- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Cervical Cancer in India
Cervical cancer, a major health concern among Indian women, stands as the second most common type of cancer in this demographic. The Indian government''s recent initiative to include the cervical cancer vaccine in the universal immunisation program for girls aged 9 to 14 is a significant step towards public health advancement.
Current Situation of Cervical Cancer Burden in India
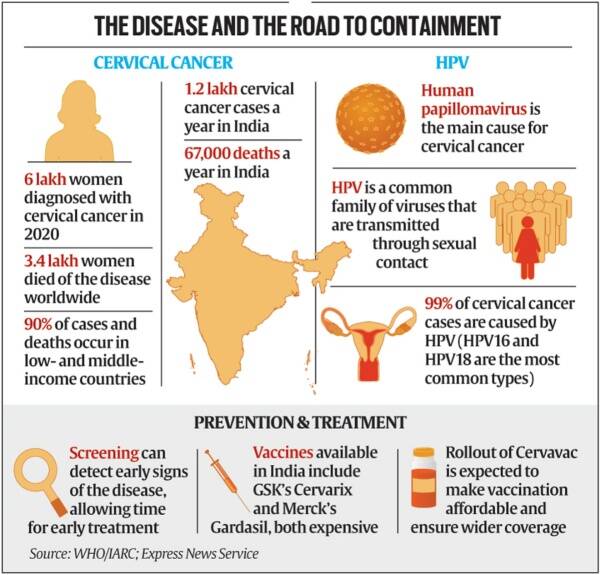
- A Formidable Challenge: 2022 witnessed 1,23,907 new cases, indicating a significant global health concern. The severity is underscored by 77,348 deaths in the same period.
- Prevalence in Middle-Aged Women: The disease''s long pre-invasive phase necessitates targeted early detection and intervention strategies.
Contributing Factors of Cervical Cancer in India
- High-Risk HPV Infection: The prevalence is primarily due to persistent high-risk Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infections. HPV, combined with other co-factors, increases the risk of developing cervical cancer.
- Co-Factors and Socio-demographic Influences: Low socioeconomic status, compromised immunity, other genital infections, and tobacco use exacerbate the risk. These factors are especially relevant for the middle-aged female demographic.
Opportunities for Early Detection and Cure
- Extended Pre-Invasive Phase: A Crucial Window: The 10–15 year pre-invasive phase offers a significant opportunity for early detection. Effective early intervention can prevent progression to advanced stages.
- Targeting the Reproductive Age Group: Focused screening and preventive measures in the reproductive age group can yield substantial benefits. Educational and screening initiatives should be tailored to this demographic.
- High Cure Rates with Early Detection: Early stage management boasts over a 93% success rate. Timely screening and diagnosis are key to improving outcomes.
- Screening Tools and Outpatient Treatment: Availability of visual screening tests and HPV tests enhances early diagnosis. Outpatient treatments for precancerous conditions are simple, painless, and widely accessible.
Government’s Initiatives
Inclusion of Cervical Cancer Vaccine into Universal Immunisation Programme
- A Proactive Step: Integrating the cervical cancer vaccine for girls aged 9 to 14 into the universal immunisation program. Targets the prevention of high-risk HPV infections, a key factor in cervical cancer development.
- Impact and Alignment with Global Practices: Aims to reduce cervical cancer incidence in the targeted age group. Aligns with global health strategies to combat cervical cancer.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Fulfilling Global Health Agendas: Complements SDG 3.4: reducing premature non-communicable disease deaths, including cancer, by one third by 2030. Targets cervical cancer elimination, contributing to the SDGs.
Implementation through National Health Programs
- Leveraging Existing Frameworks: This cervical cancer prevention strategy is part of the larger National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS).
Way Forward
Need for a Comprehensive Approach
- Integrated Strategies: Emphasizing regular cervical cancer screening and integrating advanced technologies in healthcare can significantly aid in early detection and treatment.
- Patient Care and Research Partnerships: Collaboration with NGOs, health experts, and innovators is essential for improving patient care pathways and conducting impactful research.
Focus on Innovations and Future Potential
- Advancing Indigenous Solutions Development of local HPV test kits and vaccines, single-dose vaccinations, and self-sampling methods. Exploring AI technologies for resource-limited settings.
Need for International Collaboration
- Global Learning and Sharing: Engaging in international collaborations to adopt successful cervical cancer prevention and treatment models can greatly benefit India''s healthcare strategies.
Population Awareness and Education
- Raising Public Consciousness: Implementing public health campaigns and community outreach programs to educate women about cervical cancer risks and the importance of early screening is vital for increasing public awareness and participation in preventive measures
While the government''s initiative to include the cervical cancer vaccine in the immunisation program is commendable, a holistic approach that encompasses awareness, prevention, early detection, and comprehensive treatment is essential. By connecting patient care, leveraging innovative technologies, and fostering collaborations, India can make significant strides in eradicating cervical cancer.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies