- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Cracking down on cryptocurrency
The world of money is changing with a strong push for private currency in the form of cryptocurrency. The normal world is divided into sovereign governments that regulate affairs of nation-states and issue their own currencies for economic functions. Cryptocurrency challenges this normal world of business and economy forcing several governments to think about regulating the emerging world of a potential parallel economy.
A cryptocurrency is essentially a digital currency. It is available on what is called block-chain technology. Some of the popular cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin and Ethereum. Their prices have incidentally crashed after the government listed a bill to regulate cryptocurrency in India.
Cryptocurrency is secured by cryptography, a complex software coding system. Blockchain technology of cryptocurrency could be understood as a distribute ledger that is recorded on a network of computers. Transactions in cryptocurrencies are recorded on respective blockchain ledgers.
This is a whole new world of currency, much different from the currencies known to the commoners of the world who are still getting used digital transactions of sovereign currencies. These digital transactions mean movement of money without physical transfer of currencies, what was the norm in pre-digital era.
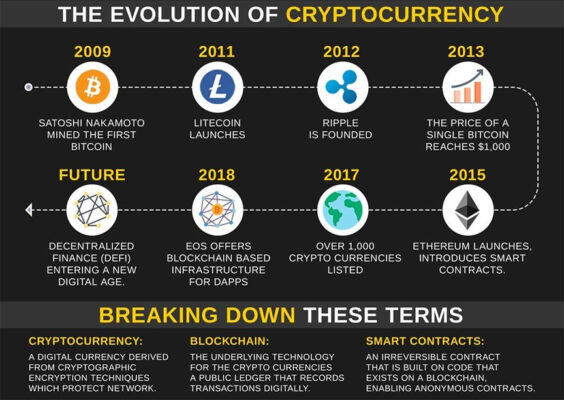 Why Crypto Currencies?
Prevent Corruption: it helps keep corruption in check by tracking the flow of funds and transactions as blocks run on a peer-to-peer network
Quicker transactions: Crypto currencies can help save money & substantial time for the remitter & the receiver, because it runs on a mechanism that involves very less transaction fees and is almost instantaneous as it is conducted entirely on the Internet
Reduced Cost - almost 3% from the total global economic output of over $100 trillion is drawn by intermediaries such as banks, credit card and payment gateways draw, as fees for their services. Integration of block chain into these sectors would result in hundreds of billions of dollars in savings.
Crypto Currencies in India
RBI in 2018 issued a circular preventing all banks from dealing in cryptocurrencies. However, it was declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 2020.
Crypto currency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill (2021)- Recently, the government has announced to introduce a bill. It is for creation of a sovereign digital currency & simultaneous ban on all private crypto currencies.
The Indian blockchain start-ups have received funds that account for less than 0.2% of the amount raised by the sector globally.
It is nearly impossible for blockchain entrepreneurs & investors to acquire much economic benefit according to the current approach towards cryptocurrencies.
Concerns w.r.t. Crypto Currencies in India
Complete ban on private currencies
The essence of Crypto currency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021 is the intended ban seeking to prohibit all private cryptocurrencies in India.
Categorization of the cryptocurrencies as public or private is inaccurate since they are decentralized but not private.
Decentralized cryptocurrencies, like bitcoin, cannot be controlled by any entity whether private or public.
Loss of talent & business
Similar to what happened after the RBI’s ban in 2018,the ban of crypto currencies may result into brain drain of both talent and business from India
Block chain experts back then moved to countries where crypto was regulated like Switzerland, Singapore, Estonia and US.
Block chain innovation has various applications in governance, data economy and energy,the blanket ban will halt all such innovative applications
Digital Revolution of financial products
The ban would mean deprivation of a transformative technology for India, its entrepreneurs & citizens, that also at a time when technology is being rapidly adopted across the world, including by some of the largest enterprises such as Tesla, MasterCard.
Encourage illegal uses
Instead of regulation, a blanket ban would create a parallel economy that would encourage illegitimate use and thus, defeat the very purpose of the ban.
Also, when any person can purchase cryptocurrency over the internet, the implementation of ban would become infeasible
Policy Uncertainty
The Draft National Strategy on Blockchain (2021) of the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), hailed blockchain technology as transparent, secure & efficient technology that puts a layer of trust over the internet, the present move contradicts this policy of MeitY
Road ahead
Regulation of crypto currencies- Regulation is necessary to protect unsuspecting investors from excessive market volatility & possible scams. It is also required to prevent serious problems and to ensure that crypto currencies are not misused
Definition of Crypto-currency: Crypto-currencies must be defined by a legal & regulatory framework as securities or other financial instruments according to the relevant national laws along with the identification of the regulatory authority .
Strong KYC Norms: By including stringent KYC norms, reporting & taxability, the government can instead regulate the trading of cryptocurrencies instead of a complete ban on crypto currencies
Accountability: To address concerns around transparency, information availability and consumer protection- record keeping, inspections, independent audits, investor grievance redressal & dispute resolution can also be considered
Boost to start up ecosystem: The entrepreneurial wave in India’s startup ecosystem can be reignited by the Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain technology. It can create employment opportunities across different levels, from blockchain developers to designers, project managers, business analysts, promoters & marketers.
Stable coins- The value is pegged to a fiat currency by maintaining equivalent reserves. These Stable coins hope to serve as viable mediums of exchange by providing greater price stability
Suggestions by IMF- According to the IMF, if crypto currencies are only used for niche purposes that is narrow cross-country transfers and remittances that are then rapidly converted back into local fiat currencies, the implications for monetary policy can be contained.
Why Crypto Currencies?
Prevent Corruption: it helps keep corruption in check by tracking the flow of funds and transactions as blocks run on a peer-to-peer network
Quicker transactions: Crypto currencies can help save money & substantial time for the remitter & the receiver, because it runs on a mechanism that involves very less transaction fees and is almost instantaneous as it is conducted entirely on the Internet
Reduced Cost - almost 3% from the total global economic output of over $100 trillion is drawn by intermediaries such as banks, credit card and payment gateways draw, as fees for their services. Integration of block chain into these sectors would result in hundreds of billions of dollars in savings.
Crypto Currencies in India
RBI in 2018 issued a circular preventing all banks from dealing in cryptocurrencies. However, it was declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 2020.
Crypto currency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill (2021)- Recently, the government has announced to introduce a bill. It is for creation of a sovereign digital currency & simultaneous ban on all private crypto currencies.
The Indian blockchain start-ups have received funds that account for less than 0.2% of the amount raised by the sector globally.
It is nearly impossible for blockchain entrepreneurs & investors to acquire much economic benefit according to the current approach towards cryptocurrencies.
Concerns w.r.t. Crypto Currencies in India
Complete ban on private currencies
The essence of Crypto currency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021 is the intended ban seeking to prohibit all private cryptocurrencies in India.
Categorization of the cryptocurrencies as public or private is inaccurate since they are decentralized but not private.
Decentralized cryptocurrencies, like bitcoin, cannot be controlled by any entity whether private or public.
Loss of talent & business
Similar to what happened after the RBI’s ban in 2018,the ban of crypto currencies may result into brain drain of both talent and business from India
Block chain experts back then moved to countries where crypto was regulated like Switzerland, Singapore, Estonia and US.
Block chain innovation has various applications in governance, data economy and energy,the blanket ban will halt all such innovative applications
Digital Revolution of financial products
The ban would mean deprivation of a transformative technology for India, its entrepreneurs & citizens, that also at a time when technology is being rapidly adopted across the world, including by some of the largest enterprises such as Tesla, MasterCard.
Encourage illegal uses
Instead of regulation, a blanket ban would create a parallel economy that would encourage illegitimate use and thus, defeat the very purpose of the ban.
Also, when any person can purchase cryptocurrency over the internet, the implementation of ban would become infeasible
Policy Uncertainty
The Draft National Strategy on Blockchain (2021) of the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), hailed blockchain technology as transparent, secure & efficient technology that puts a layer of trust over the internet, the present move contradicts this policy of MeitY
Road ahead
Regulation of crypto currencies- Regulation is necessary to protect unsuspecting investors from excessive market volatility & possible scams. It is also required to prevent serious problems and to ensure that crypto currencies are not misused
Definition of Crypto-currency: Crypto-currencies must be defined by a legal & regulatory framework as securities or other financial instruments according to the relevant national laws along with the identification of the regulatory authority .
Strong KYC Norms: By including stringent KYC norms, reporting & taxability, the government can instead regulate the trading of cryptocurrencies instead of a complete ban on crypto currencies
Accountability: To address concerns around transparency, information availability and consumer protection- record keeping, inspections, independent audits, investor grievance redressal & dispute resolution can also be considered
Boost to start up ecosystem: The entrepreneurial wave in India’s startup ecosystem can be reignited by the Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain technology. It can create employment opportunities across different levels, from blockchain developers to designers, project managers, business analysts, promoters & marketers.
Stable coins- The value is pegged to a fiat currency by maintaining equivalent reserves. These Stable coins hope to serve as viable mediums of exchange by providing greater price stability
Suggestions by IMF- According to the IMF, if crypto currencies are only used for niche purposes that is narrow cross-country transfers and remittances that are then rapidly converted back into local fiat currencies, the implications for monetary policy can be contained.

 Why Crypto Currencies?
Prevent Corruption: it helps keep corruption in check by tracking the flow of funds and transactions as blocks run on a peer-to-peer network
Quicker transactions: Crypto currencies can help save money & substantial time for the remitter & the receiver, because it runs on a mechanism that involves very less transaction fees and is almost instantaneous as it is conducted entirely on the Internet
Reduced Cost - almost 3% from the total global economic output of over $100 trillion is drawn by intermediaries such as banks, credit card and payment gateways draw, as fees for their services. Integration of block chain into these sectors would result in hundreds of billions of dollars in savings.
Crypto Currencies in India
RBI in 2018 issued a circular preventing all banks from dealing in cryptocurrencies. However, it was declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 2020.
Crypto currency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill (2021)- Recently, the government has announced to introduce a bill. It is for creation of a sovereign digital currency & simultaneous ban on all private crypto currencies.
The Indian blockchain start-ups have received funds that account for less than 0.2% of the amount raised by the sector globally.
It is nearly impossible for blockchain entrepreneurs & investors to acquire much economic benefit according to the current approach towards cryptocurrencies.
Concerns w.r.t. Crypto Currencies in India
Complete ban on private currencies
The essence of Crypto currency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021 is the intended ban seeking to prohibit all private cryptocurrencies in India.
Categorization of the cryptocurrencies as public or private is inaccurate since they are decentralized but not private.
Decentralized cryptocurrencies, like bitcoin, cannot be controlled by any entity whether private or public.
Loss of talent & business
Similar to what happened after the RBI’s ban in 2018,the ban of crypto currencies may result into brain drain of both talent and business from India
Block chain experts back then moved to countries where crypto was regulated like Switzerland, Singapore, Estonia and US.
Block chain innovation has various applications in governance, data economy and energy,the blanket ban will halt all such innovative applications
Digital Revolution of financial products
The ban would mean deprivation of a transformative technology for India, its entrepreneurs & citizens, that also at a time when technology is being rapidly adopted across the world, including by some of the largest enterprises such as Tesla, MasterCard.
Encourage illegal uses
Instead of regulation, a blanket ban would create a parallel economy that would encourage illegitimate use and thus, defeat the very purpose of the ban.
Also, when any person can purchase cryptocurrency over the internet, the implementation of ban would become infeasible
Policy Uncertainty
The Draft National Strategy on Blockchain (2021) of the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), hailed blockchain technology as transparent, secure & efficient technology that puts a layer of trust over the internet, the present move contradicts this policy of MeitY
Road ahead
Regulation of crypto currencies- Regulation is necessary to protect unsuspecting investors from excessive market volatility & possible scams. It is also required to prevent serious problems and to ensure that crypto currencies are not misused
Definition of Crypto-currency: Crypto-currencies must be defined by a legal & regulatory framework as securities or other financial instruments according to the relevant national laws along with the identification of the regulatory authority .
Strong KYC Norms: By including stringent KYC norms, reporting & taxability, the government can instead regulate the trading of cryptocurrencies instead of a complete ban on crypto currencies
Accountability: To address concerns around transparency, information availability and consumer protection- record keeping, inspections, independent audits, investor grievance redressal & dispute resolution can also be considered
Boost to start up ecosystem: The entrepreneurial wave in India’s startup ecosystem can be reignited by the Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain technology. It can create employment opportunities across different levels, from blockchain developers to designers, project managers, business analysts, promoters & marketers.
Stable coins- The value is pegged to a fiat currency by maintaining equivalent reserves. These Stable coins hope to serve as viable mediums of exchange by providing greater price stability
Suggestions by IMF- According to the IMF, if crypto currencies are only used for niche purposes that is narrow cross-country transfers and remittances that are then rapidly converted back into local fiat currencies, the implications for monetary policy can be contained.
Why Crypto Currencies?
Prevent Corruption: it helps keep corruption in check by tracking the flow of funds and transactions as blocks run on a peer-to-peer network
Quicker transactions: Crypto currencies can help save money & substantial time for the remitter & the receiver, because it runs on a mechanism that involves very less transaction fees and is almost instantaneous as it is conducted entirely on the Internet
Reduced Cost - almost 3% from the total global economic output of over $100 trillion is drawn by intermediaries such as banks, credit card and payment gateways draw, as fees for their services. Integration of block chain into these sectors would result in hundreds of billions of dollars in savings.
Crypto Currencies in India
RBI in 2018 issued a circular preventing all banks from dealing in cryptocurrencies. However, it was declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 2020.
Crypto currency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill (2021)- Recently, the government has announced to introduce a bill. It is for creation of a sovereign digital currency & simultaneous ban on all private crypto currencies.
The Indian blockchain start-ups have received funds that account for less than 0.2% of the amount raised by the sector globally.
It is nearly impossible for blockchain entrepreneurs & investors to acquire much economic benefit according to the current approach towards cryptocurrencies.
Concerns w.r.t. Crypto Currencies in India
Complete ban on private currencies
The essence of Crypto currency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021 is the intended ban seeking to prohibit all private cryptocurrencies in India.
Categorization of the cryptocurrencies as public or private is inaccurate since they are decentralized but not private.
Decentralized cryptocurrencies, like bitcoin, cannot be controlled by any entity whether private or public.
Loss of talent & business
Similar to what happened after the RBI’s ban in 2018,the ban of crypto currencies may result into brain drain of both talent and business from India
Block chain experts back then moved to countries where crypto was regulated like Switzerland, Singapore, Estonia and US.
Block chain innovation has various applications in governance, data economy and energy,the blanket ban will halt all such innovative applications
Digital Revolution of financial products
The ban would mean deprivation of a transformative technology for India, its entrepreneurs & citizens, that also at a time when technology is being rapidly adopted across the world, including by some of the largest enterprises such as Tesla, MasterCard.
Encourage illegal uses
Instead of regulation, a blanket ban would create a parallel economy that would encourage illegitimate use and thus, defeat the very purpose of the ban.
Also, when any person can purchase cryptocurrency over the internet, the implementation of ban would become infeasible
Policy Uncertainty
The Draft National Strategy on Blockchain (2021) of the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), hailed blockchain technology as transparent, secure & efficient technology that puts a layer of trust over the internet, the present move contradicts this policy of MeitY
Road ahead
Regulation of crypto currencies- Regulation is necessary to protect unsuspecting investors from excessive market volatility & possible scams. It is also required to prevent serious problems and to ensure that crypto currencies are not misused
Definition of Crypto-currency: Crypto-currencies must be defined by a legal & regulatory framework as securities or other financial instruments according to the relevant national laws along with the identification of the regulatory authority .
Strong KYC Norms: By including stringent KYC norms, reporting & taxability, the government can instead regulate the trading of cryptocurrencies instead of a complete ban on crypto currencies
Accountability: To address concerns around transparency, information availability and consumer protection- record keeping, inspections, independent audits, investor grievance redressal & dispute resolution can also be considered
Boost to start up ecosystem: The entrepreneurial wave in India’s startup ecosystem can be reignited by the Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain technology. It can create employment opportunities across different levels, from blockchain developers to designers, project managers, business analysts, promoters & marketers.
Stable coins- The value is pegged to a fiat currency by maintaining equivalent reserves. These Stable coins hope to serve as viable mediums of exchange by providing greater price stability
Suggestions by IMF- According to the IMF, if crypto currencies are only used for niche purposes that is narrow cross-country transfers and remittances that are then rapidly converted back into local fiat currencies, the implications for monetary policy can be contained.










 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies