- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
October 9 2024 Current Affairs
|
India pledges $250 million for traditional medicine centre; part of $300 million contribution to WHO for 2025-2028 India’s contribution will also be used for a new regional office for WHO, digital health and thematic funding.
World Health Organisation (WHO):
|
|
Nilgiri tahr In a significant breakthrough for conservation efforts, a newly colonised habitat of Nilgiri Tahr has been discovered in Pasumalai.
Physical Description
Habitat and Distribution
Conservation Status
|
|
Why fair returns for farmers are elusive?
Reasons for the lower realisation in case of tomato, onion & potato
A better deal for dairy & poultry farmers
Price realisation in pulses
How can the value chains be improved?
|
|
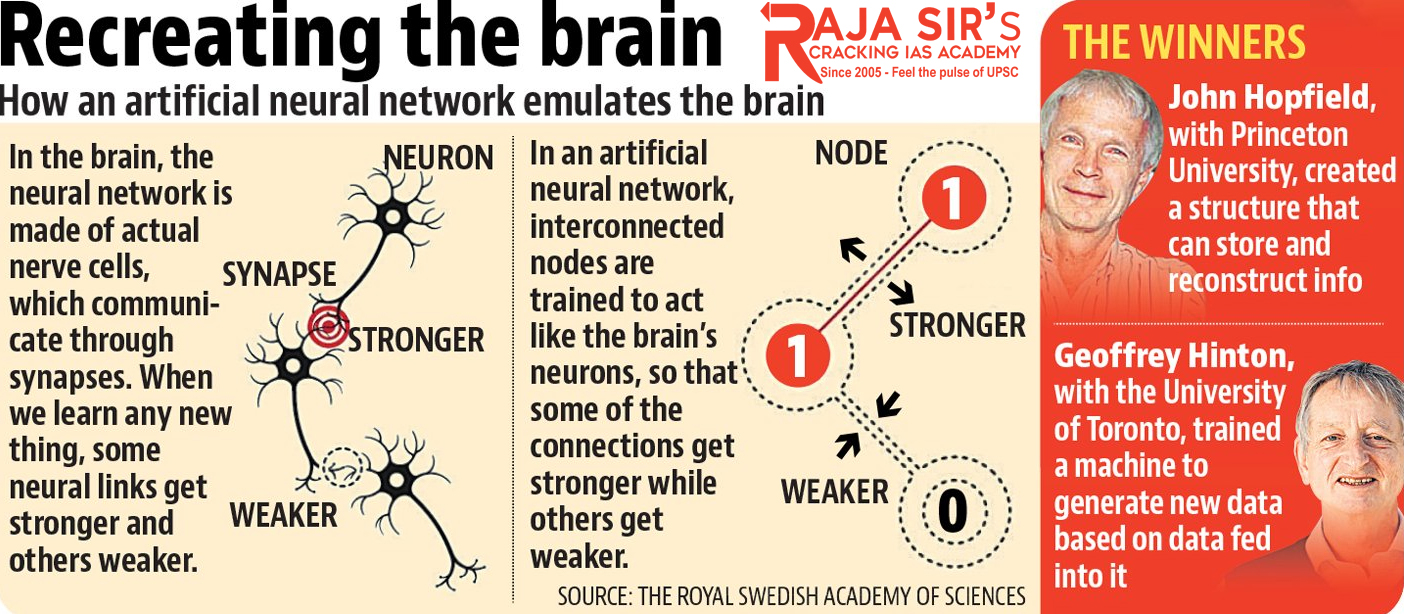
Physics Nobel awarded to neural network pioneers who laid foundations for AI U.S. scientist John Hopfield and British-Canadian Geoffrey Hinton won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics for discoveries and inventions that laid the foundation for machine learning.
o Hopfield networks could recognise simple patterns of shape or sound o Hinton’s advanced models could understand voices and pictures. o Neural networks could be strengthened, and their accuracy at pattern recognition enhanced through repeated inputs of data, called training.
o Subset of artificial intelligence (AI), it focuses on the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make decisions based on data, without being explicitly programmed for specific tasks. o Essence of machine learning is recognizing patterns within data and making predictions or decisions based on those patterns. o How it works
Examples of machine learning o Spam filtering: Uses patterns in data to identify spam emails o Natural language processing: Enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. o Neural networks: Inspired by the human brain’s neural connections, these models are used in machine learning. o Overfitting and Underfitting: Overfitting occurs when a model performs well on training data but poorly on new data. Underfitting happens when a model is too simplistic, failing to capture underlying patterns. |
|
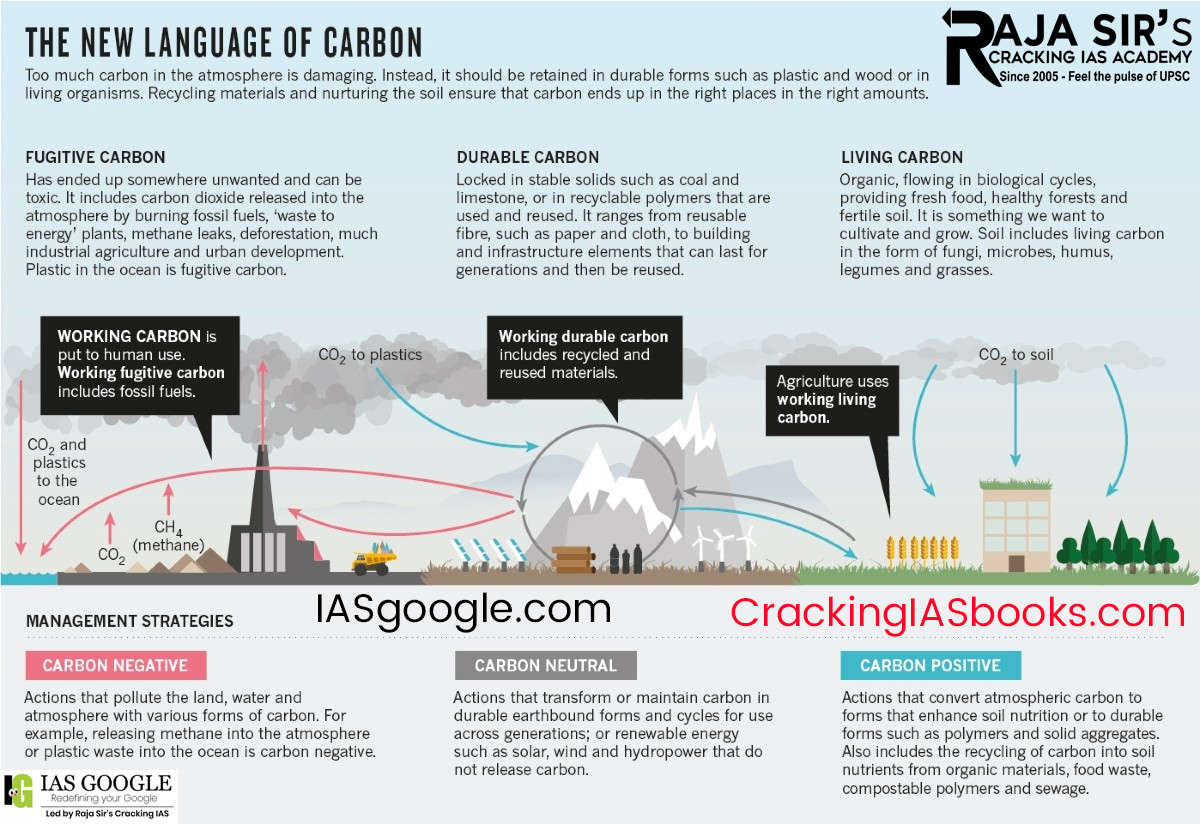
Battery Lifecycles and Environmental Implications The demand for batteries continues to grow across various sectors, the environmental implications of their life cycles have become a critical concern. Traditionally, improving battery lifespan and recycling had much of the focus.
This restoration process involves:
Economic and Environmental Benefits with Circular Economy
Aligning with Global Sustainability Goals
Future of Battery Technology: Restoration as the Norm
In the end, battery rejuvenation stands to become an essential component of sustainable energy management. By prolonging lead-acid battery lifespan and mitigating environmental harm while fitting into circular economies such as EBEP’s circular economy model, rejuvenation technologies such as this offer an immediate solution to meet rising global energy storage demands. As economies transition toward more responsible practices, adopting rejuvenation battery technologies such as these will be essential in driving both economic efficiency and environmental stewardship. |
|
India’s potent black carbon emissions from kerosene lamps make up 10% of total residential emissions
Black Carbon Emissions in India
Rural Dependency on Kerosene Lamps:
Regional Emission Contributions:
Key Government Initiatives to Reduce Black Carbon Emissions in India
Black Carbon
Impacts of Black Carbon Climate change
Air pollution
|
|
2023 driest for global rivers in 33 years, reveals WMO’s report The year 2023 was the driest for global rivers in the past 33 years, The State of Global Water Resources report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The report highlighted severe stress on global water supplies. • In fact, the past five consecutive years have recorded widespread below-average river flows and reservoir inflows, reducing the amount of water available for communities, agriculture and ecosystems. Drier than average river discharge • With 2023 being the hottest year on record, increasing temperatures and widespread dry conditions contributed to prolonged droughts. Compared to the historical period (1991–2020), rivers mostly faced conditions that were drier-than-average to average for river discharge, the report said. • Similar to 2022 and 2021, more than half of global catchment areas in 2023 showed deviations from near-average conditions for river discharge, predominantly lower than average, with fewer basins exhibiting above- or much-above-average conditions • In an era of growing water demand, the report showed a rising trend in dry areas over time, with 2023 being the driest year in the last three decades, followed by 2021 and 2015. Below- and much-below-average conditions affected North America (except Alaska), Central America and South America. • Meanwhile, in Asia, large river basins such as those of the Ganga and Brahmaputra experienced lower-than-average conditions across almost their entire territories. Discharge conditions also remained lower than average across the West and Central Asia. • The transition from La Niña (2022-2023) to El Niño (2023) appears to have been a key climatic driver in this record-breaking dry and warm situation, combined with a widespread anomalous warming over the worldwide ocean. Reservoir inflows and storage • The report, now in its third year, indicated that inflow into reservoirs in 2023 generally reflected the overall discharge conditions, with the global balance being mostly below average or average. • Specifically, reservoirs in India, especially along the west coast, experienced below- and much-below-average inflows. However, the Ganga river basin in India saw above-average reservoir storage. • Reservoir storage is influenced not only by climatic conditions and inflows but also by human regulation of the storage. Even when inflows are low, water can be stored, increasing reservoir volumes but decreasing discharge downstream. • Meanwhile in Australia, the Murray-Darling river also recorded below-average inflows. In North and South America, reduced water availability was evident, with lower-than-usual inflows into reservoirs, particularly in the Mackenzie river in North America, across Mexico and in the Paraná river in southern Brazil and Argentina. Across the West and Central Asia, inflows into reservoirs remained lower than usual. Dip in groundwater levels • In 2023, average groundwater levels were much below average in 19 per cent of monitored wells, below average in 11 per cent, average in 40 per cent, above average in 10 per cent and much above average in 20 per cent. • A large part of North America, central and northern Chile, western and southern Brazil, southern Europe (Portugal, Spain, most of France), central Europe (Hungary, Austria, Bavaria, northern Poland), as well as western and southern Australia, were regions where average groundwater levels were below or much below average in a high proportion of wells. • Conversely, groundwater levels were above or much above average in a high proportion of wells in New England (United States), the Maritime provinces of Canada, along the Atlantic coast of north-eastern Brazil, northern Europe (the British Isles and Scandinavia), Israel, southern Africa, parts of India, the Republic of Korea, eastern Australia and the North Island of New Zealand. • High precipitation also directly contributes to rising groundwater levels by recharging aquifers and this effect was observed in some parts of India. Low soil moisture • The year 2023 ranked just behind 2022 in recent historical records for dry soils. Soil moisture in 2023 was predominantly below or much below average across large areas globally throughout the year. • For example, almost all of North America, South America, North Africa and West Asia experienced much-below-average soil moisture levels, particularly during June, July and August. • During the same period (June-August), almost all of Europe, the Russian Federation, Central Asia and China experienced below- to much-below-average soil moisture conditions. • However, Alaska, north-eastern Canada, India and the north-eastern Russian Federation experienced much-above-average soil moisture conditions. • Currently, 3.6 billion people face inadequate access to water for at least one month every year and this number is expected to rise to more than five billion by 2050, according to United Nations Water. |
|
Helicase-assisted continuous editing
|
|
Fattah 2 Iran used hypersonic missiles like the Fattah-2 in the ongoing conflict with Israel. Features
|
|
Isro to build third launch pad at Sriharikota, Cabinet approval pending
|
|
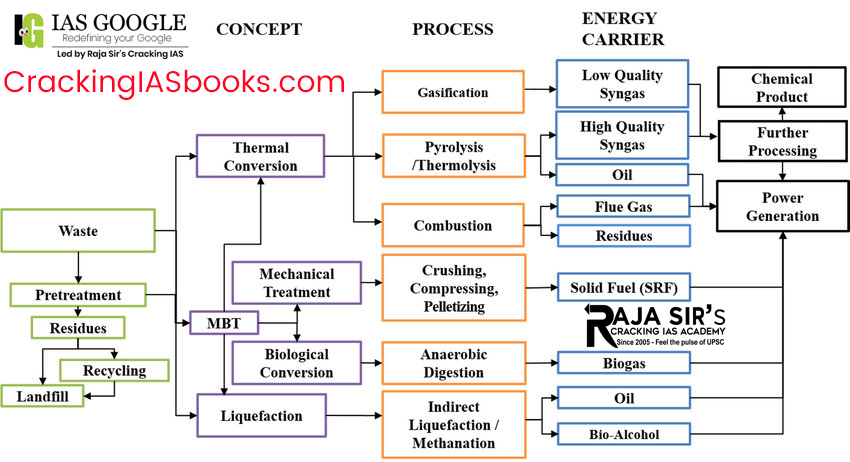
Waste Management and Waste to Energy Traditional to Modern Waste Management: Key Insights
Waste-to-Energy Technologies:
Conversion Processes:
Waste-to-Energy in India:
|









 Latest News
Latest News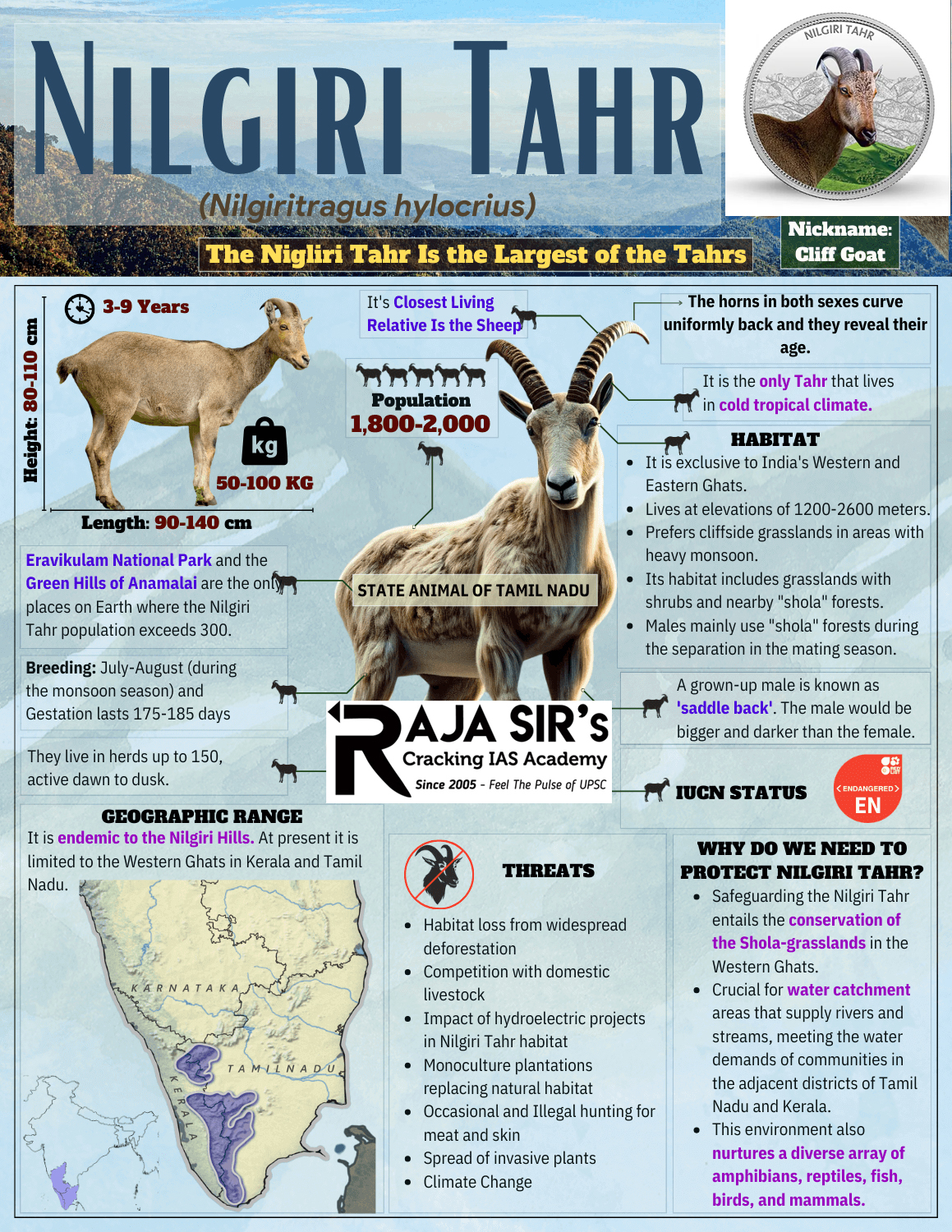
 Machine Learning
Machine Learning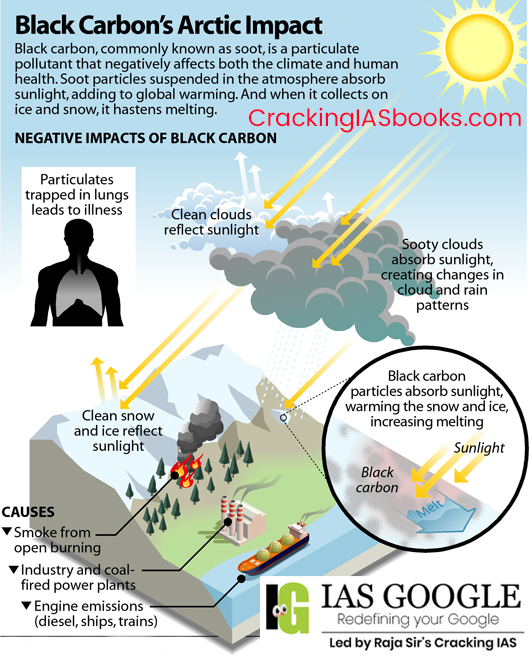

 General Studies
General Studies