- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
What is a circular economy?
The European Union has called for support for technological transfer to enhance the ‘circular economy’ at a working group meeting held ahead of the fifth session of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA 5.2).
Document Submitted by the African Group
 The need for Effective Governance
The need for Effective Governance
Proposals in Union Budget 2022-23
- According to a working document submitted by the African group to the UN, the circular economy must become an integral component of the national and regional development plans.
- The African group is one of the five UN regional groups which consists of 54 countries from the continent.
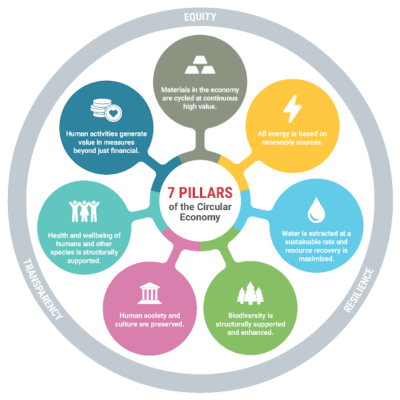
- The products and resources are made, used and disposed in a linear economy whereas they are recycled, repaired and reused in a circular economy.
- As per the Draft Resolution on Enhancing circular economy document, Integration and embedding circular principles and goals across industries and government priorities would be crucial to reaching global Net Zero pledges.
- The document has urged the UN member states to transform markets for the uptake of a circular economy.
- It includes markets for products that promote direct reuse, repair, refurbishment and remanufacturing.
- Sustainable public procurement is essential for promoting sustainable consumption as well as production.
- A circular economy recognizes that economic activities are embedded in an ecological life-support system.
- It provides incentives for reusing products rather than discarding them. In a circular economy, waste generation is minimal and the goods of today become the resources of tomorrow.

- The document underscored the need for effective governance for a transition to a circular economy.
- It recognized and asked nations to strengthen policies, legal and regulatory frameworks at local, national and regional levels.
- The Indian government claimed the country has been actively formulating policies and promoting projects to drive the country towards a circular economy.
- Policies to drive the country towards a circular economy include the Plastic Waste Management Rules, e-Waste Management Rules, Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules and the Metals Recycling Policy.
- The Extended producer responsibility (EPR) is a critical policy mechanism for advancing the circular economy.
- It promotes the principle of “polluter pays” by holding the producer accountable for the entire lifecycle of the product.
- The draft EPR policy was released for management of plastic waste in India in 2021 by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- The transition to renewable energy can address 55% of global greenhouse gas emissions, but to achieve the UN climate goals, it is important to focus on tackling the remaining 45%.
- We can address the 45% of global greenhouse gas emissions by changing the way we make and use products.
Generation of Electronic waste & Circular Economy
|
- The Union Budget 2022-23 talks of shifting to a circular economy.
- ₹2000 crore has been allocated to incentivize the production of high-efficiency solar modules, it would facilitate the 280 GW installed solar capacity goal of the government.
- Setting up business models for energy conservation and the use of biomass pellets and thermal power plants has been promoted in the budget.
- The budget underlines that transition to a circular economy is expected to improve productivity and create new jobs. It is true for many sectors including the electronics manufacturing industry.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies