- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 Latest News
Latest News
Metaverse and AI - Future perfect or imperfect
The metaverse is a virtual world where people interact using avatars, usually in 3D. It''s a digital universe that combines physical and digital reality, and is expected to be the next evolution of social connection.
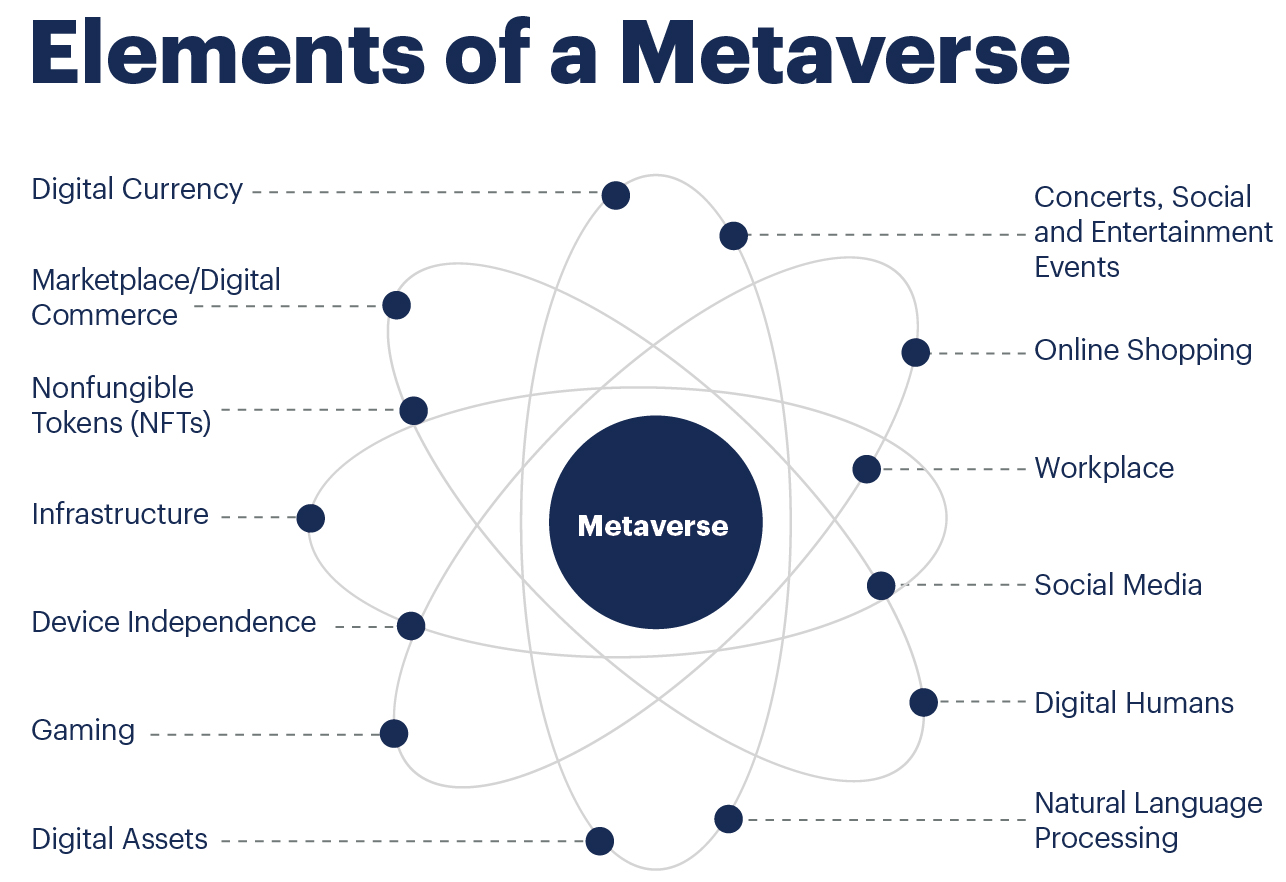 Metaverse can
Metaverse can
- Socialize: Meet friends and family, or build virtual communities
- Work: Collaborate with others in virtual offices
- Learn: Participate in activities and attend events
- Play: Dive into gaming worlds, sports, and multiplayer contests
- Shop: Interact with content created by others
- Experience films: Watch films in a new way, or catch live events from anywhere in the world
As the Metaverse continues to gain popularity, it is important to consider the challenges posed by the rise of this technology and AI. The following are some of the major challenges posed by them are as follows:
- Societal and Economic impacts:
- AI and the Metaverse have the potential to disrupt traditional industries and change the way people work and interact, which could lead to job loss and income inequality.
- Ethical concerns:
- AI systems and the Metaverse raise questions about bias, transparency, and accountability. There is also a risk that these technologies could be used to perpetuate or amplify societal problems such as discrimination and inequality.
- Dependence on technology:
- As people increasingly rely on AI and the Metaverse for daily activities, there is a risk of people becoming too dependent on technology, which could lead to a loss of important life skills.
- Governance:
- The Metaverse and AI are global and borderless, which makes it difficult to govern and regulate them. This may lead to lack of oversight and accountability.
- Psychological and emotional effects:
- Spending excessive time in the Metaverse and interacting with AI systems may have negative effects on people''s mental and emotional well-being.
- Technical challenges:
- Building and maintaining the Metaverse and AI systems requires significant technical expertise and resources, which can be a challenge for both developers and users.
- Impact on physical health and well-being:
- As the Metaverse becomes more immersive, there is a risk that users will spend increasing amounts of time in virtual worlds, potentially at the expense of their physical health and well-being.
- Data privacy and security:
- With the increasing amount of personal data being shared within the Metaverse, there is a risk of data breaches and other security threats.
Further, to curb the challenges posed by metaverse and AI we need to implement the following measures like:
- Reduce Digital Divide: Governance mechanisms for virtual worlds would need to be supported with strengthening and scaling efforts to promote digital literacy, safety and wellbeing so that participants can engage meaningfully in online communities while consciously navigating harmful content and behaviors.
- Policy Backing: It is the right time for the government to create the right policy background for its operation and leverage the metaverse for public services.
- The government needs to focus on information accessibility, information utilization and information receptiveness.
- Promote Safe and Secure Metaverse Ecosystem: There is a strong need to develop and regulate effective ecosystems to address the distinct elements of safety, privacy, and security within the DNA of this technology.
- Building a citizen-friendly meta-governance infrastructure will need a collaboration by experts from various disciplines, including designers, business model experts and lawyers, to mitigate any potential legal hurdles. Private sector intervention may be required as well.
- Meta Help Desk: In e-governance, essential information is released to a targeted audience through ICT. Meta-help desks or meta-divisions in a particular ministry/ other government agency can help in providing the critical data required.
- Transparent and Consent-based Applications: Technology companies will need to be more responsible and transparent in their data processing and safety practices.
- Fostering an informed consent-based model while collecting personal data and abiding by the principles of data minimization and purpose limitation will be critical to prevent unchecked data processing and collection for commercial gains.
- Global Cooperation: As the metaverse continues to develop, we are seeing a glimpse of a more digitally advanced borderless world that is full of promise.
- While this new world continues to expand, we have to be aware of the set of challenges it brings with every new development and to look forward towards uniform regulations across the globe.
Future Challenges and Opportunities of Meta-AI
- More Pervasive AI:
- ChatGPT has shown the world that conversational artificial intelligence is an idea whose time has come.
- The ChatGPT can answer “follow-up questions”, and can also “admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests.” but most such AI elements are now in standalone products, which is more play than work.
- In 2023, this intelligence will be seen coming into more products that we use every day —for instance Gmail that will not just auto-suggest but also write next mail to the boss.
- Beyond Social Media:
- Twitter and Facebook are struggling to remain relevant amid an increasingly younger and digital native audience. Their concepts of social engagement are very different, often sans text and notice-board behaviors.
- Meta, for instance, knows that it will have to think beyond its present social media platforms and wants to be the social link when users move to the Metaverse, if at all.
- But that might not be something that will shift soon. Till then, there seems to be a vacuum emerging in the social media space, for now plugged by users sticking to short videos. But that fad too shall pass and not all platforms are good in that segment.
- More Regional, Darker Social Bubbles:
- As the Internet spreads to new users, especially in countries like India, it is also becoming more localized and multilingual.
- Across the world, the English language internet seems to have plateaued, making platforms like Google focus more on opportunities to serve smaller, regional languages.
- This is a tech challenge in more ways than one, but also presents an opportunity to test out new technologies that can convert the content of the internet for these new users without much human intervention.
- Future of Metaverse:
- As hybrid workforces become the norm and with travel still not as easy as earlier, extended reality (XR) could become the answer to collaborate and communicate virtually.
- XR is an emerging umbrella term for all the immersive technologies, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) plus those that are still to be created.
- All immersive technologies extend the reality we experience by either blending the virtual and “real” worlds or by creating a fully immersive experience.
- Since the headsets and other paraphernalia to facilitate these virtual interactions are still very expensive, it might be up to companies to make these available to their employees for regular XR meetings. The first experience of this could end up looking like an upgraded version of video conferencing, but with the ability to interact with objects in the virtual space.
- A few more commercial versions of the Metaverse is expected to be accessible to regular users during the year. However, the challenge will be with the hardware that lets people access these virtual worlds without making people bankrupt in the real world. The big disruptor could be an affordable device that logs users into the Metaverse easily — maybe it will just be a smartphone.
Ethical Concerns related to AI
- The legal and ethical issues that confront society due to AI include privacy and surveillance, bias or discrimination, and potentially the philosophical challenge is the role of human judgment. Concerns about newer digital technologies becoming a new source of inaccuracy and data breaches have arisen as a result of its use.
- The other side of this technological revolution is a growing apprehension on the socio-political and economic implications of AI, specifically, the concerns about co-existence of these emerging technologies and core principles of modern democracies.
- Consequently, AI ethics and the safe and responsible application of AI are becoming front and centre of the technology revolution.
- Constitutional morality was envisioned as the cornerstone for AI ethics’ principles in India, thus, propelling our constitutional rights and ethos to the paramount consideration for deploying AI in a responsible manner.
Principles of a Responsible AI
- Safety and Reliability: AI systems must ensure reliability regarding their intended functions and must have built-in safeguards to ensure the safety of stakeholders.
- Equality: AI systems must be built keeping in mind that similar people in similar circumstances are treated equally.
- Inclusivity and Non-Discrimination: AI systems must be developed to be inclusive of all stakeholders, and must not discriminate through bias between stakeholders on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth or residence in matters of education, employment, access to public spaces etc.
- Privacy and Security: AI systems must ensure that the personal data of data subjects must be safe and secure, such that only authorised persons must access personal data for specified and necessary purposes, within a framework of sufficient safeguards to ensure this process.
- Principle of Transparency: The design and training of AI systems is key for its functioning. The system must be audited and be capable of external scrutiny to ensure that the deployment of the AI system is impartial, accountable and free from bias or inaccuracies.
- Principle of Accountability: Since there are various actors in the process of developing, deploying and operationalizing an AI system, the accountability structures for any effects, harms or damages by the AI system must be clearly set out in a publicly accessible and understandable manner.
- Protection and Reinforcement of Positive Human Values: This principle focuses on the possible deleterious effects of AI systems through collection of personal data for profiling, the use of AI systems in manners contrary to fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution of India.
Road ahead
- Reducing the Digital Divide: In order for participants to engage meaningfully in online communities while consciously navigating harmful content and behaviors, governance mechanisms for virtual worlds would need to be supported with strengthening and scaling efforts to promote digital literacy, safety, and wellbeing.
- Policy Support: The government should now develop the best possible policy framework to support its operations and use the metaverse to provide public services.
- Information accessibility, information use, and information receptivity must be the government’s main concerns.
- Secure and Safe Metaverse Ecosystem: To handle the unique features of safety, privacy, and security inside the DNA of this technology, effective ecosystems must be developed and regulated.
- To overcome any potential legal obstacles, the development of a citizen-friendly meta-governance infrastructure will require the cooperation of specialists from diverse fields, including designers, business model experts, and attorneys. It can also be necessary to include the private sector.
- Global Cooperation: We are catching a glimpse of a more technologically advanced, borderless society full of promise as the metaverse continues to grow.
- While this new world is still expanding, we need to be mindful of the issues it poses with each new development and anticipate universally enforceable laws.
- ICT is used in e-governance to distribute critical information to a specific audience. The necessary vital data can be supplied by meta-help desks or meta-divisions within a certain ministry or by other government organizations.
- Applications with open and informed consent: The data processing and safety practices used by technology corporations will need to be more accountable and open.
- To avoid unregulated data processing and collection for commercial advantage, it will be crucial to promote an informed consent-based approach while collecting personal data and adhere to the principles of data minimization and purpose limitation.
The Metaverse and AI are emerging concepts in technology that presents a new way for people to interact and engage in a virtual world. However, this technology also poses a number of challenges but with proper set of governance and regulation, this technology could help humanity in unimaginable ways.










 General Studies
General Studies