- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
July 22, 2024 Current Affairs
Zika virus
Zika virus is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. It can also spread through sexual contact and from mother to child during pregnancy.
- Symptoms: Most people infected with Zika virus do not show symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are usually mild and include fever, rash, joint pain, and red eyes (conjunctivitis). However, infection during pregnancy can lead to severe birth defects such as microcephaly and other neurological complications in the foetus.
- Global Spread: The Zika virus garnered international attention during its widespread outbreak in 2015-2016 in the Americas, particularly in Brazil. This led to a global health emergency declaration by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2016.
- Impact and Response: Countries affected by Zika virus outbreaks implemented measures to control mosquito populations, advised pregnant women to take precautions, and conducted research to understand the virus better. International cooperation and research efforts intensified to develop vaccines and treatment options.
- Challenges and Lessons: The Zika virus highlighted challenges in global health governance, response to emerging infectious diseases, and the need for robust public health infrastructure. It also underscored the importance of international collaboration in managing health crises.
Kanwar Yatra
The Kanwar Yatra is an annual pilgrimage of Shiva devotees, known as Kanwariyas, who travel to sacred Hindu sites, particularly to fetch holy water from the Ganges River during the Hindu month of Shravan (July-August).
- The yatra derives its name from the word ‘kanwar’, meaning a bamboo pole to which containers of holy water are tied at opposite ends.
- Millions of devotees called Kanwariyas or kriyas travel to pilgrimage places like Haridwar, Gaumukh, Gangotri in Uttarakhand, Sultanganj in Bihar, Prayagraj, Ayodhya and Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, and return by carrying Ganga water in kanwars to seek the blessings of Shiva.
- The water is then offered to Shiva temples, including the 13 Jyotirlingas across India. The ritual is known as Jal Abhishek.
- During the whole journey, Kanwars have to make sure that the earthen pots do not touch the ground.
- While carrying the water, devotees walk barefoot, and some complete the pilgrimage by lying flat on the ground.
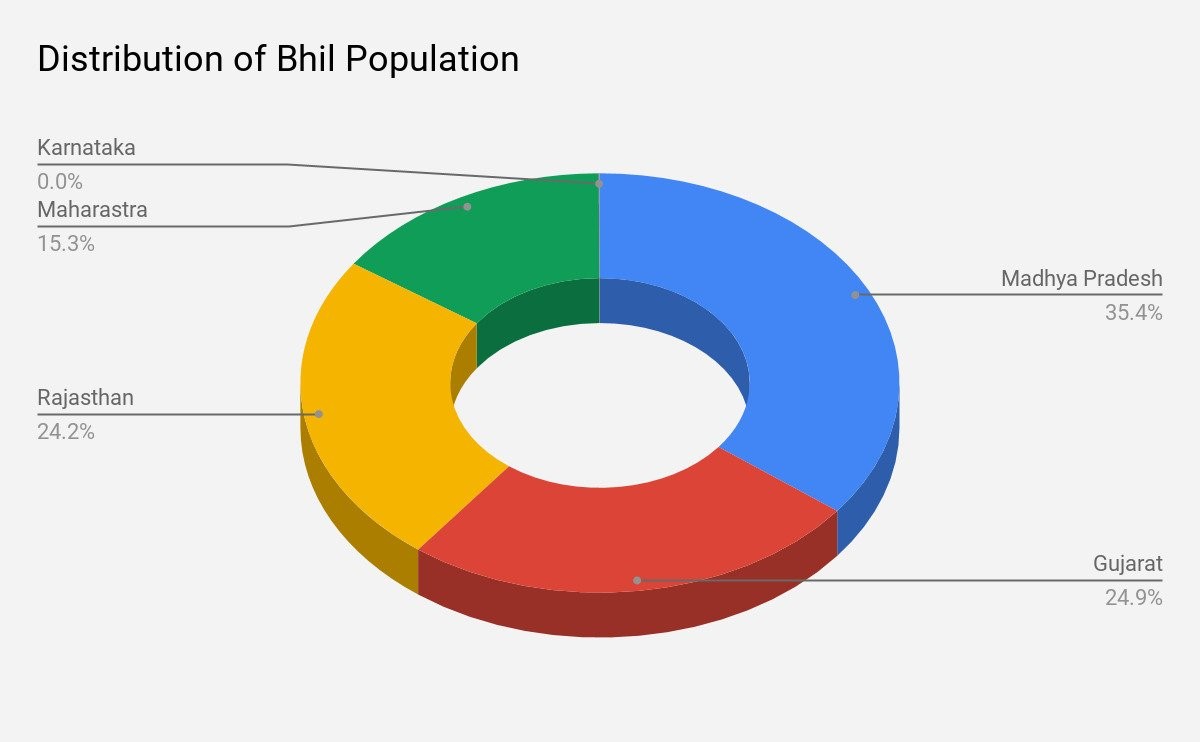
Bhil Pradesh
Bhil Pradesh is a proposed state in India primarily aimed at addressing the socio-economic and cultural needs of the Bhil tribal community. The Bhils are one of the largest tribal groups in India, predominantly residing in the western and central parts of the country.
Major Reasons for Rise in demand for Separate state
- Economic backwardness of sub-regionswithin large states has also emerged as an important ground on which demands for smaller states are being made
- Linguistic and cultural reasons, which were the primary basis for creating new states in the country, have now become secondary in most of these cases.
- Slow execution: Several Union governments brought various “laws, benefits, schemes, and committee reports” on tribal, but went slow on their execution and implementation.
- There were various measures such as the protection of tribal interests through the Fifth Schedule under Article 244(1)of the Constitution, but most of these were mere assurances by the ruling party.
Challenges
- Administrative challenges: The initial costs of setting up new state machinery are very high.
- Conflicts: Possibility of increased conflict over interstate river water, land borders, etc. Regionalism: Fragmentation and weakening national unity.
- Economical Concerns: Potential financial burden on central government, Smaller markets might be less attractive for large-scale investments, etc.
- Pandora box: Creation of new states can further lead to the demand for and creation of other new states.
Nipah virus
Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus that can cause severe illness in humans, including encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Origin and Transmission: The Nipah virus was first identified during an outbreak in Malaysia in 1998-1999. It is primarily transmitted to humans from animals (bats and pigs), and in some cases, through direct contact with infected individuals.
- Symptoms and Impact: Nipah virus infection can range from asymptomatic (no symptoms) to acute respiratory illness and fatal encephalitis. The virus has a high mortality rate, ranging from 40% to 75% in outbreaks.
- Outbreaks: Nipah virus outbreaks have occurred sporadically in South and Southeast Asia, including Bangladesh and India. These outbreaks often lead to significant public health challenges due to the high case fatality rate and potential for person-to-person transmission.
- Preventive Measures and Control: Prevention and control of Nipah virus outbreaks involve measures such as surveillance of bat populations (natural reservoirs), early detection of cases, isolation of infected individuals, infection control practices in healthcare settings, and public awareness campaigns.
- Challenges: The emergence of Nipah virus highlights challenges in global health security, including the rapid spread of zoonotic diseases, capacity building for outbreak response, and the importance of international collaboration in disease surveillance and control.
QUAD
The Quad, short for the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is an informal strategic dialogue between four democratic countries: the United States, Japan, India, and Australia.
Areas of Cooperation:
- The Quad is aimed at promoting regional securityand economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The four countries share a common interest in maintaining a free and open Indo-Pacific, promoting democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, and countering China''s expanding influence in the region.
- The Quad has held several meetings at the ministerial and leaders'' level to discuss issues such as maritime security, infrastructure development, and supply chain resilience.
- The Quad is seen as a mechanism for balancing China''s influence in the region, although its members have stressed that it is not a military alliance and is open to other countries who share their values and interests.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): Cooperating in disaster response and humanitarian assistance to support regional stability and resilience.
Issues
- Undefined Vision:Although there is potential for cooperation, the Quad remains a mechanism without a defined strategic mission.
- Maritime Dominated:The entire focus on the Indo-Pacific makes the Quad a maritime, rather than a land-based grouping, raising questions whether the cooperation extends to the Asia-Pacific and Eurasian regions.
- India’s Aversion of Alliance System:The fact that India is the only member that is averse to a treaty alliance system, has slowed down the progress of building a stronger Quadrilateral engagement.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies