- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Explain the mechanism and occurrence of cloudburst in the context of the Indian subcontinent. Discuss two recent examples. (UPSC CSE Mains 2022 - General Studies Paper 3)
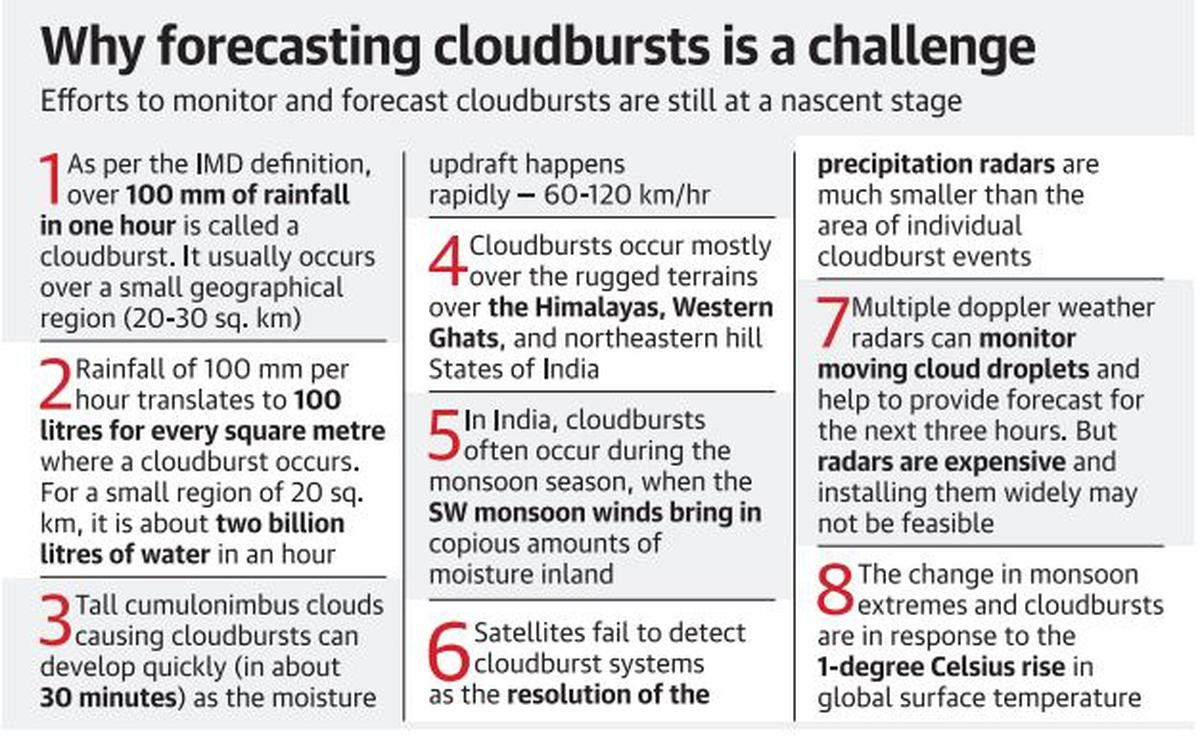
A cloudburst refers to an extreme amount of rain that happens in a short period, sometimes accompanied by hail and thunder. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) defines it as unexpected precipitation exceeding 100mm (or 10 cm) per hour over a geographical region of approximately 20 to 30 square km. All instances of cloudbursts involve heavy rain in a short period, but all instances of heavy rain in a short period are not cloudbursts if they do not fit this criterion.
Reasons behind Cloudburst:
- It is difficult to predict when exactly a cloudburst will occur. However, they are more likely to occur in mountainous zones mainly because of terrain and elevation.
- Cloudburstsare mostly caused by an excessive amount of condensation in the clouds during a thunderstorm. During a thunderstorm, the warm air currents pull the falling drops of water upwards creating an excess accumulation of water in the clouds. If it reaches a point where the upward air current is weakened, it results in sudden precipitation and downpour of all the accumulated water, in a short time causing floods in the surrounding areas.
Impacts of Cloudburst:
- Flooding: A cloudburst can have a devastating impact triggering flash floods. These floods can cause uprooting of trees and movement of boulders and other debris.
- Damage to infrastructure: Cloudbursts can also damage houses, roads, loss of bridges because of the sheer force in which the downpour occurs.
- Landslides: Sudden heavy rain caused by cloudburstsin hilly and mountainous areas can trigger landslides.
- Another effect of cloudbursts is the damage they can cause to trees, plants, and crops, loss of arable land, livestock.
Recent Examples
- Over 20 people have been killed in destruction caused by cloudbursts and flash floods in different parts of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand over the last three days. Isolated areas in these two states have reported heavy rainfall during this time, triggering landslides and flash floods that have disrupted rail and road traffic, and resulted in house and wall collapses. (July 2022)
Measures to prevent and reduce the devastating impacts of cloudbursts:
- Regulation of construction activities along river banks with special consideration to water level during heavy rainfall.
- Strengthening of embankments, barrages and dams to constrain & regulate water flow.
- Localized planning taking into consideration the ecologically fragile nature of the region and involving the local communities’
- Regulate infrastructure projects and preserve the sanctity of eco-sensitive zones.
- Better forecasting by IMD and incorporation of advanced technology to monitor and predict extreme weather events can enable early warning, evacuation and preparedness
- Adoption of ecofriendly policies and eco-sensitive tourism for development of the region.
- Incorporation of disaster management and prevention into the developmental planning process.
Utilization and leverage of local knowledge, resources, can have a multiplier effect on mitigation. Participation of local bodies such as NGOs, Gram Sabhas, Panchayats can strengthen the entire framework of disaster management.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies