- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
INDIA & G7
- Recently, Italy hosted the 50th G7 Summit in Apulia from June 13 to 15, 2024. The high-level convening came against several global concerns, including the ongoing conflict in Gaza, the war in Ukraine, climate disasters, and other emerging challenges. Thus, the G7 summit in Apulia represented a pivotal opportunity for the world’s foremost democracies to discuss pressing global challenges collectively. The Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, also participated in the G7 summit. India was invited as an Outreach Country.
Participants:
- G-7 Members: U.S., Canada, Germany, France, Japan, U.K., Italy
- Special Invitees: India, Algeria, Argentina, Brazil, Jordan, Kenya, Mauritania, Tunisia, Türkiye, UAE
- Organizations: African Development Bank, IMF, OECD, UN, World Bank
- Upcoming Summit: Scheduled for 2025 in Canada’s Alberta region, with potential changes in membership and leadership.
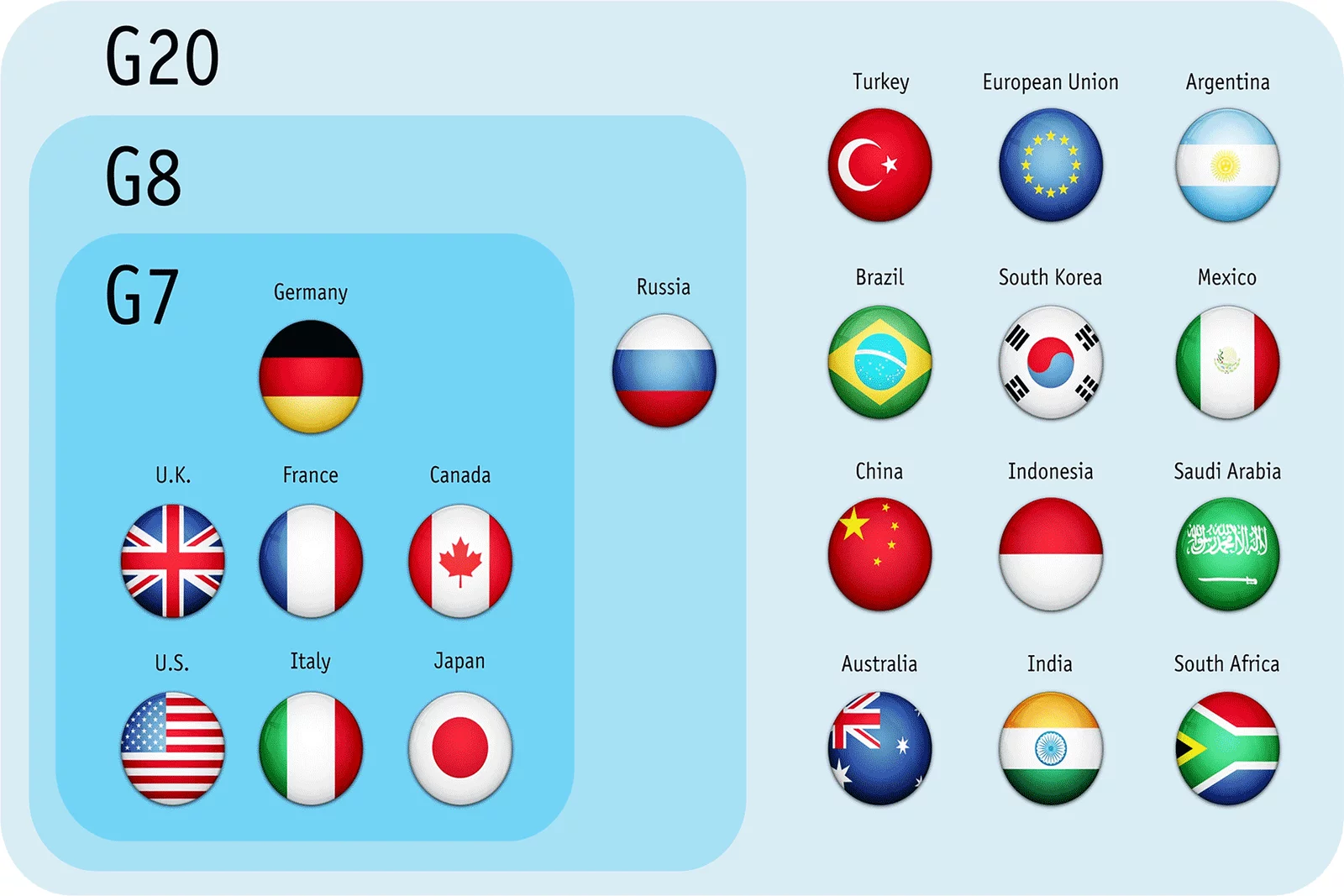
What is the G-7 Group?
- G-7 is a group of the most developed and advanced economies of the world. The members of the G7 group are France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, and Canada. Summits are held annually and hosted on a rotation basis by the group’s members.
Origin
- The G7 originated from the Oil crisis of 1973 and the resulting financial crisis, which forced the leaders of 6 major industrial nations to convene a meeting in 1975.
- The participating countries were the US, UK, France, West Germany, Japan, and Italy.
- Canada joined in 1976, leading to the formation of the G7.
- It was known as the ‘G8’ for several years after the original seven were joined by Russia in 1997, but it was renamed as G7 after Russia was expelled as a member in 2014 following its annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine.
|
Origin story
|
Nature of Grouping
- Informal Grouping: The G7 is an informal grouping that operates outside of formal treaties and lacks a permanent bureaucracy. Each member nation takes turns leading the discussions (presiding nation).
- Decision Through Consensus: Despite the absence of legal enforcement, the G7''s power stems from its members'' economic and political clout. When these major powers can agree on a course of action, it can significantly impact global issues.
- Limited Legislative Power: The G7 cannot enact laws directly. However, their pronouncements and coordinated efforts can influence international policies and shape global agendas.
|
The Oil Crisis of 1973-74 It refers to a period of sudden surge in oil prices, accompanied by a decrease in supply which has destabilised the global economy since oil is a major source of energy for many countries. Trigger:
OPEC''s Actions:
Impact:
|
Significance of India for G7
Key Global South member
- India has been a significant part of the G-7 process for years, gaining attention in the 2000s for its steady growth during the global financial crisis.
- Though not a G-7 member, India is a key Global South member and has hosted the "Voice of Global South" conference since 2023.
- It is also part of the G-20 troika with Brazil and South Africa.
Economic Growth and Stability
- India gained attention from the G7 in the 2000s due to its steady economic growth during the global financial crisis, demonstrating its resilience and potential as a major economy.
Strategic Partnerships
- India is part of the G-20 troika, along with Brazil and South Africa, which adds to its strategic importance in global economic and political discussions.
Regional Stability and Development
- India''s involvement in the G7''s outreach efforts can contribute to regional stability and development, particularly through investments and cooperation in areas like clean energy, trade, and economic development.
Geopolitical Balance
- India''s participation helps balance global geopolitical dynamics, especially in the context of rising concerns about China''s influence and trade practices.
- India''s strategic position and partnerships are crucial for maintaining global stability.
- India’s growing strategic Importance in the Indo-Pacific- India has emerged as a major strategic partner for the Western G-7 countries. This has helped in containing China’s expanding influence, particularly in the Indian Ocean.
- India’s Role in Addressing the European Energy Crisis- India’s ability to secure discounted Russian oil and supply refined fuels to Europe has made it an important player in addressing the European energy crisis.
- India’s Potential for Mediating the Russia-Ukraine Conflict- India’s long-standing relationships with both Russia and the West makes it a potential mediator in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict.
- Regulation of AI- India has been an active participant in the debate on the global regulation of AI. With the focus of G-7 countries on the regulation of Artificial Intelligence, India’s association with G-7 countries can help in the development of a common global framework for AI.
Significance of G7 for India
Crucial platform to highlight achievements and perspectives
- For India, the G-7 outreach session is a crucial platform to highlight its achievements and perspectives.
- During the session, PM Modi emphasized the importance of Indian elections, technology, artificial intelligence, and addressing climate change.
Economic Significance
- As per one estimate (2018), the G7 nations account for close to 60 percent of global net wealth ($317 trillion).
- 30 percent of global gross domestic product, and about 770 million people or 10 percent of the world''s population.
Political Significance
- Political heavyweights are capable of shaping the response of Multilateral challenges.
- In 1999, it created the Financial Stability Forum in order to manage the international monetary system
- 47th summit in June 2021 had focused on the recovery from ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. It promised to distribute 1 billion vaccines to poorer countries.
- Its theme was Global Action to Build Back Better.
Developmental Significance
- G-7 provided $300 million in 1997 to help build the containment of the reactor meltdown at Chernobyl.
- G7 played crucial role in setting up a global fund to fight malaria and Aids in 2002.
- In October 2020, G7 finance ministers backed an extension of a G20 bilateral debt relief initiative for the world''s poorest countries
Advocacy for the Global South
- India uses the G7 platform to advocate for the concerns of the Global South, such as economic inequality, climate change, and resource security.
- This advocacy helps ensure that the voices of developing nations are heard in global decision-making processes.
Technological and Climate Initiatives
- India''s participation in G7 discussions on technology and climate change allows it to contribute to and benefit from global initiatives aimed at addressing these critical issues.
- It also provides an opportunity for India to share its innovations and approaches.
Showcasing Democratic Values
- By participating in the G7, India reinforces its commitment to democratic values and principles, aligning itself with other major democracies and highlighting the importance of democratic governance on the global stage.
|
Some Key Outcomes of G-7 Group Summit
|
Challenges faced by G-7 Group:
- G7 is not representative in current times- In the initial years, it accounted for 2/3rd of global GDP. However, the G-7 group now accounts only for 1/3rd on PPP basis and less than 50% on nominal basis (market prices). The emerging 7 (E7) economies of India, China, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico, Russia, Turkey are not part of it.
- Failure in tackling Global issues- G7 failed in tackling global issues and challenges of Climate change, terrorism, West Asian crisis, COVID 19 pandemic.
- Historical Polluters- G-7 accounts for 59% of historical CO2 emissions and pledged phase out fossil fuels. There has been no visible progress of the same and they currently account for twice the CO2 emission than African continent.
- Trade Conflicts- Trade disputes among G7 members and with other countries disrupt global economic stability. Weakening of rules based of trade regime through WTO and trade wars has active role of G7 countries.
- Populism and Nationalism- The rise of populist and nationalist movements within G7 countries challenge multilateral cooperation and the G-7 group’s commitment to globalism and liberal democratic values.
Challenges with India’s further deepening of engagement with G-7 Countries
- Escalating conflict in Europe- With the escalation of conflict in Europe, India finds it hard to duck its consequences. This is reflected in the choice of Indian PM to stay away from the Ukraine peace conference in Switzerland that took place after the G7 summit.
- Defence Dependence on Russia- India’s reliance on Russia for over 60% of its military equipment creates a complex situation. A strained West-Russia relationship could disrupt supply chains and force India to diversify its defence partnerships.
- Economic Interdependence- Deep economic ties with both the US and China makes it difficult for India to balance its trade relations with both these countries.
- Geopolitical Rivalry- The intensified competition between the US and China in the Indian Ocean region forces India to take sides on issues that don’t directly align with its national interests.
- Non Inclusion of India as a permanent member- G-7 has an obsolete membership structure which does not include the emerging economies like India.
Way Forward
- India’s evolving relationship with the G7 signifies its growing importance in global economic and strategic affairs. The synergies between India and G7 nations, driven by shared values and mutual interests, present vast opportunities for collaborative growth. As India continues to rise on the global stage, its partnership with the G7 will play a pivotal role in shaping a balanced and inclusive world order. Following should be the way forward-
- Deepening Economic Ties- Encouraging investment in sectors like renewable energy, technology, infrastructure and enhancing trade liberalization efforts can bolster economic relations between India and G-7 group.
- Strategic Collaborations- Strengthening defense cooperation through joint exercises, intelligence sharing, and technology transfers can address common security challenges.
- Multilateral Engagement- India’s active participation in G7 forums can contribute to shaping inclusive global governance frameworks. Joint efforts in climate action, focusing on sustainable development and green technologies, can set benchmarks for global environmental policies.
- Technological Innovation- Collaborative efforts in digital infrastructure development, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence can drive the next wave of technological advancements. Joint research initiatives in fields like biotechnology, space exploration, and renewable energy can foster innovation.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies