- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Dec 16, 2021
CABINET CLEARS BILL ON ELECTORAL REFORMS, ALLOWING VOLUNTARY AADHAAR-VOTER ID LINKING
The Union Cabinet cleared proposed amendments to electoral law to link Aadhaar to voter ID.




 Laser Weapons:
Laser Weapons:


 Recently, a team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Kanpur has created a portable app-linked soil testing device named Bhu parikshak.
Recently, a team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Kanpur has created a portable app-linked soil testing device named Bhu parikshak.
- Aadhaar- voter id linkage will help to work towards secure electronic voting for migrant workers.

- It will amend the representation of people act and allow four qualifying dates in a year rather than one, for those who are above 18 years, to register as a voter.
- Bill proposes to make gender-neutral provision allowing only the wife of male service voter to register as voter in same constituency.
- Seeks to empower the EC to requisition premises for any purpose related to election.
- Bill proposes to amend representation of people act to empower electoral officer to seek aadhar number of existing as well as new voter, only on voluntary basis.
- It would be detrimental to our privacy and democratic right to vote.
- There might be a possibility of disenfranchisement caused by the linking of Aadhaar and voter IDs.
- In 2018, at least 55 lakh voters found they had been arbitrarily deleted from the voter database.
- Proposal of voluntary use of Aadhaar unlikely to clear Proportionality test.
- Proportionality test:
- The action must be sanctioned by law;
- The proposed action must be necessary in a democratic society for a legitimate aim;
- The extent of such interference must be proportionate to the need for such interference;
- There must be procedural guarantees against abuse of such interference.

- Article 19 (1)(a) lays down that all citizens shall have the right to freedom of speech and expression
- Article 19 (1)(b) gives the right to assemble peaceably and without arms.
- Article 19(1)(c) affirms the citizens’ right to form associations or unions.
- Article 25 of the Constitution maintains that all persons are equally entitled to freedom of conscience and the right freely to profess, practice and propagate religion, subject to public order, morality and health.
- Article 26 entitles every religious denomination to manage its own affairs in matters of religion but this right is also subject to public order, morality and health.
- All public streets and roads vest in the State, but that the State holds them as trustees on behalf of the public.
- The State as trustees on behalf of the public is entitled to impose all such limitations on the character and extent of the user, as may be requisite for protecting the rights of the public generally.
- The Supreme Court stated that the citizens have freedom of speech, freedom to assemble peaceably and freedom to form associations or unions does not mean that they can exercise those freedoms in whatever place they please.
- Constitution bench ruled that the right that flows from Article 19(1) is not a right to hold a meeting at any place, at any time.
- Footpaths or pavements are public properties which are intended to serve the convenience of the general public.
- They are not laid for private use and indeed their use for a private purpose frustrates the very object for which they are carved out from portions of public streets
- A mosque is not an essential part of the practice of the religion of Islam and namaz by Muslims can be offered anywhere, even in the open.
- It ruled that the power of acquisition is available to the State for a mosque like any other place of worship of any religion.
- At the same time, the court said that the right to worship, guaranteed under Article 25 of the Constitution of India, does not extend to the right of worship at “any and every place.
- Aim: Encouraging people to adopt digital modes of payment.

- Under this, the government will incentivise the acquiring banks by paying a percentage of the value of transactions through RuPay and BHIM-UP.
- The incentive is only for person-to-merchant transactions and not P2P ones that also use the UPI route.
- Government will invest1,300 crores, encouraging citizens to move towards digital fold through BHIM-UPI and RuPay Debit cards.
- It will help make accessible digital modes of payments to unbanked and marginalised populations outside formal banking and financial system.
- It will further spur research and development and innovation in the fintech space.
- It will facilitate acquiring banks to build a robust digital payment ecosystem and promote RuPay Debit card and BHIM-UPI digital transactions.
- India is one of the most efficient payments markets in the world.
- It saw a record number of digital transactions at 423 crore valued at 7.56 lakh crore.
- RuPay is a brand of National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) under which it operates the card scheme.
- NPCI is a body promoted by RBI and has presently ten core promoter banks like State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, Canara Bank, Bank of Baroda, Union bank of India etc.
- Aim: To provide payment services to citizens anytime, anywhere which are simple, easy to use, safe, and also cost effective.
- No separate registration required.
- User Friendly: Simplified transaction flow, effortless authentication process.
- Enhanced User Interface: Single-screen checkout
- Faster Transaction Processing: The cardholder has to enter just the card details and a One Time Password (OTP) to complete the transaction.
- Since the transaction processing will happen domestically, it would lead to lower cost of clearing and settlement for each transaction.
- This will make the transaction cost affordable and will drive usage of cards in the industry.
- RuPay, scheme is committed towards development of customized product and service offerings for Indian consumers.
- Transaction and customer data related to RuPay card transactions will reside within the domestic territory of India.
- Consumers in rural areas do not have access to banking and financial services.
- Right pricing of RuPay products would make the cards more economically feasible for banks to offer to their customers.
- Product variants would ensure that banks can target the hitherto untapped consumer segments.
- Outlay of Rs. 93,068 crores, including Rs.37,454 crore central assistance to states would be given.
- Benefits to about 22 lakh farmers.

- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Launched-2015
- Implementing Agency- Ministries of Agriculture, Water Resources, and Rural Development
- Aim-
- To provide assured irrigation to cultivated areas.
- To reduce wastage of water and improve water-use efficiency.
- To achieve convergence of investments in irrigation at the field level.
- Expand the cultivable area under assured irrigation.
- Improve on-farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage of water.
- Enhance the adoption of precision-irrigation and other water saving technologies (More crop per drop)
- Enhance the recharge of aquifers and introduce sustainable water conservation practices by exploring the feasibility of reusing treated municipal wastewater for peri-urban agriculture
- Ensure the integrated development of rainfed areas using the watershed approach towards the soil and water conservation, regeneration of groundwater, arresting runoff etc.
- Promote extension activities relating to water harvesting, water management, and crop alignment for farmers and grass root level field functionaries.
- Implementation: Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Aim- It provides financial support to irrigation projects.
- Features-
- Irrigation potential creation targeted is 13.88 lakh hectare.
- Tribal and drought prone areas have been relaxed.
- Implementation: Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Objectives-
- Creating and rejuvenating traditional water storage systems.
- Improvement in water management and distribution system for water bodies.
- Aim-To enhance physical access on the farm and expansion of cultivable area.
- Features-
- Enhancement of central assistance from 25% to 60% in general area.
- 52 lakh hectare in ground water irrigation under suitable block.
- 5 lakh hectare irrigation through surface minor irrigation and rejuvenation of water bodies.
- Sub-Components-
- Command Area Development (CAD)
- Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI)
- Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies
- Ground Water Development
- Implementation: Department of Land Resources, Ministry of Rural Development
- Aim- To regenerate ground water.
- Features-
- It focuses on development of rainfed areas towards soil and water conservation.
- It promotes extension activities related to water harvesting and management.
- To envisage completion of sanctioned projects covering 49.5 lakh hectare rainfed/ degraded lands.
- Development of spring sheds has been included.
- Implementation: Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
- Objectives-
- Promoting efficient water conveyance and precision water application devices.
- Construction of micro irrigation
- Extension activities for promotion of scientific moisture conservation and agronomic measures.
- Black money includes all funds earned through illegal activity and otherwise legal income that is not recorded for tax purposes.
- Black money proceeds are usually received in cash from underground economic activity and, as such, are not taxed.
- Recipients of black money hide it, spend it only in the underground economy, or attempt to give it the appearance of legitimacy through money laundering.
- Within similar products, there are different rates of excise duty.
- This leads to tax evasion through misclassification of output.
- In selecting commodities for control and in determining their prices, the government fails to take into account the elasticity involved in demand and supply.
- This leads to black money in the economy.
- The import quota, the export quota and the foreign exchange quota are generally misused by selling them at a premium.
- Unrealistic controls spawn a culture which encourage corporate to break the tax laws.
- Black money is also caused by scarcity and defective public distribution system.
- When essential goods become scarce, people have to pay higher than the controlled price, which generates black money.
- The increase in prices of commodities due to high increase in duties and taxes imposed by the government, diverting resources from production to speculation—all this cause inflation which in turn creates black money.
- Money laundering is the illegal process of making large amounts of money generated by a criminal activity, appear to have come from a legitimate source.
- The process of laundering money typically involves three steps: placement, layering, and integration.
- Placement surreptitiously injects the “dirty money” into the legitimate financial system.
- Layering conceals the source of the money through a series of transactions and bookkeeping tricks.
- In the final step, integration, the now-laundered money is withdrawn from the legitimate account to be used for whatever purposes the criminals have in mind for it.
- It is a money-laundering technique involving the structuring of large amounts of cash into multiple small transactions.
- Smurfs often spread these small transactions over many different accounts, to keep them under regulatory reporting limits and avoid detection.
- This involves physically smuggling banknotes to another jurisdiction and depositing them in a financial institution, such as an offshore bank, with greater bank secrecy or less severe money laundering enforcement.
- Cash-intensive businesses that typically receive a substantial proportion of its revenue as cash are set up.
- Then, business accounts are used to deposit black money.
- Such businesses operate openly and generate cash revenue from legitimate businesses in addition to the illicit cash.
- It involves the movement of luxury and mobile commodities such as diamonds, gems and gold that can be moved to other jurisdictions in an easy manner.
- This method involves under- or over-valuing invoices to disguise the movement of money.
- Trusts and shell companies disguise the true owners of money.
- Trusts and corporate vehicles need not disclose their true owner or beneficial owner in many jurisdictions.
- Shell companies do not have any active business operations but have a legal personality.
- In this method, black money is deposited in the accounts of a controlled foreign corporation offshore, preferably in a tax haven country where anti-money laundering (AML) checks are minimal.
- The money is then shipped back as a foreign direct investment, often exempt from taxation.
- Black money eats up a part of the tax and, thus, the government’s deficit increases.
- The government has to balance this deficit by increasing taxes, decreasing subsidies and increasing borrowings.
- Borrowing leads to a further increase in the government’s debt due to interest burden.
- If the government is unable to balance the deficit, it has to decrease spending, which affects development.
- Money Circulation– People generally tend to keep black money in the form of gold, immovable property and other secret manners.
- Such money does not become part of the main economy and, therefore, remains generally out of circulation.
- The black money keeps circulating among the wealthy and creates more opportunities for them.
- The infusion of unaccounted black money in the economy leads to higher inflation, which obviously hits the poor the most.
- It also increases the disparity between the rich and the poor.
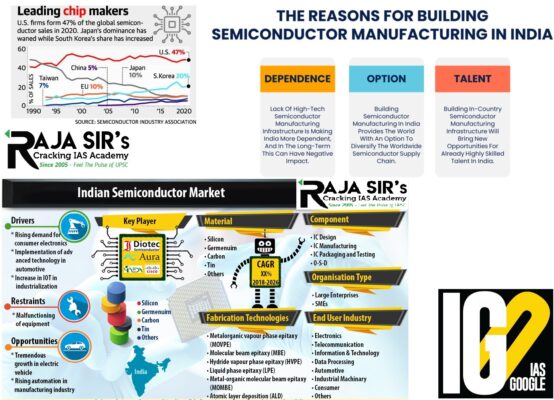
- It also approved a comprehensive programme for the development of sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
- Aim: To make India a global hub of electronic system design and manufacturing.
- It provides a globally competitive incentive package to companies in semiconductors and display manufacturing as well as design.
- It will extend fiscal support of up to 50% to set up fabrication units.
- It will include design, fabrication, packaging, testing.
- The Centre would work with the States to set up high-tech clusters with the necessary infrastructure.
- A specialised and independent ‘India Semiconductor Mission’ will be set up.
- It will be led by global experts in semiconductor and display industry.
- Aim: To develop a sustainable semiconductors and display ecosystem.
- It will act as the nodal agency for efficient and smooth implementation of the schemes on semiconductors and display ecosystem.
- The ministry of electronics and IT will take requisite steps for modernization and commercialization of semiconductor laboratory (SCL)
- The IT ministry will explore the possibility for the joint venture of SCL with a commercial fab partner.
- The government has lined up incentive support for companies engaged in silicon semiconductor fabs, display fabs, compound semiconductors, silicon photonics, sensors fabs, and semiconductor packaging and semiconductor design.
- Trusted semiconductor sources and displays have strategic importance in the current geopolitical scenario.
- They are the key to the security of critical information infrastructure.
- It will propel innovation and build domestic capacities to ensure the digital sovereignty of India.
- It will also create highly skilled employment opportunities to harness the demographic dividend of the country
- Semiconductors are silicon chips that cater to control and memory functions.
- They are used in products ranging from automobiles, cellphones and computers to other electronic devices.
- It is a concept based on a single exchange launching contracts of a specific commodity derivative.
- Aim: To help every exchange develop an exclusive set of unfragmented liquid contracts on specific commodities.
- The concept is applicable only for narrow agri-commodities which do not fall into the sensitive and broad category.
- Spices such as coriander or jeera, are examples of narrow agri-commodities.
- Here, production is concentrated in a specific region but has high volatility.
- Non-agri commodities should not fall under the purview.
- The agricultural commodities have been classified into three categories: sensitive, broad and narrow.
- A single exchange launching contracts on a specific commodity may have bigger impact locally as well as internationally.
- The multiple exchanges in India, competing contracts on the same commodity, resulted in the fragmentation of trading volumes.
- It will ensure that the concerned exchange develops all kinds of derivative contracts on a specific commodity exclusively.
- It brings about comprehensive development and deepening of the Indian commodity derivatives markets.
- The focus will be more in adequate warehousing and storage, transport, communication technologies and setting standards for that particular commodity.
- It will eventually help India to be in a position to influence the global benchmark pricing of such commodities.
- Though India is one of the largest consumers or producers of a number of commodities, it had negligible say in setting commodity prices in such products.
- It may provide a new impetus for stock exchanges to develop a market in their chosen commodities for the benefit of the stakeholders.
- Earlier, they were chasing the same set of stakeholders of a particular commodity.
- It may curb the practice of stock exchanges that merely copy products launched by other stock exchanges.
- The focus will now be on building up new demand, rather than shifting demands.
- It may create artificial barriers at the cost of other markets and value chain participants.
- This may result in increased overall costs, including trading, compliance and technology.
- Exchanges may not always meaningfully develop the products blocked by them.
- An exchange may lose interest, after an initial production.
- It may decide not to invest further in that product and block other exchanges from launching that contract.
- Allowing only one exchange to offer products in a commodity for 3-5 years may go against market development.
- It may result in failure of the exchange in building liquidity.
 Laser Weapons:
Laser Weapons:
- Laser term stands for
- Light Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
- It is very intense beam of light or infrared radiation.
- Laser weapon are a weapon that uses a high-power laser beam rather than a missile to destroy a target.
- Aim-to achieve a military advantage during armed conflict.
- Features-
- Laser weapons are large and heavy.
- It requires enormous amounts of power.
- The advertised cost per shot is low.
- It is also called a directed energy weapon.
- The transmission at the speed of light allows laser-based weapons to engage distant targets immediately after detection.
- The directed laser energy provides less collateral damage.
- It is low-profile and covert operations capabilities.
- Laser weapons can disable a vehicle from miles away without killing anyone.
- It has speed which also helps with accuracy.
- It has a near-perfectly straight trajectory.
- Power consumption is too high.
- Large systems will need large-sized generators, which will limit the mobility of the artillery systems.
- High accuracy only when firing direct fire, which dramatically reduces the effectiveness of the application on land.
- It can cause permanent blindness or diminish vision.
- Issued by- the United Nations in 1995
- Article 1: It is prohibited to employ laser weapons as it causes permanent blindness to unenhanced vision, that is to the naked eye or to the eye with corrective eyesight devices.
- The High Contracting Parties shall not transfer such weapons to any State or non-State entity.
- Article 2: The High Contracting Parties shall take all feasible precautions to avoid the incidence of permanent blindness to unenhanced vision.
- Precautions shall include training of their armed forces.
- Article 3: Blinding as an incidental or collateral effect of the legitimate military employment of laser systems is not covered by the prohibition of this Protocol.
- Article 4: For the purpose of this protocol "permanent blindness" means irreversible and uncorrectable loss of vision which is seriously disabling with no prospect of recovery.
- It is an annual Hindu festival originating in the Indian subcontinent.
- Durga Puja is celebrated predominantly by the Bengali community.
- In this, homage to the Hindu goddess Durga is paid.

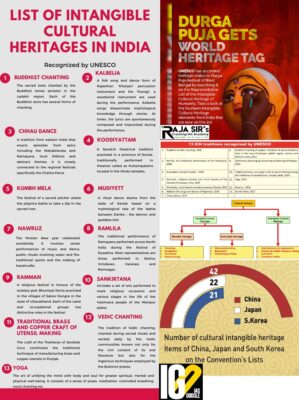
- UNESCO’s List of Intangible Cultural Heritage is published by the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
- The members of committee are elected by State Parties meeting in a General Assembly.
- Aim: Ensuring better protection of important intangible cultural heritages worldwide and the awareness of their significance.
- Following UNESCO’s 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage, the list has been classified into five broad domains in which intangible cultural heritage is manifested:
- Oral traditions and expressions, including language as a vehicle of the intangible cultural heritage.
- Performing arts
- Social practices, rituals and festive events
- Knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe
- Traditional craftsmanship
- A tradition of Vedic chanting
- Ramlila, the traditional performance of the Ramayana
- Kutiyattam, Sanskrit theatre
- Ramman, religious festival and ritual theatre of the Garhwal Himalayas.
- Mudiyettu, ritual theatre and dance drama of Kerala
- Kalbelia folk songs and dances of Rajasthan
- Chhau dance
- Buddhist chanting of Ladakh: recitation of sacred Buddhist texts in the trans-Himalayan Ladakh region, Jammu and Kashmir.
- Sankirtana, ritual singing, drumming and dancing of Manipur
- Traditional brass and copper craft of utensil making among the Thatheras of Jandiala Guru, Punjab
- Yoga
- Nawrouz
- Kumbh Mela

- Developed by: Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE), Bengaluru with Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd and the Bharat Electronics Limited.
- It has advanced capabilities and meets the requirements of the armed forces
- It will carry out surveillance and reconnaissance roles and is capable of carrying different combinations of advanced payload with auto landing.
- It technologically matches contemporary UAVs available and will be cheaper than the imported ones.
- Rustom is a Medium Altitude Long Endurance unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) developed by DRDO for the Defence Forces.
- It will replace/supplement the Heron UAVs in service with the Indian armed forces.
- Aerodynamic configurations, composite airframe integrated with propulsion system.
- Highly reliable systems with built-in redundancy for flight critical systems like flight control and navigation, data links, power management etc.
- Digital flight control and navigation system.
- Digital communication technologies to control and operate various missions
- Payloads with high resolution and precision stabilized platforms.
- Rustom-I: Tactical UAV with endurance of 12 hours.
- Rustom-H: Larger UAV with flight endurance of over 24 hours, higher range and service ceiling than Rustom-1.
- Rustom-II: An unmanned combat air vehicle based on Rustom-H model.
- It is an internet-based platform.

- The system consists of a Ground Control Station (GCS), an RPAS, and VIHANGAM portal.
- It has been deployed at two opencast mines of MCL namely Bhubaneswari and Lingaraj initially on trial basis.
- The system enables real-time transmission of aerial video of mining activities from mines to internet platform which can be accessed through VIHANGAM portal.
 Recently, a team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Kanpur has created a portable app-linked soil testing device named Bhu parikshak.
Recently, a team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Kanpur has created a portable app-linked soil testing device named Bhu parikshak.
- The app can detect soil quality in just 90 seconds.
- It is a first-of-its-kind invention based on infrared spectroscopy technology, which provides soil analysis reports on a smartphone.
- The device can detect six important soil parameters namely -Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Organic Carbon, Clay contents and Cation Exchange Capacity.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies