- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Daily Current Affairs | 27th June 2020
Reducing Import Dependence: India Finalizing List Of Countries to Replace China In Supplying Critical Components
The government is working on a list of alternative countries that could be suppliers of critical components that cannot currently be manufactured domestically. DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade) is working with the industry to line up a list of low-quality imports from China. The next step is to substitute them, internally or externally. The engagement looks to firm up tariff and non-tariff measures to curb imports of raw, intermediary and finished products from China.
 Note
Note
 India’s forex reserves drop for the first time after hitting life-time high, now $505.566 billion
India’s foreign exchange reserves retreated from a life-time high to touch USD 505.566 billion in the week ended June 19, down by USD 2.078 billion from the previous week. The forex reserves declined for the first time since April 24 when the assets dropped by USD 113 million to USD 479.455 billion. Between April 24 and June 12, forex reserves had grown by USD 28.189 billion. In the week ended June 12, the reserves had increased by USD 5.942 billion to touch a record high of USD 507.644 billion.
India’s forex reserves drop for the first time after hitting life-time high, now $505.566 billion
India’s foreign exchange reserves retreated from a life-time high to touch USD 505.566 billion in the week ended June 19, down by USD 2.078 billion from the previous week. The forex reserves declined for the first time since April 24 when the assets dropped by USD 113 million to USD 479.455 billion. Between April 24 and June 12, forex reserves had grown by USD 28.189 billion. In the week ended June 12, the reserves had increased by USD 5.942 billion to touch a record high of USD 507.644 billion.
- Once DPIIT is ready with the list, the government will reach out to countries and work out ways to incentivise supply to the Indian market, even as it tries to encourage domestic manufacturing of the goods, officials said.
- The move is a part of a large exercise undertaken by the government to relook the Free Trade Agreements to ensure cheap Chinese products do not flood the Indian market, establish stringent quality controls that would disqualify a host of Chinese imports, and incentivise producers to relocate production to India — boosting manufacturing and exports under likes of the production-linked incentive scheme.
- The government is cognisant of the fact that dependence on China cannot go away overnight…There is an overall focus on a calibrated effort to discourage imports from that country, by sourcing them from other destinations, even as India tries to ramp up its manufacturing abilities.
- The official added that Southeast Asian countries, along with Japan and South Korea, have emerged as possible destinations, but the comparative price factor vis-à-vis India remains a concern.
- For non-critical sectors like textiles, electronics, we should look for new sources in Southeast Asia as there is not much difference in respect to labour cost arbitrage.
- At the same time, we should take more and more sector-specific measures to make our small and medium enterprises produce them in a competitive manner.
 Note
Note
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade was established in 1995 and has been reconstituted in the year 2000 with the merger of the Department of Industrial Development.
- Earlier separate Ministries for Small Scale Industries & Agro and Rural Industries (SSI&A&RI) and Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises (HI&PE) were created in October, 1999.
- With progressive liberalisation of the Indian economy, initiated in July 1991, there has been a consistent shift in the role and functions of this Department.
- From regulation and administration of the industrial sector, the role of the Department has been transformed into facilitating investment and technology flows and monitoring industrial development in the liberalised environment.
- The campaign is intensely focused towards providing employment and promoting local entrepreneurship.
- In Uttar Pradesh, nearly 30 lakh migrant workers returned to their native districts following the loss of livelihood in metropolis due to Covid-19 lockdown.
- The initiative is focussed on generating employment opportunities in 31 districts of the state which have reported more than 25,000 returnee migrant workers.
- The combined population of France, Italy, Spain and the UK is equal to Uttar Pradesh's population. More than one lakh people have died in these countries but in UP only 600 died due to Covid-19.
- About 60 lakh people are being given employment in small industries i.e. MSMEs in schemes related to village development. In addition to this, a loan of about 10 thousand crore rupees has been allocated to thousands of entrepreneurs under the Mudra Yojana for self-employment.
- As part of the Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiative, 5,000 workers will be distributed tool-kits. These workers consist of ironsmiths, tailors, hairdressers, carpet weavers, soap makers, tanners and textile workers among others.
- The accord represents the largest power sector investment by an independent power producer (IPP) under Beijing's multi-billion dollars' worth China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), including the Gwadar Master Plan.
- The prime minister said the government had resolved to focus on a "green and clean power generation" through hydroelectricity in order to reduce dependence on imported fuel.
- The government welcomed the investment as it could set a precedent for the country to move towards sources of clean energy.
- The project, a part of CPEC, has been awarded to Kohala Hydropower Company (KHCL), which is a subsidiary of China's Three Gorges Corporation (CTGC).
- The country was making good progress when it was producing hydropower, but then it started banking on imported fuel. This made not only the local industry non-competitive, but also put an additional burden on foreign reserves.
- Electricity generation through imported fuel, had adversely affected the environment as Pakistan was placed by experts on a list of nine states most likely to be badly affected by climate change.
- The CPEC is a flagship infrastructure-related project conceived by Chinese President Xi Jinping as part of Beijing's expanded multi-billion dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) that aims to create more efficient commercial links between the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe. Bajwa is also the chairman of the CPEC authority.
- Since last year, the work on the CPEC-funded Kohala Hydropower Project has been in jeopardy as the Chinese contractor was demobilised following a controversy over downstream environmental flows.
- The 1,124MW (megawatt) Kohala Hydropower Project, is being built on the Jhelum River in PoK under CPEC. It has been awarded to the Kohala Hydropower Company Ltd (KHCL), a subsidiary of China Three Gorges Corporation (CTGC).
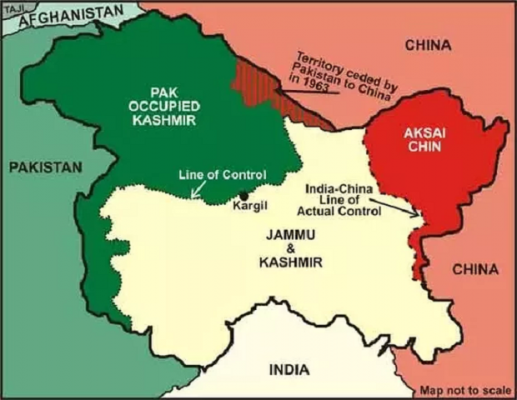
- The signing of the Hydel project comes at a time when India and China have been involved in high-level military talks to disengage following the Galwan Valley incident in the Ladakh region, where 20 Indian soldiers were killed on June 15 in a violent clash with the Chinese Army.
 India’s forex reserves drop for the first time after hitting life-time high, now $505.566 billion
India’s foreign exchange reserves retreated from a life-time high to touch USD 505.566 billion in the week ended June 19, down by USD 2.078 billion from the previous week. The forex reserves declined for the first time since April 24 when the assets dropped by USD 113 million to USD 479.455 billion. Between April 24 and June 12, forex reserves had grown by USD 28.189 billion. In the week ended June 12, the reserves had increased by USD 5.942 billion to touch a record high of USD 507.644 billion.
India’s forex reserves drop for the first time after hitting life-time high, now $505.566 billion
India’s foreign exchange reserves retreated from a life-time high to touch USD 505.566 billion in the week ended June 19, down by USD 2.078 billion from the previous week. The forex reserves declined for the first time since April 24 when the assets dropped by USD 113 million to USD 479.455 billion. Between April 24 and June 12, forex reserves had grown by USD 28.189 billion. In the week ended June 12, the reserves had increased by USD 5.942 billion to touch a record high of USD 507.644 billion.
- The reserves had crossed the half-a-trillion mark for the first timein the week ended June 5 after surging by a massive USD 8.223 billion and reached USD 501.703 billion.
- In the week ended June 19, the reserves had declined due to the fall in foreign currency assets (FCA), which is a major component of the overall reserves.
- FCA decreased by USD 1.698 billion to USD 467.039 billion in the reporting week, the RBI data showed.
- Expressed in dollar terms, the foreign currency assets include the effect of appreciation or depreciation of non-US units like the euro, pound and yen held in the foreign exchange reserves. Gold reserves in the reporting week dipped by USD 358 million to USD 32.815 billion.
- The special drawing rights with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) were reduced by USD 6 million to USD 1.447 billion.
- The country’s reserve position with the IMF also reduced by USD 16 million to USD 4.264 billion during the reporting week, the data showed.
- Forex reserves are external assets in the form gold, SDRs (special drawing rights of the IMF) and foreign currency assets (capital inflows to the capital markets, FDI and external commercial borrowings) accumulated by India and controlled by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The International Monetary Fund says official foreign exchange reserves are held in support of a range of objectives like supporting and maintaining confidence in the policies for monetary and exchange rate management including the capacity to intervene in support of the national or union currency.
- It will also limit external vulnerability by maintaining foreign currency liquidity to absorb shocks during times of crisis or when access to borrowing is curtailed.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies