- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
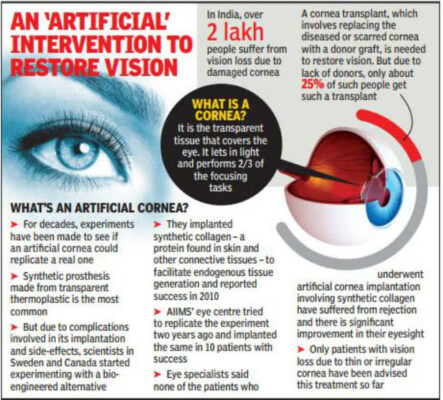
What is "Bioengineered Liquid Cornea"?
Bioengineered Liquid Cornea
 Notes on Structure, Function, Defects of Eye
The human eye is the most sensitive and incredible sense organ among all sense organs because with its help we become able to see beautiful and wonderful colors of the world. We can identify the objects around us to some extent by touch, smell, and sound. It is, however, impossible to detect colors while closing the eyes. The structure of the human eye is almost spherical in shape with a diameter of 2.3 cm. The human eye is just like a camera, its lens system also projects the images on a screen called the retina just like a camera.
Notes on Structure, Function, Defects of Eye
The human eye is the most sensitive and incredible sense organ among all sense organs because with its help we become able to see beautiful and wonderful colors of the world. We can identify the objects around us to some extent by touch, smell, and sound. It is, however, impossible to detect colors while closing the eyes. The structure of the human eye is almost spherical in shape with a diameter of 2.3 cm. The human eye is just like a camera, its lens system also projects the images on a screen called the retina just like a camera.
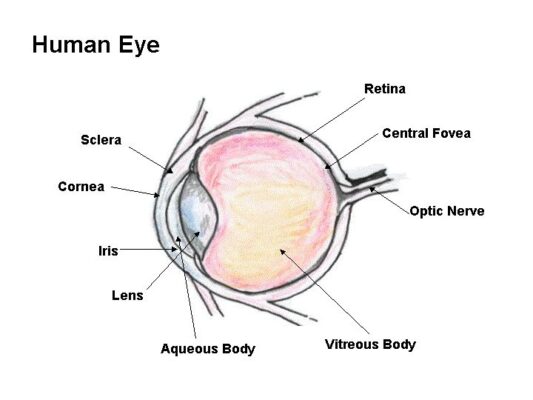 The human eye is made of three chambers, the first chamber is between cornea and iris which is filled with aqueous humor, the second chamber is between iris and crystalline lens and the third chamber is between the crystalline lens and retina which is filled with vitreous humor. Its two main lenses are the cornea and crystalline lens which refracts light rays and focus to the retina where the inverted image is formed, at the exit of the eye the optic nerve gets the signal of the inverted image, this signal transported to the brain than brain deciphers this inverted image to erected image.
Cornea.
In the structure of the eye, the cornea has a very important role. the cornea is a 5 layered transparent vascular tissue made of collagens and cells, it is the outermost lens of the eye and bulged in shape, light rays, first of all, fall on it and then refracted into the eye. The 65 to 75 % of the total refraction of the light takes place through it.
Aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor is a transparent fluid between cornea and iris and between iris and lens, it is composed of water vitamins, sugars, proteins, and other nutrients. The role of aqueous humor. is to nourish cornea and lense because both of them does not contain blood vessel. The aqueous humor maintains the intraocular pressure of the eye and protects the eye from the dust, pollen grains, wind, and microbes.
Iris.
The colored part of the eye is known as iris, it is located between the cornea and crystalline lens. Iris is made of the dark muscular diaphragm made of connective tissue and muscle covered with pigments responsible for the color of the eye, it surrounds the pupil. Iris controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil.
The pupil is actually the aperture of the eye, It is an opening at the center of the iris and circular in shape, the function of pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina. It appears black color because the light focused on the retina is completely absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back.
Christine lens.
The Christine lens is basically is an eye lens that is transparent and located behind the iris. It is not having blood vessels so it is nourished by aqueous humor that exists between iris and lens. One-third of the total net refraction of light through the eye is taken place by the Christine lens. it is made of small flexible smooth muscles called ciliary muscles, these muscles change the shape of the lens. When we see nearby objects, these muscles constrict and radius of curvature of the lens decreases so that images could be focused on the retina and when we see the far objects these muscles dilate and radius of curvature of lens increases so that images could be focused on the retina, this action of eye is known as accommodation of eye.
Vitreous humor.
Vitreous humour is a jelly-like transparent fluid that contains 99% water and it’s 1% is sugar, vitamins, proteins, hyaluronic acids, and collagens. This fluid pressurizes the retina to remain in its place and gives the spherical shape to the eye.
Retina.
The retina is located at the back end of the eye, it is made of photosensitive cells called photoreceptors, photoreceptors are of two kinds cones and rods. The rods show us images in dim light or when it is dark, cons show us light during the day time or when light is intense, we see colors of the images because of cons.
Optic nerve.
The images formed in the retina is inverted, the signal of the image is conducted through the optic nerve to the visual cortex of the brain, the image is decoded by the brain and then we see the inverted image as an erected image.
Image formation in eye
The human eye is made of three chambers, the first chamber is between cornea and iris which is filled with aqueous humor, the second chamber is between iris and crystalline lens and the third chamber is between the crystalline lens and retina which is filled with vitreous humor. Its two main lenses are the cornea and crystalline lens which refracts light rays and focus to the retina where the inverted image is formed, at the exit of the eye the optic nerve gets the signal of the inverted image, this signal transported to the brain than brain deciphers this inverted image to erected image.
Cornea.
In the structure of the eye, the cornea has a very important role. the cornea is a 5 layered transparent vascular tissue made of collagens and cells, it is the outermost lens of the eye and bulged in shape, light rays, first of all, fall on it and then refracted into the eye. The 65 to 75 % of the total refraction of the light takes place through it.
Aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor is a transparent fluid between cornea and iris and between iris and lens, it is composed of water vitamins, sugars, proteins, and other nutrients. The role of aqueous humor. is to nourish cornea and lense because both of them does not contain blood vessel. The aqueous humor maintains the intraocular pressure of the eye and protects the eye from the dust, pollen grains, wind, and microbes.
Iris.
The colored part of the eye is known as iris, it is located between the cornea and crystalline lens. Iris is made of the dark muscular diaphragm made of connective tissue and muscle covered with pigments responsible for the color of the eye, it surrounds the pupil. Iris controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil.
The pupil is actually the aperture of the eye, It is an opening at the center of the iris and circular in shape, the function of pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina. It appears black color because the light focused on the retina is completely absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back.
Christine lens.
The Christine lens is basically is an eye lens that is transparent and located behind the iris. It is not having blood vessels so it is nourished by aqueous humor that exists between iris and lens. One-third of the total net refraction of light through the eye is taken place by the Christine lens. it is made of small flexible smooth muscles called ciliary muscles, these muscles change the shape of the lens. When we see nearby objects, these muscles constrict and radius of curvature of the lens decreases so that images could be focused on the retina and when we see the far objects these muscles dilate and radius of curvature of lens increases so that images could be focused on the retina, this action of eye is known as accommodation of eye.
Vitreous humor.
Vitreous humour is a jelly-like transparent fluid that contains 99% water and it’s 1% is sugar, vitamins, proteins, hyaluronic acids, and collagens. This fluid pressurizes the retina to remain in its place and gives the spherical shape to the eye.
Retina.
The retina is located at the back end of the eye, it is made of photosensitive cells called photoreceptors, photoreceptors are of two kinds cones and rods. The rods show us images in dim light or when it is dark, cons show us light during the day time or when light is intense, we see colors of the images because of cons.
Optic nerve.
The images formed in the retina is inverted, the signal of the image is conducted through the optic nerve to the visual cortex of the brain, the image is decoded by the brain and then we see the inverted image as an erected image.
Image formation in eye
 The images we see are made up of light reflected from the objects we look at. This light enters the eye through the cornea, which acts like a window at the front of the eye. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the pupil, which is surrounded by the iris – the coloured part of the eye.
Because the front part of the eye is curved, it bends the light, creating an upside down image on the retina. The brain eventually turns the image the right way up.
The retina is a complex part of the eye, and its job is to turn light into signals about images that the brain can understand. Only the very back of it is light sensitive: this part of the retina is roughly the area of a 10p coin, and is packed with photosensitive cells called rods and cones.
Cones are the cells responsible for daylight vision. There are three kinds, each responding to a different wavelength of light: red, green and blue. The cones enable us to see images in colour and detail. Rods are responsible for night vision. They are sensitive to light but not to colour. In darkness, the cones do not function at all.
The lens is a clear disc-like structure that helps to focus light on the retina. It can do this because it is adjustable, and uses a muscle called the ciliary muscle to change shape and help us focus on objects at different distances. The automatic focusing of the lens is a reflex response and is not controlled by the brain.
Once the image is clearly focused on the sensitive part of the retina, energy in the light that makes up that image creates an electrical signal. Nerve impulses can then carry information about that image to the brain through the optic nerve.
Other parts of the eye include the aqueous humour, a liquid which sits in a chamber behind the cornea, and the vitreous humour, the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina. The sclera is the white part of the eye, forming an outer layer that protects everything inside, while the choroid is the layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. It is made up of layers of blood vessels that nourish the back of the eye.
Defects of vision and their correction
The images we see are made up of light reflected from the objects we look at. This light enters the eye through the cornea, which acts like a window at the front of the eye. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the pupil, which is surrounded by the iris – the coloured part of the eye.
Because the front part of the eye is curved, it bends the light, creating an upside down image on the retina. The brain eventually turns the image the right way up.
The retina is a complex part of the eye, and its job is to turn light into signals about images that the brain can understand. Only the very back of it is light sensitive: this part of the retina is roughly the area of a 10p coin, and is packed with photosensitive cells called rods and cones.
Cones are the cells responsible for daylight vision. There are three kinds, each responding to a different wavelength of light: red, green and blue. The cones enable us to see images in colour and detail. Rods are responsible for night vision. They are sensitive to light but not to colour. In darkness, the cones do not function at all.
The lens is a clear disc-like structure that helps to focus light on the retina. It can do this because it is adjustable, and uses a muscle called the ciliary muscle to change shape and help us focus on objects at different distances. The automatic focusing of the lens is a reflex response and is not controlled by the brain.
Once the image is clearly focused on the sensitive part of the retina, energy in the light that makes up that image creates an electrical signal. Nerve impulses can then carry information about that image to the brain through the optic nerve.
Other parts of the eye include the aqueous humour, a liquid which sits in a chamber behind the cornea, and the vitreous humour, the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina. The sclera is the white part of the eye, forming an outer layer that protects everything inside, while the choroid is the layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. It is made up of layers of blood vessels that nourish the back of the eye.
Defects of vision and their correction
 Similarities
Similarities
Differences
- The bioengineered liquid cornea is a regenerative treatment and this biopolymer acts as a sacrificial matrix for accelerating the growth of host tissue to cover the wound site.
- The trigger for this growth is provided by a bioactive component, the exosomes which are delivered to the wound site, embedded in the biopolymeric matrix.
- These exosomes are derived from the population of predominant cell types in the cornea and are programmed to promote scarless wound healing, to restore vision, the primary function of the cornea and eye.
 Notes on Structure, Function, Defects of Eye
The human eye is the most sensitive and incredible sense organ among all sense organs because with its help we become able to see beautiful and wonderful colors of the world. We can identify the objects around us to some extent by touch, smell, and sound. It is, however, impossible to detect colors while closing the eyes. The structure of the human eye is almost spherical in shape with a diameter of 2.3 cm. The human eye is just like a camera, its lens system also projects the images on a screen called the retina just like a camera.
Notes on Structure, Function, Defects of Eye
The human eye is the most sensitive and incredible sense organ among all sense organs because with its help we become able to see beautiful and wonderful colors of the world. We can identify the objects around us to some extent by touch, smell, and sound. It is, however, impossible to detect colors while closing the eyes. The structure of the human eye is almost spherical in shape with a diameter of 2.3 cm. The human eye is just like a camera, its lens system also projects the images on a screen called the retina just like a camera.
 The human eye is made of three chambers, the first chamber is between cornea and iris which is filled with aqueous humor, the second chamber is between iris and crystalline lens and the third chamber is between the crystalline lens and retina which is filled with vitreous humor. Its two main lenses are the cornea and crystalline lens which refracts light rays and focus to the retina where the inverted image is formed, at the exit of the eye the optic nerve gets the signal of the inverted image, this signal transported to the brain than brain deciphers this inverted image to erected image.
Cornea.
In the structure of the eye, the cornea has a very important role. the cornea is a 5 layered transparent vascular tissue made of collagens and cells, it is the outermost lens of the eye and bulged in shape, light rays, first of all, fall on it and then refracted into the eye. The 65 to 75 % of the total refraction of the light takes place through it.
Aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor is a transparent fluid between cornea and iris and between iris and lens, it is composed of water vitamins, sugars, proteins, and other nutrients. The role of aqueous humor. is to nourish cornea and lense because both of them does not contain blood vessel. The aqueous humor maintains the intraocular pressure of the eye and protects the eye from the dust, pollen grains, wind, and microbes.
Iris.
The colored part of the eye is known as iris, it is located between the cornea and crystalline lens. Iris is made of the dark muscular diaphragm made of connective tissue and muscle covered with pigments responsible for the color of the eye, it surrounds the pupil. Iris controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil.
The pupil is actually the aperture of the eye, It is an opening at the center of the iris and circular in shape, the function of pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina. It appears black color because the light focused on the retina is completely absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back.
Christine lens.
The Christine lens is basically is an eye lens that is transparent and located behind the iris. It is not having blood vessels so it is nourished by aqueous humor that exists between iris and lens. One-third of the total net refraction of light through the eye is taken place by the Christine lens. it is made of small flexible smooth muscles called ciliary muscles, these muscles change the shape of the lens. When we see nearby objects, these muscles constrict and radius of curvature of the lens decreases so that images could be focused on the retina and when we see the far objects these muscles dilate and radius of curvature of lens increases so that images could be focused on the retina, this action of eye is known as accommodation of eye.
Vitreous humor.
Vitreous humour is a jelly-like transparent fluid that contains 99% water and it’s 1% is sugar, vitamins, proteins, hyaluronic acids, and collagens. This fluid pressurizes the retina to remain in its place and gives the spherical shape to the eye.
Retina.
The retina is located at the back end of the eye, it is made of photosensitive cells called photoreceptors, photoreceptors are of two kinds cones and rods. The rods show us images in dim light or when it is dark, cons show us light during the day time or when light is intense, we see colors of the images because of cons.
Optic nerve.
The images formed in the retina is inverted, the signal of the image is conducted through the optic nerve to the visual cortex of the brain, the image is decoded by the brain and then we see the inverted image as an erected image.
Image formation in eye
The human eye is made of three chambers, the first chamber is between cornea and iris which is filled with aqueous humor, the second chamber is between iris and crystalline lens and the third chamber is between the crystalline lens and retina which is filled with vitreous humor. Its two main lenses are the cornea and crystalline lens which refracts light rays and focus to the retina where the inverted image is formed, at the exit of the eye the optic nerve gets the signal of the inverted image, this signal transported to the brain than brain deciphers this inverted image to erected image.
Cornea.
In the structure of the eye, the cornea has a very important role. the cornea is a 5 layered transparent vascular tissue made of collagens and cells, it is the outermost lens of the eye and bulged in shape, light rays, first of all, fall on it and then refracted into the eye. The 65 to 75 % of the total refraction of the light takes place through it.
Aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor is a transparent fluid between cornea and iris and between iris and lens, it is composed of water vitamins, sugars, proteins, and other nutrients. The role of aqueous humor. is to nourish cornea and lense because both of them does not contain blood vessel. The aqueous humor maintains the intraocular pressure of the eye and protects the eye from the dust, pollen grains, wind, and microbes.
Iris.
The colored part of the eye is known as iris, it is located between the cornea and crystalline lens. Iris is made of the dark muscular diaphragm made of connective tissue and muscle covered with pigments responsible for the color of the eye, it surrounds the pupil. Iris controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil.
The pupil is actually the aperture of the eye, It is an opening at the center of the iris and circular in shape, the function of pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina. It appears black color because the light focused on the retina is completely absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back.
Christine lens.
The Christine lens is basically is an eye lens that is transparent and located behind the iris. It is not having blood vessels so it is nourished by aqueous humor that exists between iris and lens. One-third of the total net refraction of light through the eye is taken place by the Christine lens. it is made of small flexible smooth muscles called ciliary muscles, these muscles change the shape of the lens. When we see nearby objects, these muscles constrict and radius of curvature of the lens decreases so that images could be focused on the retina and when we see the far objects these muscles dilate and radius of curvature of lens increases so that images could be focused on the retina, this action of eye is known as accommodation of eye.
Vitreous humor.
Vitreous humour is a jelly-like transparent fluid that contains 99% water and it’s 1% is sugar, vitamins, proteins, hyaluronic acids, and collagens. This fluid pressurizes the retina to remain in its place and gives the spherical shape to the eye.
Retina.
The retina is located at the back end of the eye, it is made of photosensitive cells called photoreceptors, photoreceptors are of two kinds cones and rods. The rods show us images in dim light or when it is dark, cons show us light during the day time or when light is intense, we see colors of the images because of cons.
Optic nerve.
The images formed in the retina is inverted, the signal of the image is conducted through the optic nerve to the visual cortex of the brain, the image is decoded by the brain and then we see the inverted image as an erected image.
Image formation in eye
 The images we see are made up of light reflected from the objects we look at. This light enters the eye through the cornea, which acts like a window at the front of the eye. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the pupil, which is surrounded by the iris – the coloured part of the eye.
Because the front part of the eye is curved, it bends the light, creating an upside down image on the retina. The brain eventually turns the image the right way up.
The retina is a complex part of the eye, and its job is to turn light into signals about images that the brain can understand. Only the very back of it is light sensitive: this part of the retina is roughly the area of a 10p coin, and is packed with photosensitive cells called rods and cones.
Cones are the cells responsible for daylight vision. There are three kinds, each responding to a different wavelength of light: red, green and blue. The cones enable us to see images in colour and detail. Rods are responsible for night vision. They are sensitive to light but not to colour. In darkness, the cones do not function at all.
The lens is a clear disc-like structure that helps to focus light on the retina. It can do this because it is adjustable, and uses a muscle called the ciliary muscle to change shape and help us focus on objects at different distances. The automatic focusing of the lens is a reflex response and is not controlled by the brain.
Once the image is clearly focused on the sensitive part of the retina, energy in the light that makes up that image creates an electrical signal. Nerve impulses can then carry information about that image to the brain through the optic nerve.
Other parts of the eye include the aqueous humour, a liquid which sits in a chamber behind the cornea, and the vitreous humour, the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina. The sclera is the white part of the eye, forming an outer layer that protects everything inside, while the choroid is the layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. It is made up of layers of blood vessels that nourish the back of the eye.
Defects of vision and their correction
The images we see are made up of light reflected from the objects we look at. This light enters the eye through the cornea, which acts like a window at the front of the eye. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the pupil, which is surrounded by the iris – the coloured part of the eye.
Because the front part of the eye is curved, it bends the light, creating an upside down image on the retina. The brain eventually turns the image the right way up.
The retina is a complex part of the eye, and its job is to turn light into signals about images that the brain can understand. Only the very back of it is light sensitive: this part of the retina is roughly the area of a 10p coin, and is packed with photosensitive cells called rods and cones.
Cones are the cells responsible for daylight vision. There are three kinds, each responding to a different wavelength of light: red, green and blue. The cones enable us to see images in colour and detail. Rods are responsible for night vision. They are sensitive to light but not to colour. In darkness, the cones do not function at all.
The lens is a clear disc-like structure that helps to focus light on the retina. It can do this because it is adjustable, and uses a muscle called the ciliary muscle to change shape and help us focus on objects at different distances. The automatic focusing of the lens is a reflex response and is not controlled by the brain.
Once the image is clearly focused on the sensitive part of the retina, energy in the light that makes up that image creates an electrical signal. Nerve impulses can then carry information about that image to the brain through the optic nerve.
Other parts of the eye include the aqueous humour, a liquid which sits in a chamber behind the cornea, and the vitreous humour, the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina. The sclera is the white part of the eye, forming an outer layer that protects everything inside, while the choroid is the layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. It is made up of layers of blood vessels that nourish the back of the eye.
Defects of vision and their correction
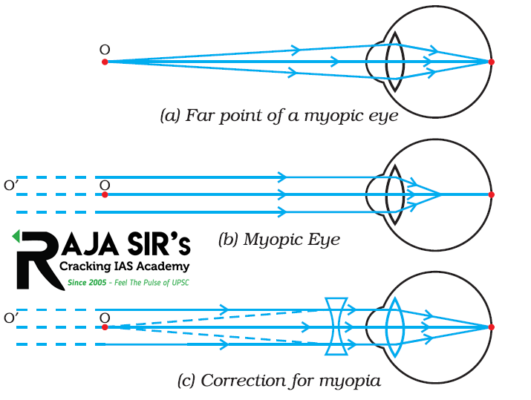
- Myopia: It is also known as nearsightedness. A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly. It’s far point is nearer than infinity. Image is formed before retina in a myopic eye. It can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power.

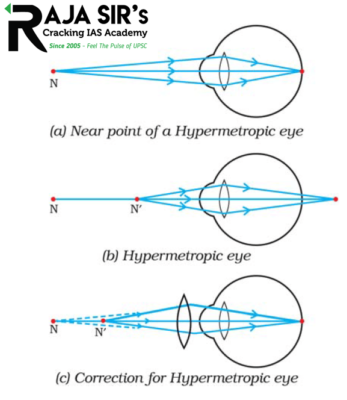
- Hypermetropia: It is also known as far-sightedness. A person with this can see distant objects clearly but cannot see nearby objects distinctly. It’s near point more than 25 cm. Image is formed behind retina in this case. It can be corrected by using a convex lens of suitable power.

- Some other defects and their correction measure are given on here:
-
Defect Symptoms Correction Presbyopia difficult to see Nearby as well as far away objects comfortably without corrective eye-glasses bi-focal lenses consisting of both concave and convex lenses Cataract crystalline lens becomes milky and cloudy; partial or complete loss of vision Cataract Surgery
 Similarities
Similarities
| Human Eye | Camera |
| 1. Light enters the eye through the pupil. | 1. Light also enters the camera through the aperture. |
| 2. The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye. | 2. The amount of light is also regulated in-camera with the diaphragm. |
| 3. Focus light and image on the retina in the eye. | 3. Focus light and image on film in the camera. |
| 4. The eye contains a lens. | 4. camera also contains a lens. |
| 5. There is a choroid that absorbs light and limits reflection in the eye. | 5. There is also black paint in the camera which absorbs lights and limits reflections. |
| Human Eye | Camera |
| 1. Focal length of the human eye lens can be changed. | 1. Focal length of the camera lens is fixed. |
| 2. Retina retains the impression of an image for only 1/16th of seconds. | 2. Photographic film of camera retains the image permanently. |
| 3. The Same retina can be used for viewing unlimited images. | 3. A photograph has to be changed for getting the next image. |
| 4. Image is formed on the retina which is further processed in the brain. | 4. Image is formed on the photographic film and processing can be done through computer. |









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies