- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
What is Lithium?
Lithium is an alkali mineral, also called ‘white gold’. It is soft, silvery-white metal, the lightest metal of the periodic table.
- Major Properties:
- High Reactivity
- Low Density
- Excellent Electrochemical Properties
- Occurrence and Top Producers:
- Lithium is found naturally in various minerals, including spodumene, petalite, and lepidolite.
- It is extracted from these minerals and refined into lithium metal or its compounds.
- The top producers of lithium are Australia, Chile, China, and Argentina.
- In 2022, Australiawas the world leader in terms of lithium mine production. Chile and China ranked second and third.
- Recently, a massive lithium deposit beneath California’s Salton Sea (US),holding an estimated 18 million tons of lithium, was discovered.
- Lithium is found naturally in various minerals, including spodumene, petalite, and lepidolite.
Properties of Lithium
- It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal.
- Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil.
- When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish.
- It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds.
- Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines.
- Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride.
- Lithium takes an active part in many reactions with organic and inorganic reactants. It reacts with oxygen to form monoxide and peroxide.
- Metallic Lithium reacts extremely vigorously with water.
- It has high specific heat which is the calorific capacity.
- It has very low density and low viscosity.
- Lithium is found only in salts and minerals.
- The alkali metalsconsist of the chemical elements lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, caesium, and francium. Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table.
- Rare Metals(RM) include Niobium (Nb), Tantalum (Ta), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Cesium (Cs) etc. and Rare Earths (RE) include Lanthanum (La) to Lutetium (Lu) besides Scandium (Sc) and Yttrium (Y). These metals are strategic in nature with wide application in the nuclear and other high tech industriessuch as electronics, telecommunication, information technology, space, defense etc.
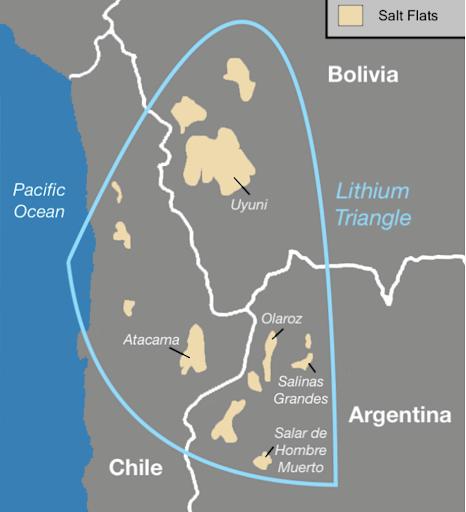
Lithium triangle made up of Argentina, Chile, and Bolivia—contain roughly half the world''s known lithium.
- Applications:
- Batteries:Lithium is a crucial component of rechargeable batteries used in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and other electronics.
- Glass and Ceramics:Lithium compounds are used to strengthen glass and ceramics, making them more durable and heat-resistant.
- Medicine:Lithium is used as a mood stabilizer in the treatment of bipolar disorder.
- Lubricants:Lithium greases are used in high-pressure and high-temperature
- Lithium in India:
- 2023 saw a surge in lithium discoveries:
- Massive reserves unearthed in Salal-Haimna areas of Reasi district of Jammu and Kashmir(estimated 5.9 million tonnes).
- Additional reserves identified in Koderma and Giridih regions of
- However, India has put up lithium blocks for auction:one in J&K and another in Chhattisgarh, with most of its domestic requirements, across categories like EVs, lithium-ion battery making, and other energy storage solutions, being met completely through imports. Import bill is pegged at around ₹24,000 crore.
- 2023 saw a surge in lithium discoveries:









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies