- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
How does cross-border terrorism impede the achievements of peace and security in South Asia?. (UPSC CSE Mains 2020 - Political Science and International Relations, Paper 2).
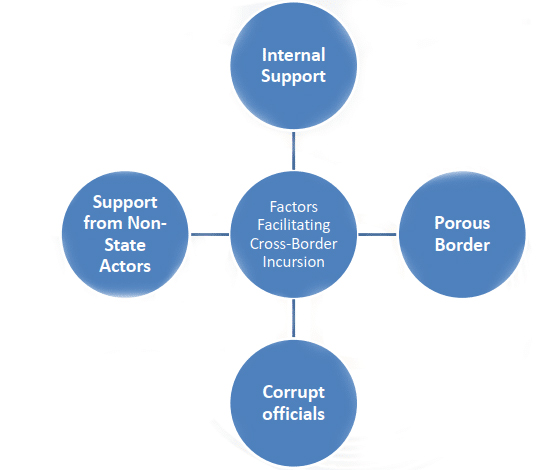
The term ‘cross-border’ implies a movement or an activity across a border between the two countries. Cross-Border Terrorism is a form in which the soil of one country is used to create terror in bordering countries. As a grey zone conflict, it is an undeclared war and considered to be the highest form of strategy to bleed a nation for a prolonged period by small efforts.
- India has 15,106.7 kms of land border and a coastline of 7,516.6 kms including island territories.
- Out of the total 29 states of India except for six states (Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Telangana, Delhi, and Haryana), the rest all states have either maritime boundary or land border with other nations.
- India has land borders with countries: Pakistan, Afghanistan (PoK), China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and Bangladesh.
- India has maritime borders with seven countries: Bangladesh, Indonesia, Myanmar, Pakistan, Thailand, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives.
 Consequences Of Cross Border Terrorism
Consequences Of Cross Border Terrorism
- Geographers identified numerous consequences associated to cross border terrorism which are as follows:
- Threat to the national integrity
- Hurdles in the implementation of regional planning
- Strengthening of cultural regionsand notion of regionalism.
- Loss of property, human resource, flora and fauna, and overall diversity.
- Cross border terrorism also disturbs the demographic dividendand attributes for any given geographical region and causes the push factor for migration. Therefore, some regions are underutilised and some are over utilised
Strategies To Control Cross Border Terrorism
- Political geographers suggested some of the political and geographical strategies to control cross border terrorism which are as follows:
- Effective implementation of international laws on borders and frontiers
- Satisfying the economic needs of region specific people,
- Effective implementation of UNCLOS
- Best utilisation of recent technologyin form of Indian Space Program and related satellite like RISAT-1 and GSAT-1.
- Regional cooperation between SAARC nation, Indian Ocean RIM countries and national agencies like NCTC, IB, RAW.
- India is also a member ofFATF (Financial Action Task Force) whose aim is to establish international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS)has replaced manual surveillance/patrolling of the international borders by electronic surveillance to enhance detection and interception capabilities.
Way Forward
- There is a need to reassess our policies on number of issues pertaining to the management of India’s international borderssuch as intelligence apparatus, internal security and border management.
- Impose tight control over immigration.
- Promote moreeffective domestic coordination and international cooperation to combat the financing of terrorism.
- Military should also look at alternative means to strike at the terror camps across the LoC and LAC through mechanisms like Precision Engagement Capability.
- Technical solutions are necessary to augment and complement the traditional methods of border guarding.
- Maintain close andeffective coordination between intelligence and security agencies at the centre and state level.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies