- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Phosphorus Bombs
Recently, Ukrainian police has accused Russian forces of launching phosphorus bomb attacks (chemical weapon) in the Lugansk and Donetsk regions of eastern Ukraine, collectively known as the Donbas.
-
International law prohibits the use of white phosphorus shells in heavily populated civilian areas, but allows them in open spaces to be used as cover for troops.
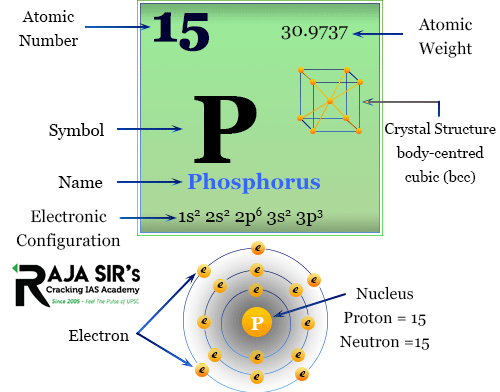
Phosphorus
Phosphorus compounds and phosphorus-based compounds are important sources of energy for many living organisms. Phosphorus can be divided into organic and inorganic forms. Organic phosphorus contains the element phosphorus combined with an organic compound, like phytic acid and folic acid.
Inorganic phosphorus is present in a variety of minerals like rock phosphate and bone phosphate. Phosphorus plays an essential role in biological processes and is the only element known to occur naturally in all living cells and organisms. As such, it is an important factor in maintaining life.
P is a vital nutrient for all forms of life on earth. Phosphorus-deficient diets can result in death. Phosphorus is the third most abundant element in the Earth’s crust after oxygen and silicon, and its chemical properties make it potentially attractive for many different energy-related applications.
The term "white mineral" was coined to describe phosphate rock because it contains phosphorus in the form of phosphoric acid. Phosphate rock is an important raw material in the chemical industry for the production of phosphoric acid, detergents, cosmetics, fertilizers, detergents, detergents, medicines, and pesticides.
The chemical compound phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) has been used as an explosive since the beginning of the twentieth century. Inorganic phosphorus is a vital nutrient for all forms of life on earth. Phosphorus-deficient diets can result in death.
Phosphorus is the fifth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and the third most abundant non-metal. Its abundance is over 100,000 times that of phosphorus in all soil. Phosphorus is a major component of many minerals, including apatite (calcium phosphate), phosphate, the major component of bone and tooth enamel, hydroxyapatite, monosodium hydrogen phosphate, diphosphate, and dihydrogen phosphate. It is a vital component of nucleotides and coenzymes. In nature, Phosphorus occurs naturally as monatomic phosphorus, as a divalent cation (P2+), as trivalent phosphorus (P3+), and as phosphorus(V).
Diseases of the skeletal system, particularly rickets and osteomalacia, which occur in both humans and animals, may be traced to dietary deficiency of phosphorus. The most widely used form is monobasic sodium phosphate. Phosphorus in phosphate form, in contrast, is generally considered to be a necessary part of the diet.
-
Allotropes: White phosphorus munitions are weapons that use one of the common allotropes of the chemical element phosphorus.
- Allotropes are two or more forms of the same element existing in the same physical state (either solid, liquid, or gas) that differ from each other in their physical, and sometimes also in chemical, properties.
-
Pyrophoric: White phosphorus is pyrophoric (it is ignited by contact with air), burns fiercely, and can ignite cloth, fuel, ammunition, and other combustibles.
-
Apart from this, it is also used in smoke, illumination, and burning elements of tracer ammunition.
-
-
Chemical Reaction: In addition to its offensive capabilities, white phosphorus is a highly efficient smoke-producing agent, reacting with air to produce an immediate blanket of phosphorus pentoxide vapour.
-
Effects: In addition to direct injuries caused by fragments of their casings, white phosphorus munitions can cause injuries in two main ways: burn injuries and vapour inhalation.
|
Property |
White phosphorous |
Red phosphorous |
|
Physical state and colour |
It is a white waxy solid. It is soft and can be cut using a knife. It turns yellow in colour in exposure to light, hence, it is also called as yellow phosphorus. |
It is red coloured hard crystalline solid. It is lustrous in nature. |
|
Odour |
It has garlic like odour. |
It is odourless. |
|
Physiological properties |
It is poisonous in nature and prolonged working this phosphorus leads to a disease known as Phossy jaw. |
It is non-poisonous in nature. |
|
Structure |
White phosphorus exists in P4P4 tetrahedral structure. |
Red phosphorus exists in polymeric form. Each P4P4 tetrahedral is linked to another to form a polymer through covalent bonds. Its melting point is higher than that of white phosphorus, |
|
Solubility |
It is insoluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents for example, ether, carbon disulphide, alcohols, etc |
It is not soluble in water as well as organic solvents |
|
Action of air |
It shows phosphorescence. Due to high angle strain, it is very reactive. It burns in air. The greenish glow is visible in the dark |
It does not glow in the dark. Due to its polymeric, it is less reactive than white phosphorus. On reaction with oxygen it gives P4O10P4O10. |
It is to be noted here is that red phosphorus exists in polymeric form and thus, is less reactive than white phosphorus. White phosphorus being less stable than red phosphorus, can be converted to red phosphorus by heating at 573K for several hours.
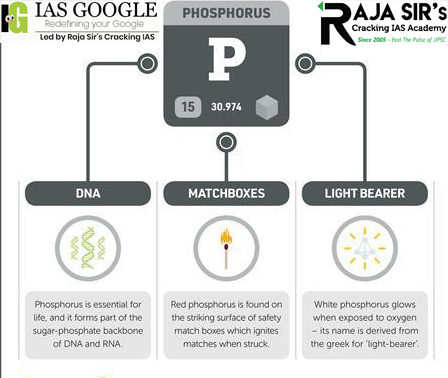 Uses of Red Phosphorus
Uses of Red Phosphorus
Red phosphorus is used in many fields. Few of its uses are listed below –
-
It is used in the production of semiconductors.
-
It is used in matchsticks.
-
It is used in production of pyrotechnics, fertilizers, and pesticides.
-
It is used in electroluminescent coatings.
-
It is used in many organic synthesis reactions.
-
Due to its stable but reactive nature, it is used in smoke bombs.
-
It is an important component of steel production.
-
Its few compounds are used in water softening as well.
Uses of White Phosphorus
-
Industries use white phosphorus to manufacture chemicals used in fertilizers, food additives, and cleaning compounds.
-
In the past, it was used as a pesticide and in fireworks.
-
The military uses white phosphorus in various types of ammunition as an incendiary agent, because it spontaneously catches fire in air. They also use it as a smoke agent, because it produces clouds of irritating white smoke.
-
It has a match-like or garlic-like, acrid odor, but do not depend on odor for detection of white phosphorus.
-
White phosphorous is least stable and most toxic of all allotropes. Upon coming on contact with air it is toxic and causes severe liver damage on digestion so it is used as rat poison.
White Phosphorus Bombs Affect Humans
White phosphorus bombs can have a worse effect on human health than other weapons of similar explosive power.
On the skin, white phosphorus causes very painful burns that may be second-degree (partial thickness of skin) to third-degree (full thickness of skin). The burns typically have a yellowish color and a garlic-like odor. You may notice smoke coming from the injury as the white phosphorus continues to burn.
In addition, because white phosphorus dissolves easily in fat, it gets absorbed easily through the skin and into the body, where it can cause other serious symptoms.
In fact, burns from white phosphorus on less than 10% of your body could lead to death because of damage to the kidneys, liver, and heart.
In addition, white phosphorus can cause serious injury and death if you inhale or swallow it.
Regular exposure to white phosphorus can make the bones of the jaw start to break down (necrosis, or “phossy jaw”).
Chemical Weapons
-
A Chemical Weapon is a chemical used to cause intentional death or harm through its toxic properties.
-
Munitions, devices and other equipment specifically designed to weaponize toxic chemicals also fall under the definition of chemical weapons.
International conventions
White phosphorus bombs are, however, not classified as chemical weapons and hence not banned. The use of chemical weapons has been prohibited by the Convention on the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons since 1997.
White phosphorous bombs are categorised as incendiary weapons. Their use is codified by Protocol III in the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW), signed in Geneva and enforced since 1983. Their usage against civilians and civilian structures is prohibited by Protocol III.
However, the protocol has legal loopholes that prevent its complete implementation or effective containment.
These loopholes relate to the definition of incendiary weapons. The definition excludes those that can be of multipurpose usage and it imposes weaker restrictions for those launched from the ground.
This has led to continued calls to strengthen Protocol III and ban the usage of white phosphorus bombs.
It''s a UN-prohibited weapon since it''s employed in smoke, lights, and during wartime to make bombs more lethal. Its use in open areas is legal under international law, but air-bursting phosphorus over inhabited areas is prohibited since it puts civilians in danger and can result in an indiscriminate attack due to the wide dispersion of burning fragments. This weapon is deadly because it burns quickly when it comes into contact with air, resulting in tremendous heat and poisonous smoke that can instantly kill a person.
Chemical Weapons Convention
-
Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) is a multilateral treaty banning chemical weapons and requiring their destruction within the stipulated time.
-
Negotiations for the CWC began in 1980 at the United Nations Conference on Disarmament.
-
The convention was drafted in September 1992 and opened for signature in January 1993. It became effective from April 1997.
-
It makes it mandatory to destroy old and abandoned chemical weapons.
-
Members should also declare the riot-control agents (sometimes referred to as ‘tear gas’) in possession of them.
-
India signed the treaty in January 1993. The Chemical Weapons Convention Act, 2000 was passed to implement the CWC.
-
Convention Prohibits:
-
The development, production, acquisition, stockpiling, or retention of chemical weapons.
-
Transferring of chemical weapons.
-
Using chemical weapons.
-
Assisting other States to indulge in activities that are prohibited by the CWC.
-
Using riot-control devices as ‘warfare methods’.
-
-
Apart from CWC, Australia Group seeks to check proliferation of chemical or biological weapons.
Australia Group
-
The Australia Group (AG) is an informal forum of countries which, through the harmonisation of export controls, seeks to ensure that exports do not contribute to the development of chemical or biological weapons.
-
The formation of the Australia Group (AG) in 1985 was prompted by Iraq’s use of chemical weapons during the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988)
-
Coordination of National export control measures assists Australia Group members to fulfil their obligations under the Chemical Weapons Convention and Biological & Toxin Weapons Convention.
-
It has 43 members (including the European union). The members work on a consensus basis. The annual meeting is held in Paris, France.
-
India joined (as 43rd Participant) the Australia Group (AG) on 19th January 2018.
-
The Australia Group decided to admit India as the Group’s through a consensus decision.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies