- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
June 08, 2024 Current Affairs
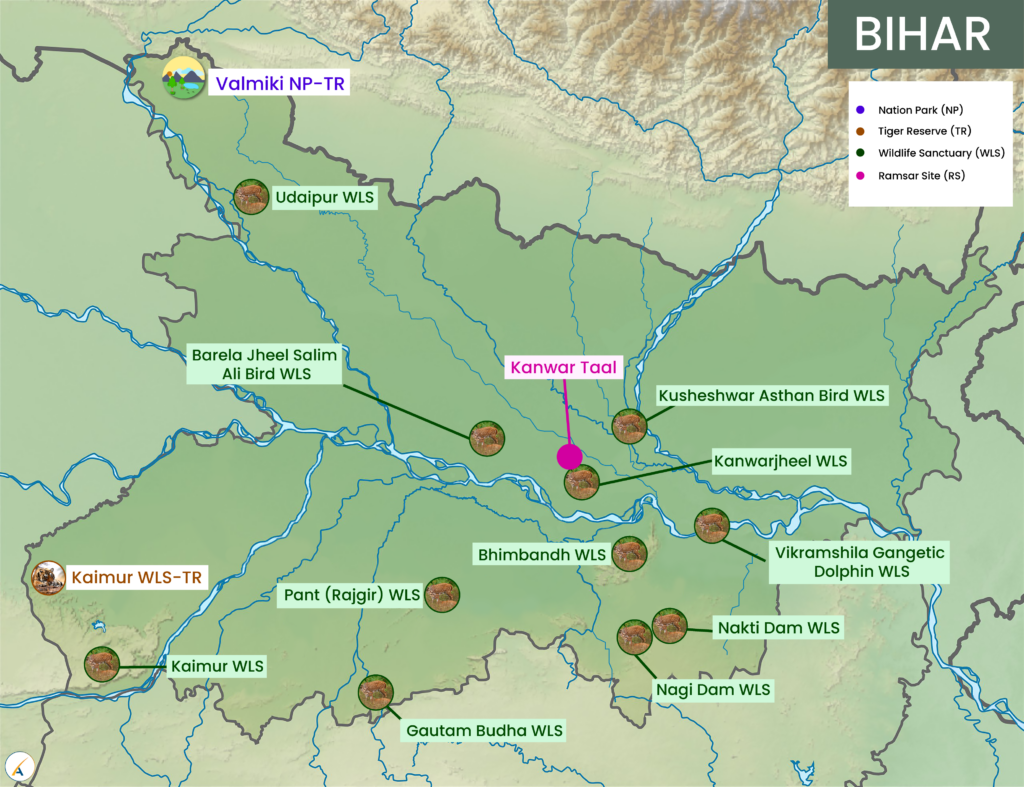
Recently, 2 Human-made wetlands from Bihar, The Nagi and Nakti Bird Sanctuaries, have been recognised as wetlands of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Two bird sanctuaries of Bihar added to Ramsar list.
- The sites were declared on the World Environment Day (5 June 2024).
- India now hosts 82 Ramsar wetland sites with this inclusion.
- Currently, the highest number of such sites is in the UK (175), followed by Mexico (144).
- Kanwar Lake in Begusarai district was designated Bihar’s first Ramsar Site in 2020.
- Tentative sites for Inclusion from Bihar: Kusheshwar Asthan in Darbhanga, Tal Baraila in Vaishali, Gogabeel in Katihar, Nagi and Nakati dams in Jamui.
Nagi and Nakti Bird Sanctuaries:
- The wetland was designated as a Bird Sanctuary in 1984.
- Location: The wetlands are deemed protected areas in the Jhajha forest range of Bihar’s Jamui district.
- Size: They are spread across 791 and 333 hectares, respectively.
- Human-made: The Nagi and Nakti bird sanctuaries are human-made wetlands that were developed primarily for irrigation purposes through the construction of the Nakti Dam.
- Wildlife support: The sanctuary supports globally threatened species, including the endangered Indian elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) and a vulnerable native catfish (Wallago attu).
- The catchment area: It is a largely dry deciduous forest surrounded by hills.
- Wintering Habitat for Migratory Birds: Over 20,000 birds congregate during the winter months, including one of the largest congregations of red-crested pochards (Netta rufina) on the Indo-Gangetic plain.
- As per Asiatic Waterbird Census(AWC) 2023: The Nakti bird sanctuary is the wetland with the highest number of birds reported with a count of 7,844 birds, followed by Nagi bird sanctuary with 6,938 birds.
Ramsar Convention:
- Establishment: A Ramsar site is a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention (also known as the ‘Convention on Wetlands’), an intergovernmental environmental treaty established by UNESCO in 1971 and named after the city of Ramsar in Iran, where the convention was signed that year.
- Identification: Ramsar recognition is the identification of wetlands that are of international importance, especially if they provide habitat to waterfowl (about 180 species of birds).
- First Ramsar Site in India: Chilika Lake in Orissa and Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan
- Largest Ramsar Site in India: Sundarbans in West Bengal
Wetlands:
- A Saturated Ecosystem: A wetland is where the land is covered by water (salt, fresh, or somewhere in between) seasonally or permanently. It functions as its own distinct ecosystem.
- Consists Of: They include mangroves, marshes, rivers, lakes, deltas, floodplains and flooded forests, rice fields, coral reefs, marine areas no deeper than 6 meters at low tide, as well as human-made wetlands such as waste-water treatment ponds and reservoirs.
- Contribution: They cover only around 6% of the Earth’s land surface, but about 40% of all plant and animal species live or breed in wetlands.
The Securities Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI) recently slapped a fine of Rs 7.75 crore on 11 individuals for allegedly operating a ‘pump and dump’ scheme.
Pump and Dump Scheme:
- In the stock market, a pump and dump scheme is a type of manipulation activity that involves artificially inflating the price of a stock through false and misleading information, only to sell the stock at the inflated price and leave investors with significant losses.
- It is particularly prevalent in the micro-cap and small-cap sectors, where companies often have limited public information and trading volumes are lower.
How does pump and dump work?
- First, a significant amount of stock in a relatively small or thinly traded company is acquired. These stocks are often referred to as ‘penny stocks’ because they trade at low prices and are more susceptible to price manipulation due to low trading volumes.
- Then the stock is aggressively promoted to create a buzz and attract investors. This promotion can take various forms, including sending out mass emails or newsletters with exaggerated claims about the company’s prospects, as well as misleading social media posts. Promoters aim to create buzz and drive interest in the stock.
- As the promotion gains traction, more investors buy into the stock, driving up its price due to increased demand. Sometimes, fraudsters may also engage in coordinated buying to further boost the price. During this phase, the stock often experiences rapid and significant price increases, creating the illusion of a hot, high-potential investment.
- Once the stock price has been pumped up sufficiently, the sell-off begins at the inflated prices. This selling pressure causes the stock price to plummet, often leaving unsuspecting investors with significant losses as the stock returns to its actual value or even lower.
Impact:
- Those who bought into the hype and purchased the stock at inflated prices typically face substantial losses when the stock price crashes.
- These schemes undermine confidence in the financial markets, making legitimate investors wary of potential fraud.
- Under the SEBI guidelines, pump and dump schemes are completely banned.
The Space Agency ISRO recently announced a satellite mission, TRISHNA. This TRISHNA mission is a joint infrared earth observation satellite mission between India and France.
TRISHNA Mission:
- TRISHNA refers to Thermal Infra-Red Imaging Satellite for High-Resolution Natural Resource Assessment.
- Objectives: The Primary Goal of TRISHNA mission is to monitor surface temperature and water management globally.
- It will address extreme heat issues in India and Europe.
Launch Details:
- Tentative Launch: 2025
- Mission Lifespan: 5 years
- Features: There are two primary payloads in satellites.
- The Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) payload
- It will be provided by the French space agency CNES
- The TIR payload will feature a four-channel long-wavelength infrared imaging sensor for studying high-resolution surface temperatures.
- It will also map the heat radiated back from land in different regions.
- The Visible Near Infrared-Red Short Wave Infrared-Red (VNIR-SWIR) payload
- It will be developed by ISRO
- The VNIR-SWIR payload will map the reflectivity (albedo) of the Earth’s surface across seven bands.
- This mapping will measure the amount of heat reflecting off the Earth’s surface.
- It will also calculate various biophysical and radiation budget variables.
Benefits of TRISHNA Mission:
- Improved Water Management:TRISHNA mission will provide data on evapotranspiration.
- Evapotranspiration Monitoring: Includes soil evaporation and water transpiration from plants.
- It helps monitor agricultural water use and maintain soil moisture levels during droughts.
- It also provides vital data to manage the increasing droughts affecting Indian farmers.
- Study of water presence: It will also study water presence and concentration, including melting glaciers, to improve water resource management globally.
- Enhanced Climate Monitoring: The mission will track thermal anomalies, surface energy balance, and urban heat islands to understand the impact of climate change.
- It will study aerosols, water vapour, and cloud cover to improve our understanding of atmospheric processes.
- Sustainable Practices Policies:The data will be used to develop new policies for sustainable water management by watershed managers, agro-industries, and farmers.
- The high-resolution, high-repeat imaging will improve our understanding of Earth’s natural processes to aid in global climate change mitigation efforts.
- Advancement in Remote Sensing Technology:TRISHNA is expected to be a significant advancement in remote sensing technology, which is crucial for monitoring Earth from space during extreme weather events.
Global Impact of the Trishna Mission:
Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)-
- Water Scarcity and Management: Addresses issues related to water scarcity and management (SDG 6).
- Climate Action: Supports initiatives for climate action (SDG 13).
International Cooperation and Knowledge Transfer-
- Strengthening Ties: Enhances cooperation between participating nations.
- Expertise Exchange: Promotes the exchange of expertise in space technology.
- Capacity Building: Facilitates capacity building in space technology among the involved countries.
India, South Korea, the United States, Japan, and the European Union (EU) have formed a Biopharmaceutical Alliance to address drug supply shortages during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Biopharmaceutical Alliance:
- It was launched in response to the drug supply shortages experienced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- The announcement was made at the inaugural meeting of the Biopharmaceutical Alliance, held in San Diego, California, during the Bio International Convention 2024, the world’s largest biopharmaceutical exhibition.
- The initiative originated from discussions between South Korea and the U.S. and expanded to include Japan, India, and the EU.
Aim of the Alliance:
- The alliance aims to coordinate bio policies, regulations, and research and development support measures among participating countries.
- Emphasized the importance of a reliable and sustainable supply chain.
Free equitable and fair drug supply ensures:
- Access to essential medicines for all populations.
- Availability of affordable treatments, especially in developing countries.
- Equitable distribution of medications, reducing disparities in healthcare.
- Promotion of public health by addressing global health challenges.
- Supports disease prevention, treatment, and eradication efforts worldwide.
India as pharmacy of the world:
- India has earned the title “Pharmacy of the World” due to its robust generic pharmaceutical industry, supplying affordable and quality medicines globally. This reputation grew during the HIV/AIDS pandemic when Indian companies provided affordable antiretroviral drugs to African countries. India’s generic industry became a major supplier after the establishment of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
India’s Vaccine Diplomacy:
- Widespread Vaccine Access: India ensures COVID-19 vaccines are globally accessible.
- IPR Waiver: Proposes a WTO waiver on intellectual property rights to make vaccines more affordable.
- Major Supplier: Becomes a significant vaccine supplier, notably through partnerships with Serum Institute of India (SII) and Bharat Biotech International Ltd.
- Neighbourhood Focus: Implements a “Neighbourhood First” policy, prioritizing vaccine assistance to South Asian countries.
- Global Assistance: Provides vaccine aid to African countries and UN health workers through COVAX.
Significance of India’s Vaccine Diplomacy:
- Development Partnership: Reflects India’s long-standing commitment to global health and development.
- Commercial Terms: Exports vaccines on commercial terms to upper-middle-income countries.
- Diplomatic Relations: Restores strained relations, as seen with Canada, through vaccine diplomacy.
- Countering Vaccine Nationalism: India’s sharing policy contrasts with the trend of vaccine hoarding by other nations.
- Global Health Diplomacy (GHD): Positions India as a key player in GHD, contributing to peace, equity, and global health security.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies