- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 Latest News
Latest News
NOVEMBER 6, 2025
Quantum Leap: India Successfully Demonstrates Robust QKD Infrastructure
Startup QNu Labs, supported under the National Quantum Mission (NQM), successfully demonstrated India''s first extensive QKD network, spanning over 500 kilometers.
- It involved a network deployed over existing optical fiber infrastructure, marking a significant milestone in quantum-secure communication.
- This demonstration was made under a project funded through the I-Hub Quantum Technology Foundation, under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NMICPS).
What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)?
- QKD leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure secure distribution of the encryption keys, used for data communication.
- Quantum mechanics is the field of physics that explains how extremely small objects simultaneously have the characteristics of both particles (tiny pieces of matter) and waves (a disturbance or variation that transfers energy).
- QKD is an example of quantum cryptography (also known as quantum encryption).
- QKD can be deployed through different mediums: optical fiber, free space, and through satellites
- Benefits:
- Capable of detecting and mitigatingeavesdropping attacks (sniffing or snooping attack)
- Suitable for Critical Infrastructure (defence, government communications, healthcare, financial services, data centres, and telecommunication networks), etc.
|
The Prime Minister presented two path breaking Quantum innovations to the nation. QSIP (Quantum Random Number Generator System in Package)
25-qubit QPU
|
Amul and IFFCO Ranked World’s Top Cooperatives
- Amul and IFFCO emerged as the top two global cooperatives, ranking first and second, respectively, in the World Cooperative Monitor (WCM) 2025.
- The WCM 2025 was released at the ICA CM50 Conference held in Doha, Qatar; it ranked cooperatives by GDP per capita performance, highlighting their contribution to the economy.
|
Amul and IFFCO
- Amul: It is India’s pioneering dairy cooperative that became the model for the nationwide “Operation Flood“; it is managed by the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF).
- It includes more than 18,600 village dairy societies and 3.6 million milk producers.
- IFFCO: The Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited, based in New Delhi, is a multi-state cooperative society that manufactures and markets fertilisers and agricultural inputs.
- IFFCO supports around 50 million farmers through 35,000 member cooperatives across India.
Cooperatives
- A cooperative is a voluntary, democratic, and autonomous enterprise controlled by its members.
- Part IXB of the Indian Constitution grants constitutional status to cooperative societies. It was incorporated through the 97th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2011.
- Legal Framework: Single-state cooperatives are regulated by State Acts, while multi-state cooperatives follow the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (MSCS) Act, 2002.
- Institutional Support: The Ministry of Cooperation, established in 2021, offers a dedicated administrative and policy framework to strengthen India’s cooperative movement.
|
The United Nations (UN) declared 2025 the International Year of Cooperatives (IYC) to highlight the role of cooperatives in promoting social inclusion and sustainable economic growth. |
Tidal Disruption Event (TDE)
Astronauts have observed the biggest and most distant Flare from black hole which originated due to tidal disruption event (TDE).
- Meaning: Tidal disruption events occur when a star approaches a supermassive black hole and gets violently ripped apart, causing outflows of radiation.
- Significance: TDEs help researchers understand how black holes change their surroundings.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- The Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is facing irregularities and corruption issues in its implementation.
- PMKVY is a flagship outcome-based skill development scheme launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Objective: The scheme aims to provide large-scale, short-term skill training to Indian youth to enhance their employability and livelihood opportunities.
- Implementation: It is implemented under the Skill India Mission through the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC).
- Current Phase: PMKVY 4.0 (FY 2022–23 onwards) functions as a Central Sector Scheme emphasising new-age skills like AI, robotics, and data analytics, while mandating On-the-Job Training (OJT).
- Training Components:
- Short-Term Training (STT): Offers National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF)-aligned courses for school dropouts and unemployed youth.
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL): Certifies informal skills of existing workers with industry-recognised credentials.
- Special Projects: Provides customised training for marginalised groups, aspirational districts, and emerging job sectors.
- Achievements: PMKVY has trained over 1.64 crore youth, with 45% of beneficiaries being women and a significant share from the SC, ST, and OBC categories.
Sports Need to Be a National Priority Sector
- India’s recommendation to host the 2030 Commonwealth Games in Ahmedabad coincides with the release of the National Sports Policy 2025.
- Together, they underline the need to treat sports as a national investment, not discretionary spending, integral to achieving Viksit Bharat 2047.
|
Current Scenario
|
Economic & Social Significance of the Sports Sector
- GDP Boost Potential: SAPA can contribute up to 2% of GDP and 4% of national jobs by 2047.
- Employment Engine: Expanding sports tech, fitness services, and sports media.
- Preventive Healthcare: Active lifestyles could save up to ₹15 lakh crore in health costs by 2047.
- Social Cohesion: Sports build inclusivity, national pride, and community participation.
Key Challenges Faced by the Sports Sector
- Infrastructure Gaps: Only 30% of rural schools have playgrounds (UDISE+ 2022–23), limiting early participation and grassroots sports development.
- Funding Deficit: Sports receives less than 0.08% of the Union Budget, far below the 1–2% allocation seen in sports-driven economies (NSP Draft, 2025).
- Fragmented Governance: India has 10+ agencies managing sports at different levels, leading to poor coordination and duplication of efforts (NITI Aayog Review 2024).
- Low Private Participation: Private-sector contribution to sports infrastructure is below 20%, compared to 60–70% in developed economies (CII Sports Report 2023).
- Talent Pipeline Weakness: Only 15% of athletes identified at sub-junior levels reach state-level championships (Sports Authority of India Data 2024).
- Gender Disparity: Female participation in organised sports remains below 30%, especially in rural belts (Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, 2024).
Way Forward
- Grassroots Integration: Include daily sports periods in schools under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020; expand Khelo India School Games to every district.
- Health Mainstreaming: Integrate SAPA goals into the National Health Mission (NHM) for NCD prevention through active lifestyle campaigns.
- Private Sector Incentives: Introduce sports infrastructure PPP models with CSR tax deductions and viability gap funding for private academies. E.g. Australia’s “Sport Investment Framework”
- Infrastructure Development: Create district-level sports complexes under the PM YASASVI Scheme and urban planning mandates for open play spaces.
- Sports Industry Boost: Align sports tech, apparel, and analytics startups with Make in India 2.0 to localise production and create employment. E.g. The U.S. “SportTech Innovation Network” links startups with training academies and research institutions for scalable innovation.
Threat of US Secondary Sanctions on Russian Oil Producers
- The US-imposed sanctions on Russian oil producers Rosneft and Lukoil have raised concerns among Indian refiners about potential secondary sanctions.
- Russia’s crude oil exports to India declined to 1.19 million bpd in late October from 1.95 million bpd.
|
Sanctions
|
Key Concerns for India
- Supply Disruption: The sanctions threaten India’s crucial energy security since India is the second-largest importer of Russian crude, sourcing over 35% of its oil from Russia.
- Rising Import Costs: Decline in discounted Russian oil, which saved India nearly $13 billion between 2022 and 2024, significantly increases import expenses and fiscal pressure.
- Refinery Adjustments: Refineries optimised for Russian crude blends need to reconfigure their operations, which reduces efficiency and profits.
- Diplomatic Strain: The sanctions complicate India’s strategic balance between the United States and Russia, limiting its energy autonomy and challenging its policy of non-alignment.
India–UAE Cultural Cooperation
- At the 2nd Joint Steering Committee Meeting of the India–UAE Cultural Council, both nations agreed to deepen cultural, educational, and youth cooperation.
India–UAE Cultural Cooperation Highlights
- Cultural Landmark: India House to be built in Abu Dhabi as a hub for art, yoga training, and heritage exhibitions, symbolising the creative bond between the two nations.
- Yoga Recognition: To formalise Yoga as a competitive sport, first in the Gulf via UAE Yoga Committee.
- Archival Linkages: Plans for cooperation between National Archives of India and UAE’s archival institutions to document shared maritime and cultural history.
- Youth, Education, Tourism: Roadmap for student mobility and co-branded tourism events.
|
Yoga
|
Inequalities in Global Health Security
- The UNAIDS Global Council warned that widening inequalities are making pandemics more severe and prolonged, urging nations to embed equity into health-security planning.
Inequality in Global Health Security
- Unequal Access: Low-income nations received < 20 % of vaccines during COVID-19 (WHO 2023).
- Fiscal Divide: Developed economies spend ≈ 2 % of GDP on preparedness; poorer nations < 1 %.
- Health Infrastructure Gap: Weak primary-care and surveillance systems heighten disease impact.
- Gender Inequity: 70 % of the health workforce is Women, but underpaid and underprotected.
Impact of Global Health Inequality
- Higher Fatality Rates: Countries with high income gaps recorded 2× COVID-19 mortality (Lancet 2023).
- Slower Recovery: Poorer economies lost > 6 % GDP vs 3 % global average (IMF 2023).
- Poverty Surge: 120 million pushed into extreme poverty (World Bank 2023).
- Education Loss: School closures deepened learning inequality and child malnutrition.
- Cycle Effect: Pandemics worsen inequality, which in turn amplifies future pandemic risk.
Way Forward
- Fiscal Reform: Expand the global Pandemic Fund to support low-income countries (World Bank 2022).
- Technology Sharing: Adopt open licensing for vaccines. E.g. WHO mRNA Hub, South Africa.
- Public Health Systems: Strengthen primary care and data surveillance – E.g. India’s IHIP Platform 2023.
- Gender Mainstreaming: Equal pay for frontline workers – E.g. UN Women Health Leadership 2024.
- Global Treaty: Advance the WHO Pandemic Accord for equitable access to countermeasures.
SEBI Proposes Changes to Mutual Fund Regulations
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has proposed changes to mutual fund regulations aimed at reducing costs and improving transparency for investors.
|
SEBI functions as India’s capital market regulator under the Ministry of Finance. It was established in 1988 and was granted statutory powers under the SEBI Act, 1992. |
Key Proposals
- Statutory Levies: GST, Securities Transaction Tax (STT), Commodity Transaction Tax (CTT), and stamp duty will be excluded from the Total Expense Ratio (TER); they will be charged separately.
- Exit-Load Charge: The additional five bps charge on schemes introduced in 2012 that levies an exit load will be removed.
- Revised TER Slabs: A slight five basis points increase in the base TER slabs for initial assets of active schemes to offset revenue loss.
- Performance-Based Fees: SEBI is considering a voluntary framework that allows AMCs to charge fees based on a scheme’s performance.
- Brokerage Fees: Maximum brokerage fees will be reduced; execution and research costs will be separated to prevent double-charging investors.
|
Total Expense Ratio (TER)
|
UN raises concerns regarding Neurotechnology
Neurotechnology encompasses both hardware and software that directly measure, access, monitor, analyse, predict or modulate the nervous system to understand, influence, restore or anticipate its structure, activity and function. E.g., brain-computer interface (BCI)
- In recent times, the integration of AI with neuroscience can impact key aspects of the human brain, including reasoning, learning, perception, prediction, planning, and control.
Concerns related to Neurotechnology
- Mental Integrity: Unlike many other frontier technologies, it can directly access, manipulate and emulate the structure of the brain.
- Personal Identity & Psychological Continuity: Protection of one’s sense of self (compromises freedom of thought) and memory including autonomy and privacy from Memory modification or manipulation changing “who a person is”.
- Use of Neural Data: Corporations might exploit neural data collected through neurotech devices for targeted marketing or commercial gain.
- Social Inequalities: Unequal deployment of neurotechnology could intensify existing social divides, potentially leading to greater social tension and conflict.
Way Forward (Recommendations by UNESCO)
- Legal Protection and Regulation: Enact laws to control neurotechnology use, especially beyond scientific, medical, or judicial purposes.
- Data Policy: Develop robust, fair and agile regulatory and legal frameworks to govern the collection, processing, sharing and all other uses of neural data.
- Equitable Access: Promote equitable access to science- and evidence-based, safe and reliable neurotechnology.
Gogabeel Lake
Bihar''s Gogabeel Lake has been designated a Ramsar site, marking India''s 94th wetland of international importance.
- Overview: It is an oxbow wetland situated in katihar district, bihar.
- Gogabeel is formed from the flow of the rivers Mahananda and Kankhar in the north and the Ganga in the south and east
- Significance: It is the first community reserve of Bihar.
- It is a habitat for a wide variety of birds some of which are even migratory birds
- Other Recent Additions to Ramsar Site: Gokul Jalashay (92nd) of Buxar district and Udaipur Jheel (93rd) of West Champaran in Bihar.
Enforcement Directorate (ED)
Cases investigated by ED have been cited as models of effective asset recovery practice by Financial Action Task Force in ‘Asset Recovery Guidance and Best Practices’ guidelines.
ED (HQ: Delhi)
- Genesis: 1956.
- Administrative Control: Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- It is a multi-disciplinary organization mandated with investigation of the offence of money laundering and violations of foreign exchange laws.
- Key Laws Enforced:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA)
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA)
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA)
- Powers: Searches and seizures, summon any person, arrest and prosecute, etc.
Supreme Court Allows Reassessment of AGR Dues
- The Supreme Court has permitted a complete reassessment of Vodafone Idea’s (Vi) Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR) dues up to FY 2016–17.
Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR)
- AGR is the revenue base used by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) to determine usage and licensing fees that the GoI charges telecom operators.
- India shifted from a fixed annual license fee to a revenue-sharing model in 1999 to support the struggling telecom sector; operators now pay a percentage of their AGR to the government.
AGR Dispute
- A legal dispute over the definition of AGR emerged after the 1999 revenue-sharing reforms, with court challenges appearing soon afterwards.
- DoT’s Stance: AGR should include total company revenues, both telecom income (calls, data, SMS) and non-telecom income (interest, asset sales, rent, dividends, etc.).
- Telcos’ Stance: AGR should only include revenues from core telecom services, excluding non-telecom sources of income.
- 2019 Ruling: The Supreme Court upheld DoT’s broader definition, directing firms to pay dues based on total revenues.
- 2025 Ruling: The Supreme Court allowed a review of AGR dues, including interest and penalties, specifically limiting the decision to Vodafone Idea.
India’s Fortified Rice Kernel Export to Costa Rica
- Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) facilitated India’s first export of Fortified Rice Kernels (FRK) from Chhattisgarh to Costa Rica.
|
Costa Rica is a Central American country bordered by Nicaragua (north), Panama (southeast), Pacific Ocean (west), and the Caribbean Sea (east). Its capital is San José, and the official language is Spanish.
|
Fortified Rice Kernels
- Fortified Rice Kernels (FRK) are reconstructed grain kernels created from rice flour enriched with micronutrients like iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12.
- Process: They are produced through hot extrusion, where rice flour and micronutrients are blended, cooked, and shaped to resemble natural rice grains.
- Purpose: FRK aims to tackle ‘hidden hunger’ and reduce micronutrient deficiencies (e.g., anaemia) in rice-dependent populations.
- Standards: FSSAI mandates fortification with iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12, while zinc, vitamin A, and other B-vitamins remain optional.
- Blending Ratio: FRK is blended with regular rice in a 1:100 ratio.
- Framework: The Food Safety and Standards (Fortification of Foods) Regulations, 2018, govern FRK production, quality, and labelling across India.
PRS Legislative research releases State of state Finances 2025 Report
According to report, rising levels of committed expenditure are constraining the fiscal space of states, thereby squeezing their ability to undertake development-oriented spending.
Key findings of the Report
- High committed spending: States spent 62% of revenue receipts on salaries, pensions, interest, and subsidies in 2023-24.
- Lower GST revenue share: Revenue from GST-subsumed taxes fell from 6.5% of GDP (2015-16) to 5.5% (2023-24), leaving states with weaker own-tax capacity.
- 15th Finance Commission had estimated a medium-term ratio of 7% revenue from GST.
- Reduction in untied transfers: Untied transfers fell to 64% under the 15th Finance Commission, reducing states’ flexibility in spending priorities.
- High debt burden: Outstanding debt of states at 27.5% of GDP (2024-25) is far above the FRBM target of 20%; only Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Odisha meet the benchmark.
- Interest payments rising fast: Interest costs grew 10% annually (2016-17 to 2024-25), outpacing revenue growth.
- Unconditional cash transfers for women led to fiscal pressure: In 2025-26, the number of states providing unconditional cash transfers to women has increased to 12 states.
- Per-capita income gaps between states have increased: Because high-income states raise more revenue per capita and spend more on development.
|
Way Forward
|
High Seas Treaty
- The High Seas Treaty (Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction: BBNJ) has been ratified by over 60 countries and will be effective in January 2026.
|
High Seas Treaty
|
Key Provisions of the Treaty
- Marine Genetic Resources (MGRs): Recognise them as the common heritage of humankind, intended to ensure equitable benefit sharing.
- Area-Based Management Tools (ABMTs): These tools enable the creation of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) to conserve ecologically sensitive zones.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Mandatory prior assessment for any activity that may cause transboundary or cumulative ecological damage.
Significant Challenges of the High Seas Treaty
- Principle Ambiguity: Unclear balance between common heritage and freedom of the high seas, creating confusion in implementation.
- Benefit Sharing: No defined mechanism for sharing profits from Marine Genetic Resources, raising biopiracy concerns.
- Power Participation: Major ocean powers (the U.S., China, and Russia) have not ratified the treaty, weakening global enforcement.
- Institutional Overlap: Coordination issues are likely with bodies like the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) & International Seabed Authority (ISA), risking fragmented ocean governance.
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) Satellite
- ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan announced that the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite will soon be fully operational.
NISAR Satellite
- NISAR is the first Earth-observation satellite jointly developed by NASA (U.S.) and ISRO (India).
- It was launched aboard ISRO’s GSLV-F16 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota.
- Key Feature: It is the world’s first such satellite to utilise a dual-frequency Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system (L-band and S-band) from a single platform.
- L-Band (NASA): Operates at a lower frequency that can penetrate forest canopies and measure soil moisture, forest biomass, and the motion of land and ice surfaces.
- S-Band Radar (ISRO): Operates at a higher frequency, increasing its sensitivity to smaller vegetation structures, soil moisture changes, crop conditions, and snow cover variations.
|
A SAR system is a type of radar that produces detailed, high-resolution images of objects and landscapes on Earth’s surface, even in dark or cloudy conditions. |
- Specifications: The satellite weighs approximately 2,400 kg and has a minimum mission life of 3 years.
- Orbit and Coverage: It will orbit the Earth at an altitude of 747 km in a Sun-synchronous orbit, mapping its land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days.
|
Other Scheduled ISRO Missions
|
Baku to Belém Roadmap to 1.3T report
The Baku to Belém Roadmap to 1.3T report released ahead of COP-30 underscores the need for enhanced and predictable financial commitments from developed countries.
- Report identifies five action fronts on finance - Replenishing, Rebalancing, Rechanneling, Revamping, and Reshaping (5R) to deliver the 1.3 T by 2035 with USD 300 billion being a part of the overall goal.
5R Mechanism
- Replenishment: Developed countries need to increase delivery of grants and concessional climate finance.
- Rebalancing: Creditor countries, the International Monetary Fund and multilateral development banks shall work together to alleviate onerous debt burdens faced by developing.
- Rechanneling: Multilateral development banks, development finance institutions, public development banks and multilateral climate funds need to significantly scale the availability and quality of catalytic financial and risk mitigation instruments such as foreign exchange hedging, etc.
- Revamping: Governments should mainstream climate, nature and just transition objectives into planning, budgeting and investment frameworks, etc.
- Reshape financial structures: for enhanced capital flows.
Meghalaya’s Umngot River
- The Umngot River in Meghalaya has turned unusually murky this winter, triggering concern among local communities and environmental bodies.
Umngot River
- It is located in Meghalaya’s West Jaintia Hills near the Bangladesh border and is famous for its crystal-clear waters. Dawki and Shnongpdeng are the main tourism spots.
- For years, the river was considered among the cleanest in Asia. Tourists could clearly see the riverbed from boats, making it a key attraction for boating, kayaking, and eco-tourism.
- Local Khasi communities depend on the river for fishing, drinking water, agriculture, and tourism, which are major sources of income.
- In Oct 2025, the river suddenly turned brown and muddy. Investigations linked this to uncontrolled dumping of soil and debris from hill-cutting for the Shillong–Tamabil (Dawki) road project.
Doha declaration
Doha declaration adopted at the Second World Summit for Social Development.
- The 1st summit took place in Copenhagen, Denmark in 1995.
- Summit was convened by the United Nations General Assembly.
- It renews and updates the 1995 Copenhagen commitments, calls for:
- Treating poverty eradication, decent work and social inclusion as interconnected priorities.
- Expanding universal, gender-responsive social protection, and equitable access to health and education, etc.
Neurotoxin Found in Cycad Plants
- Scientists and medical experts at a recent AIIMS Bhubaneswar workshop cautioned against serious health risks from ancient Cycad plants.
- Neurotoxin: Researchers identified BMAA (β–N–methylamino–L–alanine), a potent neurotoxin, in several Cycad species native to Odisha.
Cycad Plants
- Cycads are ancient dioecious (either male or female) gymnosperm plants that resemble palms or ferns but form a distinct evolutionary group.
- Morphology: They have stout, unbranched trunks with crowns of large, stiff, evergreen leaves.
- Longevity: Cycads exhibit slow growth &remarkable longevity, often surviving for thousands of years.
- Symbiosis: Their coralloid roots host nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria that supply essential nutrients.
- Habitat Range: They thrive in diverse habitats, including rainforests, savannas, and semi-arid regions with well-drained soils.
- Global Spread: Cycads occur in tropical and subtropical regions across all continents, except Europe and Antarctica.
- Indian Range: They are found in Odisha, Assam, Meghalaya, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Toxic Compounds: All parts of the cycad plant contain toxins like Cycasin, BMAA, and MAM to protect against herbivores.
- Health Risk: BMAA exposure is associated with neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinsonism, motor neuron disease, and dementia.
- Human-Use: Cycads are grown as ornamental plants and valued for their starch-rich seeds, medicinal extracts, and fibrous materials used in traditional handicrafts.
- Cycad gum is traditionally used as an antidote for snake bites and to treat malignant ulcers.
INS Savitri
- Indian Naval Ship INS Savitri recently arrived at Port Louis, Mauritius, during a Long-Range Operational Deployment to the South-West Indian Ocean Region.
- INS Savitri (P53) is an indigenously built Sukanya-class offshore patrol vessel of the Indian Navy, commissioned on 7 June 1990.
- The ship serves under the Eastern Naval Command, based in Visakhapatnam.
- The INS Savitri undertakes multiple offshore patrol roles, including maritime surveillance, coastal security, search and rescue, and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) monitoring.
- It has participated in several long-range operational deployments, including patrols off the Maldives, Seychelles, and Mauritius, strengthening maritime cooperation.
Satellite-based internet
Elon Musk-owned Starlink has signed an agreement with Maharashtra government to deliver satellite-based connectivity to remote and underserved regions.
- Definition: Satellite internet is wireless broadband delivered via communication satellites orbiting the Earth.
- Difference: Unlike fibre, cable, or DSL, it does not depend on physical ground-based wiring.
- How does it work? Data is transmitted from a user’s dish to a satellite and then to ground stations connected to the global internet.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, like Starlink, offer faster speeds and lower latency than traditional geostationary ones.
- Significance: Helps bridge the digital divide by connecting remote and underserved regions.
Project Suncatcher
Google launches Project Suncatcher to test AI data centres in space.
Project
- Objective: Explore AI computing in space using solar-powered satellites in low-Earth orbit.
- The initiative envisions a constellation of compact satellites, each carrying Google’s custom-built Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) chips—processors designed specifically for machine learning and AI applications.
- Two prototype satellites will launch by 2027 to test power generation, chip performance, and data transmission.
G20 releases a report on Global Inequality
Findings of the report:
- Income: 83% of countries have high income inequality (i.e., a Gini coefficient above 0.4), accounting for 90% of the world’s population.
- Wealth: Between 2000 and 2024, the richest 1% captured 41% of all new wealth, in contrast to just 1% being captured by the bottom 50%.
- In India, the top 1% has grown their share of wealth by 62% over this period.
Drivers of Inequality
- Neoliberal Policies: Deregulation of financial and labor markets, the weakening of competition policies, and a shift toward less progressive taxation.
- Growth of monopoly power: Increases corporate owners'' incomes and decreases workers'' real incomes.
- International Setting: Greater mobility of capital across borders and new technologies used in production have lowered bargaining power of less-skilled workers.
- Influence of economically powerful elites: on politics and policymaking both drives and reinforces economic inequality
- Historical legacy of high inequality in developing countries. E.g. Distribution of land.
Recommendations
- Establishing an International Panel on Inequality (IPI) to provide policy-relevant assessments on inequality trends, drivers and impact.
- Implementing more progressive taxation through a global minimum tax on ultra-rich individuals.
- Rewriting IP rules to include compulsory licenses/waivers for critical technologies, especially related to climate change and pandemics.
- Ensuring universal access to high-quality essential services such as health, education, and social security.
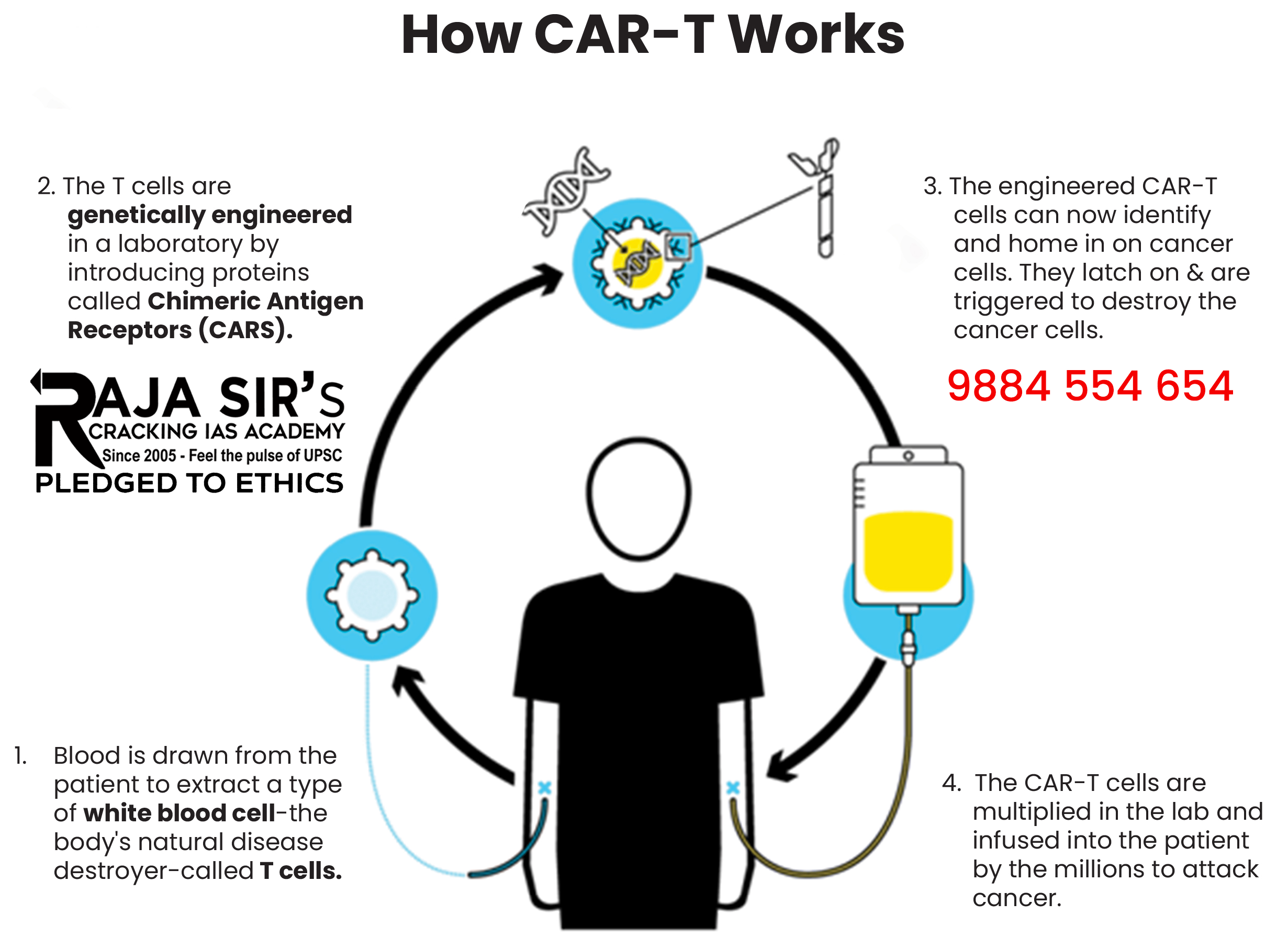
NexCAR19 revolutionizes cancer treatment with affordable innovation & enhanced patient safety
NexCAR19 therapy was developed for B-cell blood cancers by ImmunoACT (a company incubated under IIT Bombay, and Tata Memorial Hospital), supported by DBT and BIRAC.
- NexCAR19, India’s 1st indigenous CAR T-Cell therapy, was granted market authorization by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) in 2023.
CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor) T-Cell Therapy
- It modifies immune cells, specifically T-cells, by turning them into potent cancer fighters known as CAR-T cells.
- T-cells are special cells (types of white blood cells) whose primary function is cytotoxic, meaning killing other cells.
- This treatment is designed for specific types of blood cancer and is given to patients whose cancer has either relapsed or not responded to first-line treatment.
Benefits of CAR T-Cell therapy
- Short treatment duration: Unlike aggressive chemotherapy or stem cell transplants, it allows for a faster recovery.
- Sustained Benefits: CAR T-cells persist in the body, offering long-term protection against cancer relapse.
- Accessibility: Nexcar19 cost is lower compared to imported CAR-T therapies.
Challenges: Therapy for one cancer won''t work for another type of cancer, can have negative effects on the nervous system, Cytokine Release Syndrome (Over activation of immune cells), risk of infection, etc.
Baliyatra Festival
President Extends Greetings On Baliyatra Festival.
- Baliyatra festival is generally celebrated in coastal Odisha on the day of “Kartika Purnima”.
- It commemorates the past association of the people of Odisha with Bali and the glorious maritime tradition of transoceanic voyages they undertook to South East Asian Countries.
- It is also associated with legend ‘Taapoi’ and rituals like ‘Bhalukuni Osha’ or ‘Khudurukuni Osha’ and ‘Bada Osha’.
Water Convention
Bangladesh became the first country in South Asia to join the U.N.’s Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (Water Convention).
- Adopted in Helsinki in 1992 and entered into force in 1996.
- Legally binding convention for sustainable management of shared water resources.
- Requires parties to prevent, control, and reduce transboundary impacts.
- Ensures reasonable, equitable, and sustainable use of shared waters.
- Mandates cooperation through agreements and joint bodies among riparian states.











 General Studies
General Studies