- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Mosquito Control Approaches - PPP 100 - PRELIMS 2024 - 1
1. Wolbachia Method
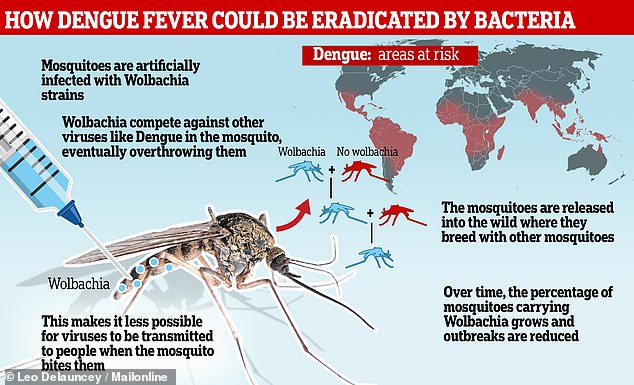
The Wolbachia Method is a biological method to manipulate mosquito populations and hence reduce transmission of mosquito-borne diseases such as Dengue, Zika, Chikungunya, etc. Wolbachia is a bacteria naturally present in many insects. The Wolbachia method involves introducing this bacteria in mosquito populations through one of the following methods:
- Egg Injection: Wolbachia bacteria is injected into the eggs of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Thereafter, they are released into the wild.
- Larval Exposure: Wolbachia bacteria is introduced into Larvae by exposing it to Wolbachia-infused water.
- Male Releases: This method involves releasing Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes into the wild. These male mosquitos then mate with wild female mosquitos, passing on the bacteria to their offspring.
Wolbachia, once introduced into mosquitoes, has two types of effects:
- Interfering with the reproduction process of mosquitos through a phenomenon called cytoplasmic incompatibility. This incompatibility reduces the number of viable offspring of the mosquitos. Thus, the result is a potential decline in the mosquito population.
- Inhibiting the replication of certain pathogens within the mosquito. This reduces the ability of mosquitoes to transmit diseases.
As Wolbachia infects the eggs or sperm of its host organism, it is transmitted from one generation of mosquitos to the next. Thus, the bacterium spreads rapidly within the mosquito population, making it a powerful tool in mosquito-borne disease control.
 Significance of the Wolbachia Method
Significance of the Wolbachia Method
- It has the potential to emerge as a groundbreaking strategy for vector-borne disease control.
- By providing an effective tool to fight against fatal diseases such as Dengue, Zika, Chikungunya, etc, it can significantly reduce the global burden of illness and mortality.
- It could provide a revolutionary approach to control the population of mosquitoes and other unwanted insects.
- By providing valuable insights into the intricate relationships between microorganisms and their hosts, it underscores the importance of addressing global health challenges through an interdisciplinary approach.
Pros of the Wolbachia Method
| Sustainable | As Wolbachia bacteria are transmitted from one generation of mosquitos to the next, the Wolbachia-infected population can persist for years. Thus, one introduced, this intervention requires minimal intervention to keep it ongoing. |
| Cost-effective | Compared to traditional methods of mosquito control like insecticide spraying, the Wolbachia Method is relatively cost-effective. |
| Targeted | The method specifically targets the Aedes aegypti mosquito, and has almost nil impacts on other insect species. |
| Environmentally Friendly | By reducing the use of chemicals like insecticides, it protects the environment as well as public health. |
Cons of the Wolbachia Method
- It is not effective in controlling all vector-borne diseases.
- Implementing and scaling up Wolbachia-based interventions have its own challenges.
- It raises a concern regarding the manipulation of reproductive processes in other organisms.
Despite these cons, the Wolbachia Method can offer a sustainable and targeted approach to combating vector-borne diseases. Its successful implementation can help improve public health and well-being across the world.
2. The Mosquito fish Approach
-
- Mosquitofish, native to fresh waters of the southeastern United States, are known for their appetite for mosquito larvae.
- They can consume up to 250 larvae per day, making them a potential weapon against mosquito populations.
- Two species of mosquitofish,Gambusia affinis and Gambusia holbrooki, were considered environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Yet, the unintended result was the worldwide dissemination of these fish from the U.S., causing ecological disturbances.
- Introduction of Mosquitofish in India:
- Gambusia was first introduced in India in 1928 during British rule, as a way to combat rapid mosquito spread.
- Subsequently, government bodies and private organizations in India collectively joined efforts to combat malaria through this method.
- The initial idea was for the fish to control mosquito larvae, but the strategy backfired, resulting in their transformation into invasive alien species.
- Negative Impacts of Mosquitofish:
- Invasive Nature:Their adaptability and high tolerance to fluctuating environmental conditions contribute to their extensive dispersion, making them highly invasive.
- Mosquitofish are now considered among the hundred most detrimental invasive alien species.
- Disruption of Native Fish Communities:They are aggressive feeders, consuming not only mosquito larvae but also eggs of native fish species.
- This can lead to the extinction of local species, particularly smaller, less competitive fishes.
- Loss of Unique Species:Their introduction can threaten the existence of endemic and ecologically important fish species, potentially leading to a loss of biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
- Reports indicate a decline in Microhyla tadpoles (rice frogs or narrow-mouthed frogs)following the introduction of Gambusia in India.
- Related Significant Steps:
- The World Health Organization stopped recommending Gambusia as a mosquito control agent in 1982.
- In 2018, the National Biodiversity Authorityof the Government of India designated affinis and G. holbrooki as invasive alien species.
- Invasive Nature:Their adaptability and high tolerance to fluctuating environmental conditions contribute to their extensive dispersion, making them highly invasive.
- Mosquitofish, native to fresh waters of the southeastern United States, are known for their appetite for mosquito larvae.
3. Gene Drive Technology
Gene-drive technology, was developed by Austin Burt ( Professor at Imperial College London) in 2003. A gene drive is a type of genetic engineering technique that modifies genes so that they don’t follow the usual genetic rules explained by Mendel. Gene drives dramatically increase the likelihood that a particular suite of genes will be passed onto the next generation, allowing the genes to rapidly spread through a population and override natural selection. With gene drive technology "you can modify evolutionary trajectory. You can cause extinction".
Gene drive is a genetic phenomenon that occurs in nature and causes a selected trait to spread rapidly through a species via sexual reproduction over several generations. Gene drive works by increasing the likelihood that a modified gene will be inherited by its offspring. Normally, genes have a 50/50 chance of being inherited, but gene drive systems could increase that chance to upwards of 99 percent. This means that over the course of several generations, a selected trait could become increasingly common within a specific species.
- Under this technique, mosquitoes will selectively inherit some genes rather than the inheritance to follow the rules of Mendelian genetics.
- In this, a protein cuts the mosquito’s DNA at a part that doesn’t encode a particular sequence in the genome.
- This triggers a natural mechanism in the cell containing the DNA to repair it and forces the cell to incorporate a sequence called the drive sequence into the damaged portion.
- Researchers at Imperial College London genetically enhanced a gene in mosquitoes to secrete antimicrobial substances called magainin 2 and melittin. They are detrimental to the Plasmodium parasite’s development in the midgut and also reduce the lifespan of female mosquitoes. Computational modelling studies have suggested that this approach could significantly disrupt malaria transmission.
The genetically modified OX5034 mosquito, authorized by the US Environmental Protection Agency, was released in 2020. It is developed with a gene sensitive to an antibiotic, It carries a self-limiting gene that prevents female offspring from surviving,leading to a reduction in mosquito populations.
Benefits of Genetic Engineering for Mosquito Control:
-
- Targeted Mosquito Control:Genetic engineering allows for the precise modification of mosquito populations, focusing on disease-carrying species.
- This targeted approach reduces the need for broad-spectrum insecticides,minimizing harm to non-target species.
- Reduced Environmental Impact:Compared to traditional insecticides, genetic engineering may have a lower environmental impact because it does not involve chemical pollution of ecosystems.
- This can help protect other beneficial insects and aquatic life.
- Sustainability:Once released, genetically modified mosquitoes can continue to pass on their modified genes, providing a sustainable and self-perpetuating method of mosquito control without the need for frequent reapplications.
- Public Health: By reducing mosquito-borne diseases, genetic engineering can have a significant positive impact on public health, potentially saving countless lives and reducing healthcare costsassociated with treating these diseases.
- Targeted Mosquito Control:Genetic engineering allows for the precise modification of mosquito populations, focusing on disease-carrying species.
Risks and Concerns of Genetic Engineering for Mosquito Control:
-
- Unintended Consequences:Genetic modifications can have unforeseen consequences in ecosystems.
- Altered mosquito populations may disrupt food chains or create ecological imbalances,impacting other species in unintended ways.
- Ethical Concerns: Critics haveethical objections to manipulating the genes of organisms, particularly when it involves altering the genetics of wild populations. Questions of ecological responsibility arise.
- Risk of Invasion:Genetically modified mosquitoes may unintentionally acquire traits that enhance their ability to invade new habitats, potentially causing unforeseen ecological disruptions in regions outside their natural range.
- Unintended Consequences:Genetic modifications can have unforeseen consequences in ecosystems.
Major Challenges Related to Mosquito and Related Disease Control
- Challenges in Mosquito Control:
- Complex Environment:Diverse climates, geography, and socio-economic conditions across India lead to varied breeding patterns of mosquitos.
- Insecticide Resistance:Mosquitoes have developed resistance to commonly used insecticides and repellents, necessitating frequent rotation and development of new alternatives.
- Poor Sanitation:Open drains, uncollected garbage, and stagnant water sources in urban and rural areas in India provide abundant breeding grounds.
- Challenges in Disease Control:
- Underreporting:Many cases of mosquito-borne diseases, especially in rural areas, go unreported or misdiagnosed, hindering accurate data and targeted interventions.
- Also, limited access to proper healthcare in remote areas delays treatment and increases complications.
- Vaccine Limitations:Currently, no effective vaccines exist for all mosquito-borne diseases, making prevention mainly reliant on vector control and personal protection measures.
- Underreporting:Many cases of mosquito-borne diseases, especially in rural areas, go unreported or misdiagnosed, hindering accurate data and targeted interventions.
Road ahead
- Improved Sanitation and Infrastructure:Efficient waste collection and disposal can eliminate breeding grounds in urban areas.
- Proper drainage systems can prevent stagnant water accumulation, a major breeding source for mosquitoes.
- Providing communities withclean water storage solutions can reduce dependence on open containers, which attract mosquitoes.
- Integrated Vector Management (IVM):Implement a comprehensive approach that combines various strategies such as biological control, insecticide use, and environmental management to address mosquito-related challenges by accelerating the implementation of the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme.
- Community Engagement and Education:Foster public awareness and involvement in mosquito control through educational campaigns, emphasizing preventive measures, and encouraging community participation.
PYQs
2008
The release of which one of the following into ponds and wells helps in controlling the mosquitoes ?
(a) Crab
(b) Dogfish
(c) Gambusia fish
(d) Snail
Note:
The Gambusia fish, also known as the mosquito fish, is a small freshwater fish that is native to North and Central America. It has been widely used as a biological control agent for mosquitoes due to its ability to consume large numbers of mosquito larvae.
There are several reasons why the release of Gambusia fish is an effective method for controlling mosquitoes:
1. Mosquito larvae consumption:
- Gambusia fish feed on mosquito larvae, which are the immature stages of mosquitoes.
- The fish are voracious feeders and can consume large quantities of mosquito larvae, helping to reduce the mosquito population.
- By reducing the number of mosquito larvae, the population of adult mosquitoes is also reduced, leading to a decrease in mosquito-borne diseases.
2. Reproduction rate:
- Gambusia fish have a high reproductive rate, with females giving birth to live young every 30-40 days.
- This rapid reproduction allows the fish population to quickly increase and maintain a stable presence in ponds and wells.
- As long as there is a constant supply of mosquito larvae, the Gambusia fish will continue to feed and reproduce, providing ongoing control of mosquitoes.
3. Adaptability:
- Gambusia fish are highly adaptable and can survive in a range of aquatic habitats, including ponds, wells, and even temporary water bodies like puddles.
- They tolerate a wide range of water conditions and can thrive in both stagnant and flowing water.
- This adaptability makes them suitable for release in various types of water bodies where mosquitoes breed.
4. Non-toxic and environmentally friendly:
- Gambusia fish are a natural predator of mosquito larvae and do not require the use of chemical pesticides.
- Their release does not pose any harm to humans, animals, or the environment.
- Unlike chemical pesticides, which can have harmful effects on other aquatic organisms and the ecosystem, Gambusia fish provide a safe and sustainable method of mosquito control.
In conclusion, the release of Gambusia fish into ponds and wells is an effective and environmentally friendly method of controlling mosquitoes. These fish feed on mosquito larvae, reproduce quickly, adapt to different water conditions, and do not pose any harm to the environment or other organisms.
2021
Which one of the following is used in preparing a natural mosquito repellent?
(a) Congress grass
(b) Elephant grass
(c) Lemongrass
(d) Nut grass
(a) Congress grass – Also known as Parthenium hysterophorus, Congress grass is an invasive weed and is not known to be used as a mosquito repellent.
(b) Elephant grass – Also known as Napier grass or Pennisetum purpureum, Elephant grass is typically used as a fodder crop and doesn’t have properties that make it suitable for mosquito repellent.
(c) Lemongrass – Lemongrass, scientifically known as Cymbopogon, is widely recognized for its insect-repelling properties. It contains citral and geraniol, which are natural compounds known to repel mosquitoes. Many natural mosquito repellents contain lemongrass oil or extracts. Hence Option (c) is correct.
(d) Nut grass – Also known as Cyperus rotundus, nut grass has been used in traditional medicine but isn’t specifically known for its mosquito repellent properties.
2023
‘Wolbachia method’ is sometimes talked about with reference to which one of the following?
(a) Controlling the viral diseases spread by mosquitoes
(b) Converting crop residues into packing material
(c) Producing biodegradable plastics
(d) Producing biochar from thermo-chemical conversion of biomass
The Wolbachia method is simple. When Aedes aegypti mosquitoes carry Wolbachia, the bacteria compete with viruses like dengue, Zika, chikungunya and yellow fever. This makes it harder for viruses to reproduce inside the mosquitoes. And the mosquitoes are much less likely to spread viruses from person to person. This means that when Aedes aegypti mosquitoes carry natural Wolbachia bacteria, the transmission of viruses like dengue, Zika, chikungunya and yellow fever is reduced.
Advantages of Wolbachia
Wolbachia is a good bacterium for certain insects.
- The flies and mosquitos infected with Wolbachia bacteria are more resistant to RNA viruses such as West Nile virus, Chickungunya virus, cricket paralysis virus, flock house virus and Norovirus.
- In leafminers, the bacteria help their hosts to produce green islands. The leafminers are insects that lives and easts the leaf tissues in their larval stage.
- The Wolbachia bacteria help the leafminers to produce green islands on the leaves that are yellowing. This allows the larva to grow to their adult forms. It helps in iron metabolism in some of the insect species.
- The occurrence of Wolbachia in household mosquitos help them remain resistant to insecticides. The Wolbachia induce fecundity in some of their hosts.
- Fecundity is fertility selection. It is the fitness advantage that increase the number of offspring.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies