- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
How do we solve antibiotic resistance?
- Since antibiotics were introduced to the world in the mid-20th century, deaths attributable to infections dropped from over 50% to 10-15%.
- Experts have been warning for decades that the threat of antibiotic resistance could take us back in time to when even simple infections were deadly.
What are antimicrobials?
- Antimicrobials – including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals and antiparasitics – are medicines used to prevent and treat infections in humans, animals and plants.
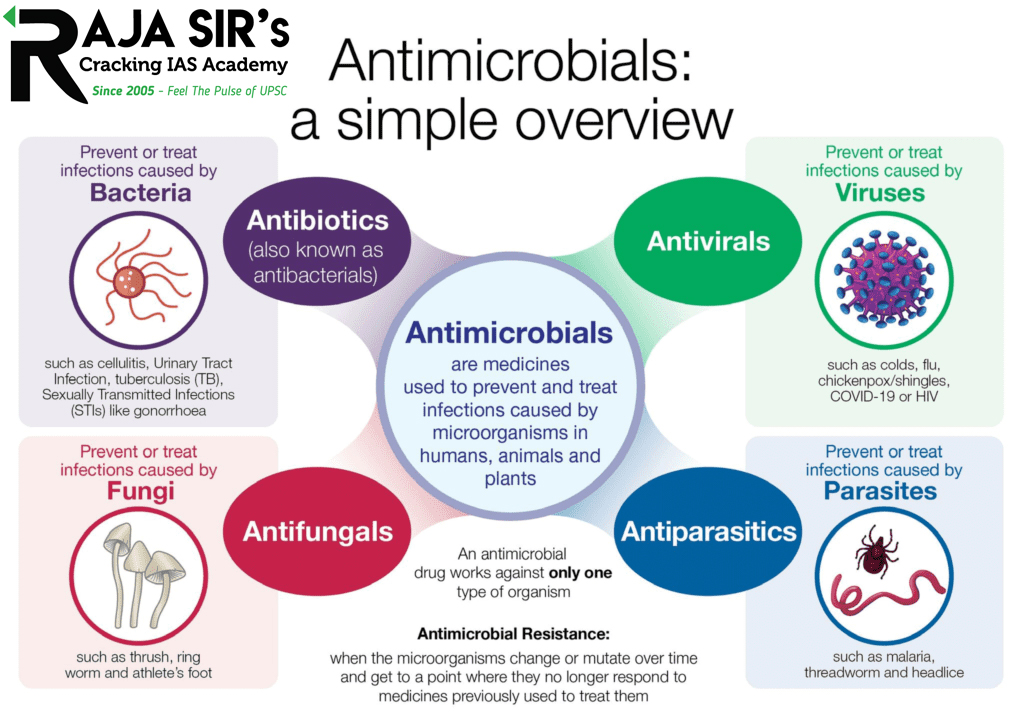
What is antimicrobial resistance?
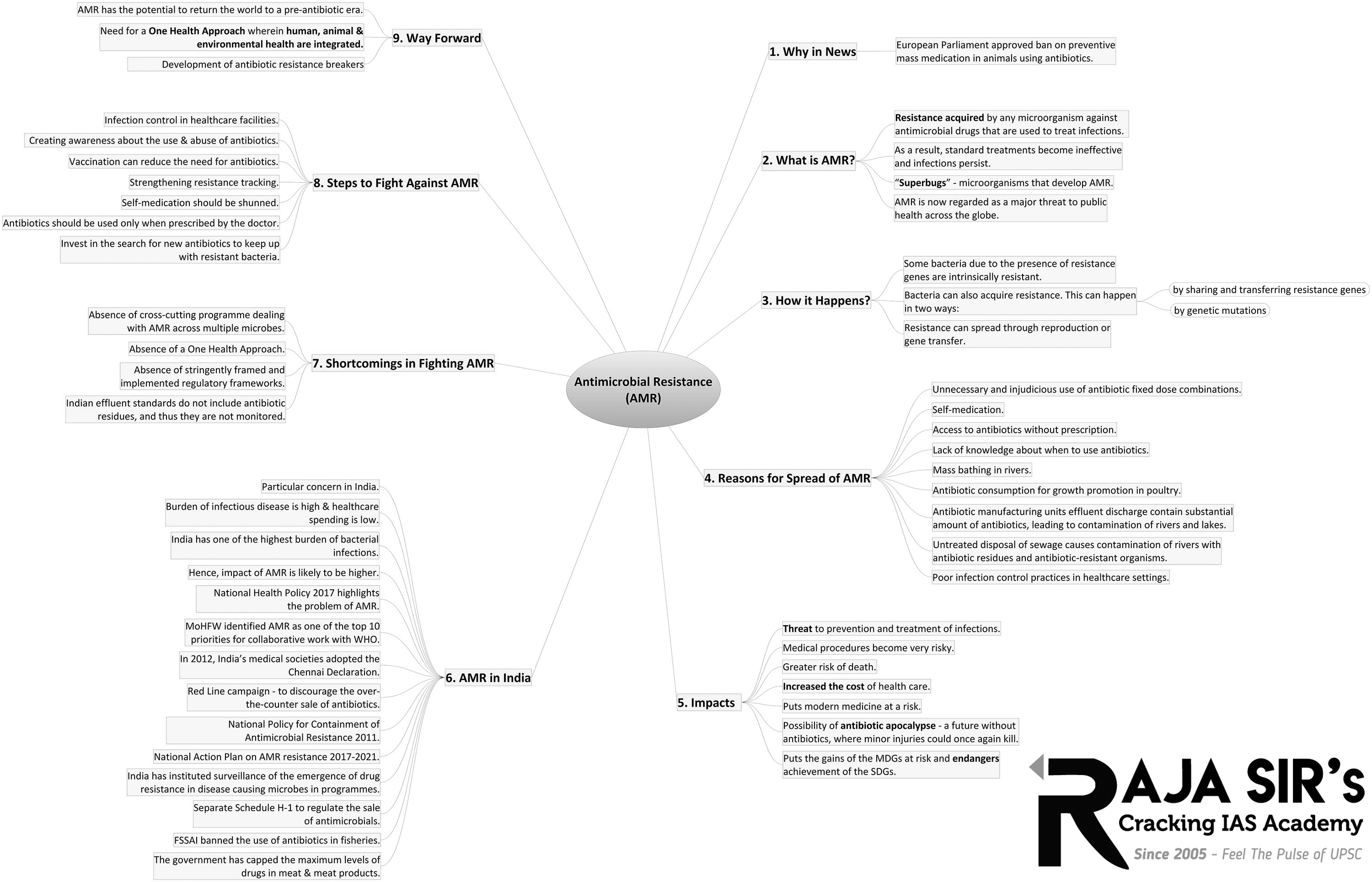
- AMR happens when microorganisms (such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites) change and are still able to grow, even when they are exposed to antimicrobial medicines that are meant to kill or limit their growth (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics).
- As a result, the medicines become ineffective and infections persist in the body, increasing the risk of spreading to others.
Impact of AMR:
- Treatment failure leading to chronic problems
- Increased morbidity (disability, poor outcomes) and mortality
- Adverse effects of alternative treatments (potentially less effective, possibly more toxic)
- Relapse of the infection after treatment
- Increased spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their associated community- and healthcare-acquired infections
- Increased use of antibiotics
- Lack of availability of clinically effective antibiotics
- Longer and more complicated stays in hospital
- Excess healthcare costs
- Decreased societal productivity
Statistics:
- India is one of the largest consumers of antibiotics in the world.
- Antibiotic use in India has risen sharply, with about a 30% increase in their per capita use during the past decade, according to the State of the World’s Antibiotics 2021 report.
- 5 lakh people die annually due to AMR worldwide.
Findings of the recent Global Research on Antimicrobial Resistance (GRAM) Report:
- 10-fold: Variation between countries in total antibiotic consumption rates, ranging from as low as 5 DDD to 45.9 DDD per 1000 population per day.
- 46% up: Between 2000 and 2018, global antibiotic consumption rates increased from 9.8 to 14.3 DDD per 1000 population per day).
- 76%:Increase observed between 2000 and 2018 in low- and middle-income countries (from 7.4 to 13.1 DDD per 1000 per day). In high-income countries, consumption rates remained stable.
- 116%:Increase in antibiotic consumption rates in South Asia. The second largest increase was in the North Africa and Middle East region (111%).
Factors leading to AMR:
- The main drivers of antimicrobial resistance include the
- Misuse and overuse of antimicrobials;
- Lack of access to clean water,
- Sanitation and hygiene (wash) for both humans and animals;
- Poor infection and disease prevention and control in health-care facilities and farms;
- Poor access to quality, Affordable medicines, Vaccines and diagnostics;
- Lack of awareness and knowledge; and Lack of enforcement of legislation.
- Lack of access to timely and appropriate treatments for infections,
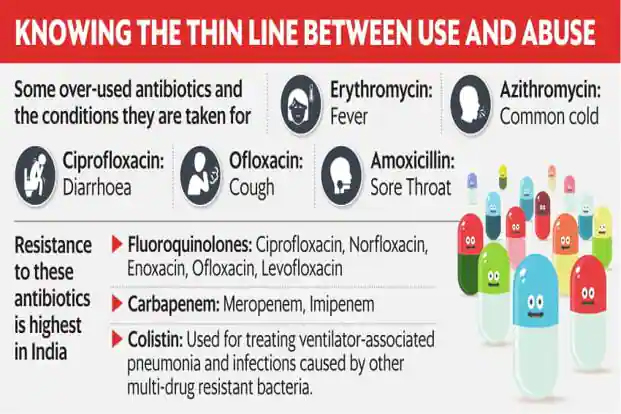
- Self-medication, prescription sharing, over-the counter sale of antimicrobials,
- Non-compliance with the prescribed treatment.
- Genetic mutation of bacteria.
- By one species acquiring resistance from another.
- Antimicrobial Waste.
Antimicrobial Waste:
- Antimicrobials given to humans, animals and plants are entering the environment and water sources (including drinking water sources) via wastewater, waste, run-off and sewageand through this spreading drug-resistant organisms and antimicrobial resistance.
- This could fuel a rise in the emergence and spread of ‘superbugs’that are resistant to several types of antimicrobial drugs. It could also harm organisms in the environment.
Measures to curb Antimicrobial waste:
- Develop and implement regulations and standards to better monitor and control the distribution and release of antimicrobials and drug-resistant organisms into the environment.
- In the manufacturing sector, developing national antimicrobial manufacturing pollution standards to better control and monitor antimicrobial pollution.
- In the human and animal health sector, enforcing laws and policies to reduce or eliminate antimicrobial use that is not under the guidance of a trained healthcare provider.
- In food systems, implementing standards to treat and manage discharge from food-animal farms, aquaculture farms and crop fields.
Inaction will have dire consequences for human, animal, plant and environmental health.
- Countries should develop guidance, implement and monitor release of antimicrobials from food systems, manufacturing facilities and human health systems into the environment.
- This should be done considering the prevention and management measures in national action plans on AMR, its aid.
- For the human health sector, countries should develop and implement antimicrobial stewardship policies. Antimicrobial stewardship ensures the sustainable use of antimicrobials and effective waste management approaches.
- Governments should enforce laws to reduce antimicrobial use that’s not done under the guidance of a trained healthcare provider, ensuring equitable access to quality antimicrobials.
- International technical organisations working on food systems should develop tools and guidance to support the implementation of the Codex Code of practice to minimise and contain foodborne AMR.
- Strengthening One Health surveillance of use and discharge of antimicrobialsand determinants from various sectors. Research and development in this area should be enhanced to gain a comprehensive understanding of the risks to human and animal health posed by antimicrobials in the environment.
- Cost-effective and greener waste management technologies should be explored, as this is critical for policymakers who want to support evidence-based policymaking.
Steps taken to curb AMR in India:
Red Line Campaign
- It urges people not to use medicines marked with a red vertical line, including antibiotics, without a doctor’s prescription. These medicines are called as the ‘Medicines with the Red Line’.
National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance
- India has a National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance in place
Delhi Declaration on Antimicrobial Resistance
- Delhi Declaration on Antimicrobial Resistance, was endorsed at the Inter-Ministerial Consultation on Antimicrobial Resistance in 2017.
AMR Surveillance Network
- ICMR has established AMR surveillance and research network (AMRSN) in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- This network comprises of 30 tertiary care hospitals, both private and government.
AMR Research & International Collaboration
- ICMR has taken initiatives to develop new drugs /medicines through international collaborations in order to strengthen medical research in AMR:
- ICMR along with Research Council of Norway (RCN) initiated a joint call for research in antimicrobial resistance in 2017.
- ICMR along with Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany has a joint Indo-German collaboration for research on AMR.
Initiatives to control overuse or misuse of antibiotics
- ICMR has initiated an antibiotic stewardship program (AMSP)on a pilot project basis in 20 tertiary care hospitals across India to control misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
- On the recommendations of ICMR, DCGI has banned 40 fixed dose combinations (FDCs) which were found inappropriate.
- ICMR worked in collaboration with Indian Council of Agriculture Research, Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairy and Fisheries and the DCGI to ban use of Colistin as growth promoter in animal feed in poultry.
Guidelines issued
- National Guidelines for Infection Prevention and Control in Healthcare Facilitie shave been released by MoHFW in Jan 2020.
- ICMR has developed evidence based treatment guidelines for treatment of ten syndromes of infections. It aims to rationalize the usage of antibiotics on Essential Medicines Formulary (EMF) and to establish consistency in the treatment of various infectious conditions.
- Further, ICMR has also issued the Treatment Guidelines for Antimicrobial Use in Common Syndromes” in 2019.
Looking Forward
Option 1: Modify existing antibiotics
- Scientists have been working on the issue from many different angles. One approach is to modify old antibiotics so they overcome resistance.
- “Penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics have undergone many rounds of modifications by medicinal chemists to improve their drug-like properties and overcome resistance. The ability to tinker with these structures is not infinite.
Option 2: Develop new antibiotics
- Another strategy is to make brand-new drugs, but this approach hasn’t been very successful in recent decades.
- The reality is that the last genuinely new chemical structure that has resulted in a drug that is currently being used in humans was discovered in the mid-1980s.
- But there are some signs of progress. For one, scientists are now armed with much more sophisticated drug discovery technologies, not least artificial intelligence (AI).
- Examples of scientific innovations include computational machine learning approaches to screen drugs in silico, and methods to screen many different combinations of compounds for antibiotic effects. “In silico” refers to experiments performed via computer simulation.
- These new innovations are helping scientists overcome older challenges in drug discovery. The hope is that antibiotic-resistant drugs can be pushed through drug development pipelines quickly enough for them to make an impact in global health care.
Buying time with antibiotic regulation
- In the short term, some experts want more regulation of antibiotics so their use is limited to situations when they are strictly necessary. The hope is this will buy us some time to slow down antibiotic resistance while drug discovery catches up.
- Antibiotics are not well regulated in many parts of the world. For example, antibiotics were “flying off the shelves” during the COVID-19 pandemic in India, where people can buy them over the counter in pharmacies.
- Limiting the use of antibiotics in agriculture would also have a major impact, experts say.
- The EU and US have banned the use of antibiotics for livestock growth, and in 2022, the EU brought in legislation to prohibit all forms of routine antibiotic use in farming.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies