Temple Building & Architecture:
- The Mutharaiyars were among the early temple builders of Tamil Nadu, contributing to rock-cut and structural temples.
- Their architectural innovations influenced the early Chola temple tradition, even before the rise of Vijayalaya Chola.
Cultural & Religious Patronage:
- Patronised Shaivism, while also hosting philosophical debates involving Jain scholars such as Acharya Vimalachandra, reflecting religious pluralism.
- Supported Tamil language, literature, and religious institutions, as evidenced by inscriptions.
Public Works:
- Inscriptions attest to his contributions to temple endowments, irrigation systems, and agrarian infrastructure, strengthening the Cauvery delta economy.
Significance
- Historical significance: Represents the rise of powerful regional chieftains during the weakening of imperial Pallava authority.
- Cultural legacy: Acts as a bridge between Pallava and Chola traditions, especially in temple architecture and governance.
- Social relevance: Revered as an icon by the Mutharaiyar community, classified among Most Backward Classes (MBCs) in Tamil Nadu.
|
About Pallava Dynasty
|
Dandami Maria Tribe
- The Bison Horn Maria dance of the Dandami Madia (Maria) tribe of Bastar, Chhattisgarh, has drawn attention for its enduring cultural vitality despite modern influences.
Dandami Maria Tribe:
- The Dandami Maria, also known as Bison Horn Maria or Khalpati Maria, are a tribal community belonging to the broader Gond (Koytorias) ethnic group.
- They are recognised for their distinctive ceremonial dance and headgear resembling bison horns, which has become a cultural marker of their identity.
Origin:
- The Dandami Maria trace their lineage to the ancient Gondwana region, once spread across central India.
- They identify as part of the Gond tribal tradition, one of the oldest indigenous groups of the Deccan plateau.
- Linguistically, they speak Dandami Maria, with many also using Gondi dialects, an oral language of Dravidian origin.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Predominantly inhabit the Bastar region of southern Chhattisgarh, especially in Darbha, Tokapal, Lohandiguda, Dantewada, and surrounding forested tracts.
- Their settlements are closely integrated with dense forests, shaping their subsistence patterns, rituals, and worldview.
- They practice agriculture, supplemented by hunting and fishing.
Key Cultural Characteristics
Bison Horn Maria Dance:
- Performed by both men and women during festivals, rituals, and communal gatherings.
- Men wear horn-shaped bamboo headgear decorated with bison or cattle horns, feathers, cowries, and cloth strips, along with bead necklaces and ankle bells.
- Women wear handwoven saris, heavy silver and brass jewellery, coin ornaments, and ceremonial crowns.
Social and Cultural Life:
- The ghotul (youth dormitory) plays a vital role in socialisation, cultural transmission, and community cohesion.
- Distinct hairstyles, traditional ornaments, and ceremonial objects such as tobacco boxes and combs are culturally significant.
- They permit divorce and widow remarriage, reflecting flexible social norms.
Significance
- Represents a living tribal heritage that preserves Gond identity and pre-Aryan cultural traditions.
- Embodies a nature-centric worldview, celebrating hunting traditions, seasonal cycles, and forest deities like Budhadev and Danteshwari Mai.
Bondi Beach attack
- Australia was shaken by a deadly terror-linked mass shooting at Sydney’s Bondi Beach during a Jewish festival, prompting the government to consider tougher gun laws.
About Bondi Beach:
- Bondi Beach is a world-famous ocean beach and adjoining suburb in Sydney, known for its surf culture, tourism, and public recreation. It is among the most visited beaches in Australia and a major symbol of the country’s coastal lifestyle.
Location:
- Situated 7 km east of Sydney’s Central Business District (CBD).
- Lies in the Eastern Suburbs of Sydney within the Waverley Council local government area.
- Neighbouring suburbs include North Bondi, Bondi Junction, Rose Bay, and Bellevue Hill.
Key features
- Natural setting: Crescent-shaped sandy beach facing the Tasman Sea, popular for surfing and swimming.
- Cultural prominence: Featured in global TV series such as Bondi Rescue and Bondi Vet.
- Demographics: Historically multicultural, with a strong Jewish community and migrant heritage.
- Indigenous heritage: Traditionally inhabited by Bidjigal, Birrabirragal, and Gadigal Aboriginal peoples.
- Name origin: Derived from the Dharawal word “Bondi”, meaning a loud thud, like waves crashing on rocks.
Significance
- Tourism & economy: A key contributor to Sydney’s tourism-driven economy and international image.
- Cultural history: Site of major social movements, including early 20th-century debates on public decency and beach culture.
- Public safety relevance: The recent attack highlights challenges of urban security, counter-terrorism, and public space safety.
National Energy Conservation Awards
- The President of India felicitated the winners of the National Energy Conservation Awards (NECA) 2025 on National Energy Conservation Day at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
About National Energy Conservation Awards:
- The National Energy Conservation Awards (NECA) are annual national-level awards that recognise industries, institutions, establishments, and innovators for outstanding achievements in energy efficiency and reduction of energy consumption while maintaining or improving productivity.
Launched in:
- Instituted in 1991 (under the Energy Conservation framework)
- Presented annually on 14 December, observed as National Energy Conservation Day
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Power
- Implementing Agency: Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- BEE was established under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001
Aim:
- Promote energy conservation and efficiency across sectors of the economy.
- Encourage adoption of energy-efficient technologies and practices.
Key Features of NECA 2025
- Wide sectoral coverage: Industry, Buildings, Transport, Institutions, Appliances, Innovation, and Professionals
- High participation: 558 applications received across categories
- New category introduced: Social Media Influencers & Digital Content Creators to promote behavioural change through digital outreach
Transparent selection process:
- Technical Committee (headed by Member–Thermal, CEA)
- Award Committee chaired by Secretary (Power)
Significance of NECA
- Energy security: Promotes “energy saved = energy produced” approach without resource depletion.
- Climate action: Supports India’s decoupling of GDP growth from GHG emissions.
- Policy alignment: Complements schemes like PAT, Standards & Labelling, RCO, and ADEETIE.
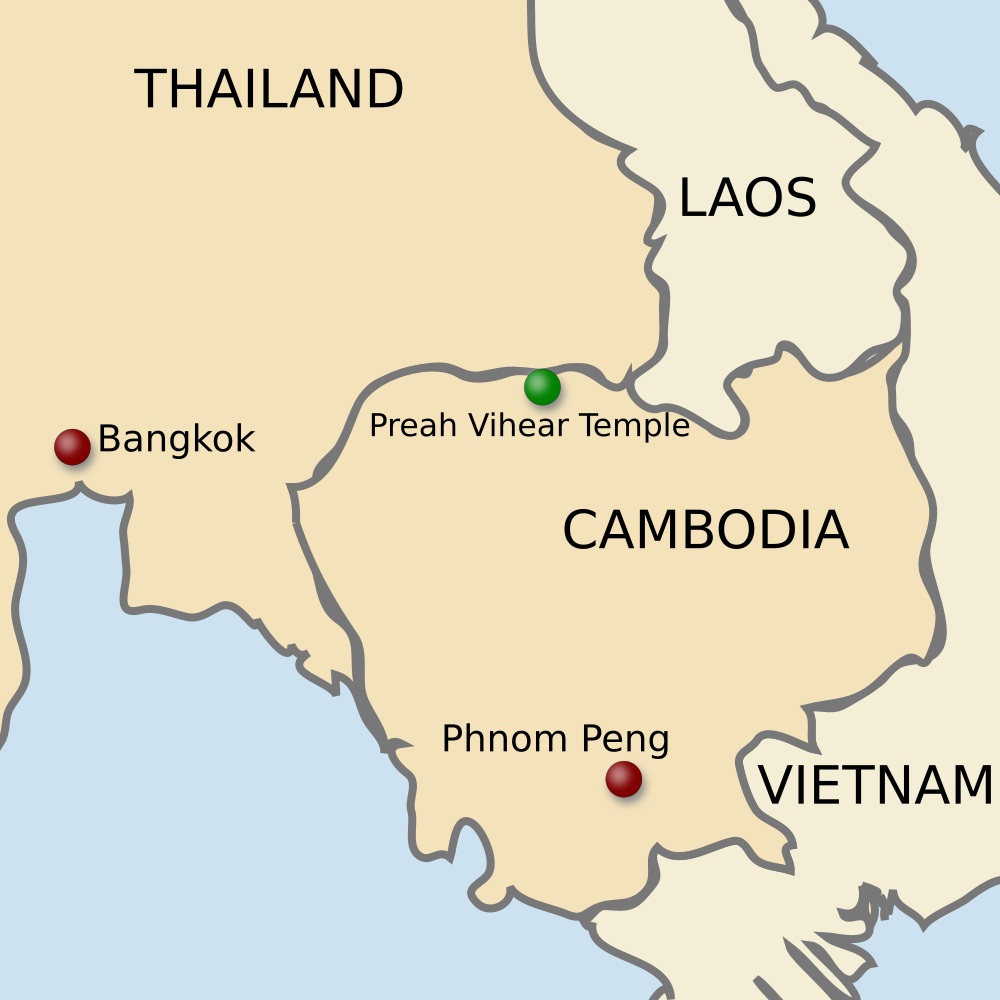
Preah Vihear Temple
- India expressed concern over reported damage to conservation facilities at the Preah Vihear temple amid ongoing Thailand-Cambodia border clashes.
About Preah Vihear Temple
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, located in Preah Vihear province, northern Cambodia, situated atop a cliff in the Dangrek Mountains along the Cambodia-Thailand border.
- It was constructed during the Khmer Empire in the 11th-12th centuries CE, initially built under Suryavarman I (1002-1050 CE) and later expanded by Suryavarman II (1113-1150 CE).
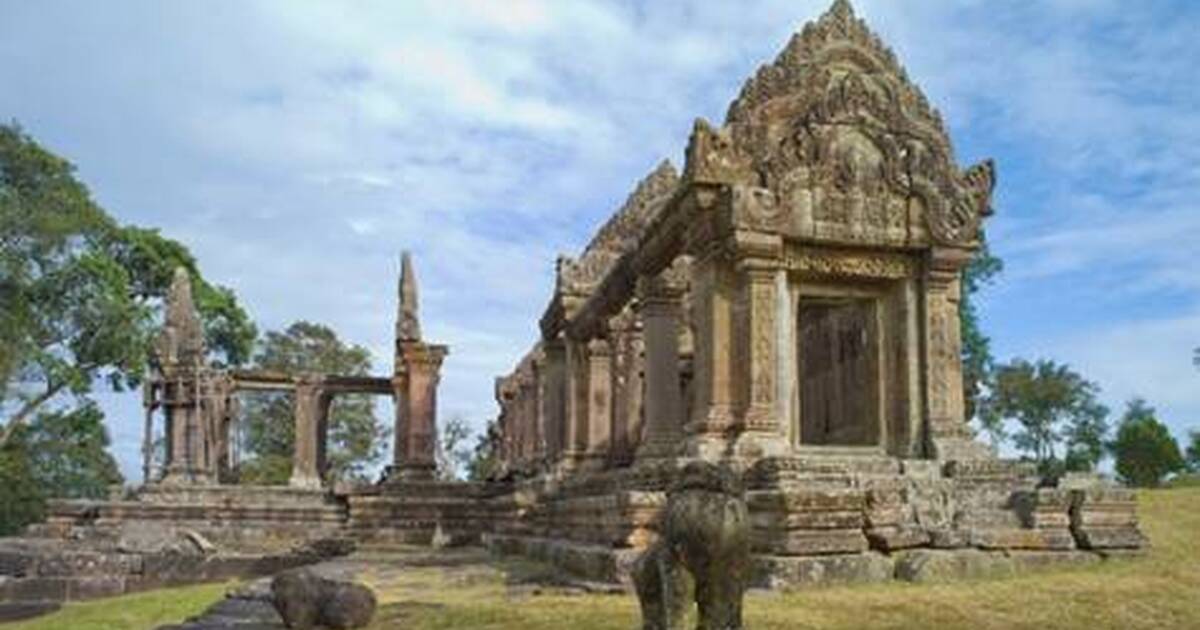

- It embodies the Khmer temple architecture, aligned along an ~800-metre axial processional path with a sequence of five gopuras connected by stairways and pavements.
- It was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2008) for its architectural significance and outstanding testimony to the Khmer civilisation.
Sahyog Portal
- Disclosures show a rising number of unlawful content removal orders issued through the Sahyog Portal.
Recent Trends in Sahyog Portal
- 2,312 blocking orders were issued between October 2024 and October 2025, averaging about 6 daily.
- Each blocking order typically contained multiple links or user accounts.
- Meta platforms accounted for over 78% of all blocking orders, with WhatsApp receiving the highest.
- More than 118 online intermediaries have been onboarded to the Sahyog Portal.
About Sahyog Portal
- Sahyog is a centralised portal designed to streamline the removal of unlawful content from the internet.
- Objective: It creates a single window for government agencies to report unlawful online content.
- Nodal Ministry: The portal functions under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) manages the Sahyog portal.
- Mechanism: Authorised officials flag unlawful URLs on the portal instead of emailing grievance officers.
- The system automatically forwards takedown requests to intermediaries as formal notices.
- Legal Basis: The portal operates under Section 79(3)(b) of the Information Technology Act, 2000, and Rule 3(1)(b) of the 2021 IT Rules.
- Section 79(3)(b): Creates a legal obligation for intermediaries to remove unlawful content.
- Rule 3(1)(b): Defines categories of content that users are prohibited from hosting.
- Intermediaries lose safe harbour immunity if unlawful content is not removed after ‘actual knowledge’.
MahaCrimeOS AI
- Maharashtra launched MahaCrimeOS AI to strengthen its response to rising cybercrime using artificial intelligence.
About MahaCrimeOS AI
- Platform: It is an advanced AI co-pilot system, in collaboration with Microsoft, utilizing Azure OpenAI Service.
- Objective: To streamline the workflow by analyzing vast, unstructured and multilingual data (e.g., FIRs, bank statements) and reducing investigation turnaround time by up to 80%.
- Function: It automates data extraction, guides investigators through protocols, and identifies complex crime linkages.
Operation Thunder 2025
- 30,000 live animals were seized under Operation Thunder 2025.
About Operation Thunder
- It was coordinated by INTERPOL and the World Customs Organization (WCO), with the support of the International Consortium on Combating Wildlife and Forestry Crime (ICCWC).
- It sought to intercept and seize illegally traded wildlife and forestry commodities across the global supply chain and identify, disrupt and dismantle criminal networks involved in these types of environmental crime.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies