- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Discuss various theoretical perspectives on the family. (UPSC CSE Mains 2022 - Sociology, Paper 1)
The family is a social institution, that is, an established social system that emerges, changes, and persists over time. We can define the family to refer to a primary group of people—usually related by ancestry, marriage, or adoption—who form a cooperative economic unit to care for offspring and each other and who are committed to maintaining the group over time. Families are part of what are more broadly considered to be kinship systems.
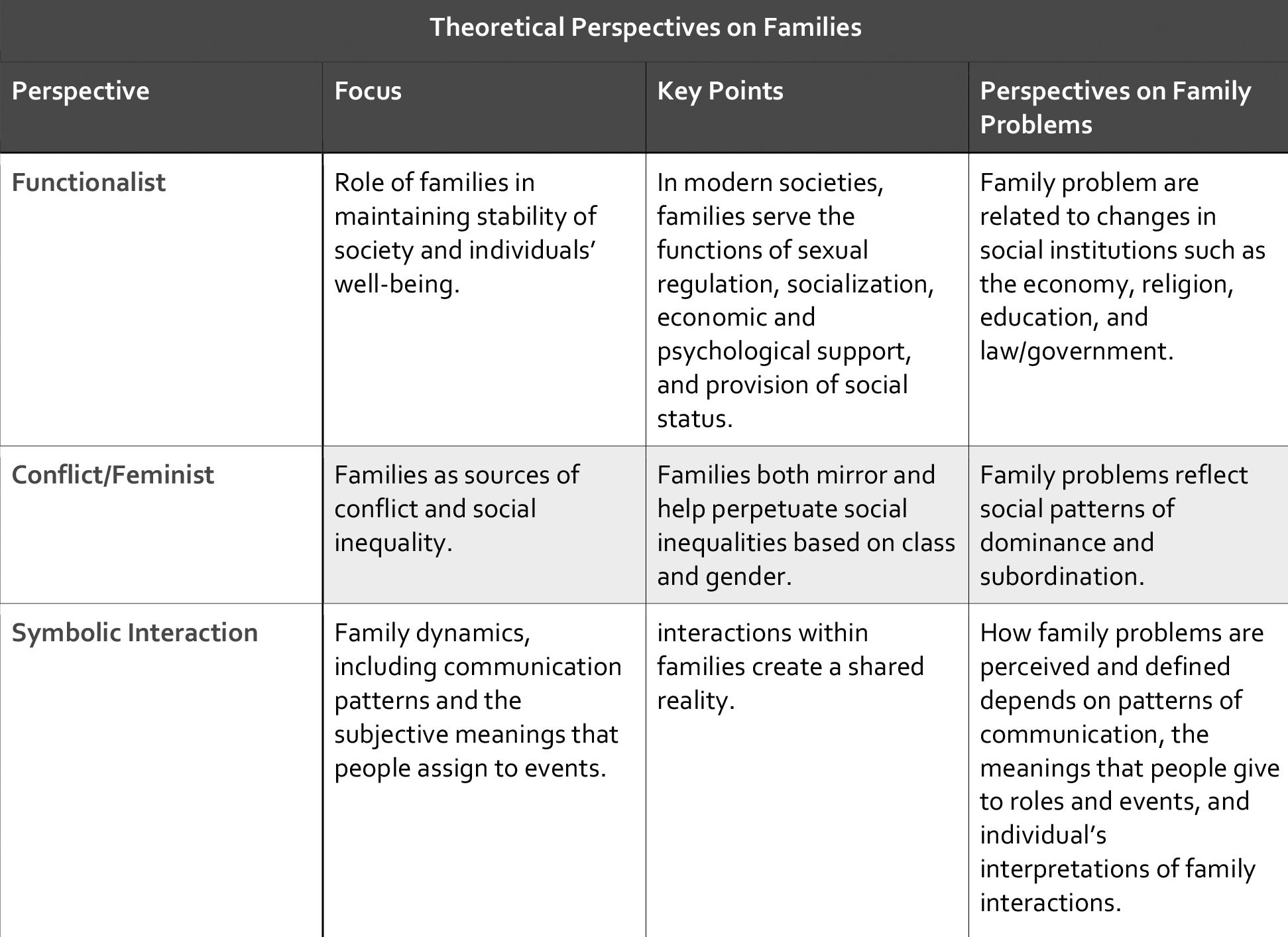 Functionalist perspective - Functionalists emphasize the importance of the family in maintaining the stability of society and the well-being of individuals. According to Emile Durkheim, marriage is a microcosmic replica of the larger society; both marriage and society involve a mental and moral fusion of physically distinct individuals(Lehmann, 1994). Durkheim also believed that a division of labor contributes to greater efficiency in all areas of life— including marriages and families—even though he acknowledged that this division imposes significant limitations on some people.
Functionalist perspective - Functionalists emphasize the importance of the family in maintaining the stability of society and the well-being of individuals. According to Emile Durkheim, marriage is a microcosmic replica of the larger society; both marriage and society involve a mental and moral fusion of physically distinct individuals(Lehmann, 1994). Durkheim also believed that a division of labor contributes to greater efficiency in all areas of life— including marriages and families—even though he acknowledged that this division imposes significant limitations on some people.
Conflict and Feminist Perspective - Conflict and feminist analysts view functionalist perspective on the role of the family in society as idealized and inadequate. Rather than operating harmoniously and for the benefit of all members, families are sources of social inequality and conflict over values, goals, and access to resources and power.
According to some conflict theorists, families in capitalist economies are similar to the work environment of a factory. Women are dominated by men in the home in the same manner that workers are dominated by capitalist and managers in factories. Although childbearing and care for family members in the home contribute to capitalism, these activities also reinforce the subordination of women through unpaid (and often devalued) labor. Other conflict analysts are concerned with the effect that class conflict has on the family. The exploitation of the lower classes by the upper classes contributes to family problems such as high rates of divorce and overall family instability.
Some feminist perspectives state that "Women’s subordination is rooted in patriarchy and men’s control over women’s labor power. Men have benefited from the privileges they derive from their status as family breadwinners.
Symbolic Interactionist Perspective - Symbolic interactionists such as Charles Horton Cooley and George Herbert Mead provide key insights on the roles we play as family members and how we modify or adapt our roles to the expectations of others—especially significant others such as parents, grandparents, siblings, and other relatives. According to the sociologists Peter Berger and Hansfried Kellner (1964), interaction between marital partners contributes to his shared reality. Symbolic interactionists explain family relationships in terms of the subjective meanings and everyday interpretations that people give to their lives.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies