- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
July 13, 2024 Current Affairs
1. Centre declares June 25 as Samvidhaan Hatya Diwas
- 25th June 2024 marked the 49th anniversary of the declaration of the national emergency in India.
What is an Emergency?
- It refers to legal measures and clauses within a country''s constitution or laws that enable the government to respond swiftly and effectively to extraordinary situations, such as war, rebellion, or other crises that threaten the nation''s stability, security, or sovereignty and democracy of India.
- The emergency provisions in the Indian Constitution draw inspiration from Germany''s Weimar Constitution.
Types of Emergencies in Indian Constitution
The Indian Constitution provides for three types of emergencies as listed below:
- National Emergency (Article 352)
A National Emergency refers to an emergency that is imposed due to war, external aggression, or armed rebellion.
2. President’s Rule (Article 356)
President’s Rule refers to an emergency that is imposed due to the failure of the Constitutional Machinery in the States. It is also known by two other names – ‘State Emergency’ or ‘Constitutional Emergency’.
3. Financial Emergency (Article 360)
A Financial Emergency refers to an emergency that is imposed due to a threat to the financial stability or credit of India.
How Many Times Emergency was Imposed in India?
National Emergency has been proclaimed 3 times so far in India:
- Indo-China War (1962): Declared due to "external aggression" in 1962 during the Sino-Indian War.
- Indo-Pak War (1971): Imposed on the grounds of "external aggression" in 1971 during the Indo-Pakistani War.
- (1975-1977): The third andmost controversial national emergency was declared in 1975, primarily due to "internal disturbance" amidst internal political unrest. This period witnessed a significant suspension of civil liberties.
Arguments in Favour of Emergency Provisions
- National Security and Integrity– Emergency Provisions are seen as necessary to safeguard the nation’s security and territorial integrity in the face of external aggression, armed rebellion, or other threats to the constitutional order.
- Effective Crisis Management– The enhanced powers granted during emergencies enable the Central Government to quickly mobilize resources, coordinate responses, and take swift action to address urgent situations.
- Maintaining Constitutional Order– The emergency provisions, particularly the power to declare a President’s Rule in a State, are seen as a crucial mechanism for maintaining the constitutional order in India.
- Ensuring Effective Governance– In situations of crisis or breakdown of normal governance mechanisms, emergency provisions allow for the centralization of power, ensuring swift and effective decision-making to address pressing issues.
Arguments in against of emergency:
- Authoritarianism: The declaration of Emergency was widely criticized for its authoritarian nature, with accusations of suppressing democratic freedoms.
- Abuse of Power: The government’s actions during this period were criticized for being excessive and for infringing upon the rights of citizens.
- Opposition and Resistance: Many political leaders and activists, both from within and outside the Congress, resisted the Emergency and faced repression.
2. New species of dogfish shark discovered in Kerala harbour
Scientists from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) recently discovered a new species of deep-water dogfish shark Squalus hima from a fishing harbour in Kerala along the Arabian Sea.
Squalus hima:
- It is a new species of dogfish shark discovered from southwest coast of India.
- Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae. commonly known as spurdogs and are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines.
- They also have an angular short snout, a small mouthalmost as wide as the snout, first dorsal fin origin behind the pectoral fins, and body without anyspots.
- They are exploited for their liver oil,which contains high levels of squalene (or squalane when it is processed for products).
- It is in high demand for the pharmaceutical industry,particularly for making high-end cosmetic and anti-cancerous products.
- On the Indian coast, two species of Squalus are found from the southwest coast of India, and the new species, Squalus hima n.sp., very similar to Squalus lalannei, but differs in many characteristics.
- The newly discovered Squalus hima differs from other species by the number of precaudal vertebrae, total vertebrae, teeth count, trunk & head heights, fin structure, and fin colour.

Zoological Survey of India (ZSI)
- Establishment and Purpose: Founded on July 1, 1916, the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) is dedicated to the systematic survey, exploration, and research of India’s fauna. Initially established to promote zoological studies, ZSI is headquartered in Kolkata.
3. India shows good progress on SDGs: NITI Aayog report
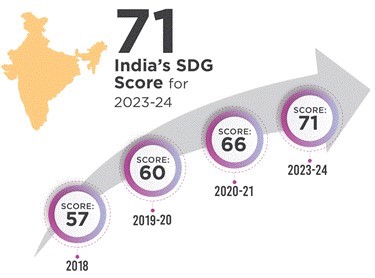
- The SDG India Index 2023-24 reveals India’s overall score improved to 71, up from 66 in 2020-21 and 57 in 2018. Significant advances were noted in poverty alleviation, health, water, sanitation.
Key highlights and results from the fourth edition of the SDG India Index:
- The composite score for India improved from 57 in 2018 to 66 in 2020-21 to further to 71 in 2023-24.
- India has taken significant strides in accelerating progress on the SDGs between the 2020-21 and 2023-24 editions of the Index. Noteworthy advancements have been observed in Goals 1 (No Poverty), 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), 13 (Climate Action). These are now in the ''Front Runner'' category (a score between 65–99).
- Among these, Goal 13 (Climate Action) has shown the most substantial improvement, with its score increasing from 54 to 67. Goal 1 (No Poverty) follows closely, with its score rising significantly from 60 to 72. The progress underscores the effects of the focused programmatic interventions and schemes of the Union and State Governments in improving the lives of citizens.
- Since 2018, India has witnessed substantial progress in several key SDGs. Significant progress has been made in Goals 1 (No Poverty), 3 (Good Health and Well-being), 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure) and 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
- Government''s focus on ensuring food & nutrition security, health, education, electrification, housing for all, sanitation, clean cooking fuel & energy has significantly contributed to the improvements.
State and UT results
- The SDG India Index 2023-24 reports a positive trend in the performance of States and UTs in their SDG journey. The scores for States now range from 57 to 79, while UTs score between 65 and 77. This represents an improvement over the 2020-21 scores, where the range was 52 to 75 for States and 62 to 79 for UTs.
- The Index records a significant increase in the number of States and UTs achieving Front Runner status. This year, 32 States/UTs have scored between 65 and 99, up from 22 in the 2020-21 edition. Notably, there are 10 new States and UTs in the Front Runner category. These include Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Manipur, Odisha, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
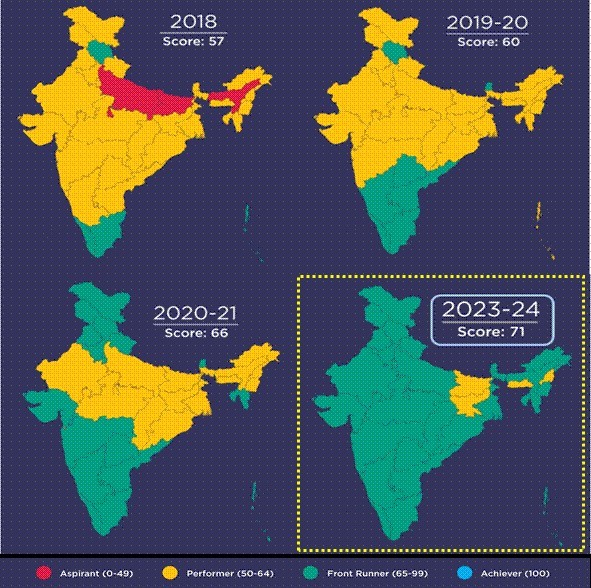
- The SDG India Index 2023-24 demonstrates the increase in composite scores across all States, with improvements ranging from 1 to 8 points. Leading the way in terms of score improvement are Assam, Manipur, Punjab, West Bengal, and Jammu and Kashmir, each achieving a positive change of 8 points since the 2020-21 edition.
4. National Gopal Ratna Award
Since 2021, the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying has been conferring the National Gopal Ratna Award every year under the Rashtriya Gokul Mission.
It is one of the highest national awards in the field of livestock and dairy, instituted for farmers rearing indigenous livestock.
The Award is conferred into the following categories:
- Best Dairy farmer rearing Indigenous Cattle/buffalo breeds
- Best Dairy Cooperative Society(DCS) / Milk Producer Company (MPC) / Dairy Farmer Producer Organization (FPO).
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT).
Objective: To encourage the Milk producing farmers, dairy cooperative societies/MPC/FPOs, and Artificial Insemination Technicians (AITs).
The awards will be conferred on the occasion of National Milk Day on 26th November.
5. RBI’s Financial Inclusion Index
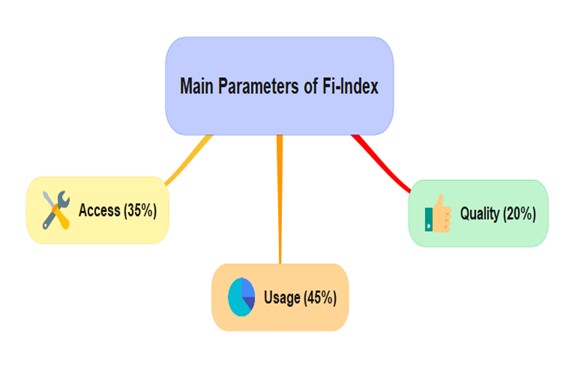
The Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index), which measures the extent of financial inclusion across India, reached 64.2 in March 2024, up from 60.1 in March 2023, according to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index)
- The FI-Index is a comprehensive measure of financial inclusion, ranging from 0 to 100, with 0 representing complete financial exclusion and 100 indicating full financial inclusion.
- The FI-Index is published annually in July every year.
RBI''s Perspective:
- The FI-Index supports inclusive growth by facilitating access to credit and safety nets, crucial for economic stability.
- Enhanced by digital initiatives like Aadhaar and mobile proliferation, it underscores the role of payment systems in fostering financial inclusion.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies