- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Maglev trains
- Magnetic levitation, maglev, or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational acceleration and any other accelerations.
- The two primary issues involved in magnetic levitation are lifting forces: providing an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity, and stability: ensuring that the system does not spontaneously slide or flip into a configuration where the lift is neutralized.
Magnetic levitation is used for maglev trains, contactless melting, magnetic bearings and for product display purposes
- Maglev, the name derived from magnetic levitation, is a transport method that uses magnetic levitation to move vehicles without touching the ground
- It hovers 10 centimeters above the tracks and is propelled by electrically charged magnets. The use of a magnetic charge helps the train to lift and move it above a guide way
- The technology used in the train provides a smooth, quiet ride in almost twice as a traditional high-speed rail
Central Japan Railway has planned to bring the train into service in 2027 by plying it on the 286 kilometer route between Tokyo and the central city of Nagoya. It is expected that the maglev trains will link Tokyo and Osaka by slashing the journey time to its half by 2045. Japan is well-established as the world leader in high-speed trains. It developed the first bullet train in 1964.
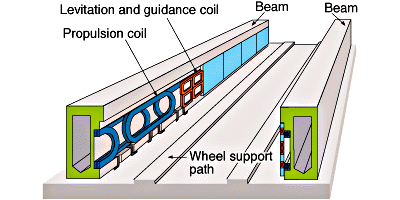
- The main difference between both the trains is that conventional trains need steel wheels and a steel track for their movement and MAGLEV does not need wheels. They travel under the principle of electromagnetic suspension.
- Another difference is in the engine used. MAGLEV trains do not need engines like conventional trains. The engine used for conventional trains provide power to pull a chain of compartments along steel tracks. In MAGLEV trains, the power to propel the train is provided by the magnetic fields created by the electric coils kept in the guidance tracks which are added together to provide huge power.
- The track along which the train moves is called the guide way. Both the guide way as well as the train’s undercarriage also have magnets which repel each other. Thus the train is said to levitate about 0.39 inches on top of the guide way. After the levitation is complete, enough power has to be produced so as to move the train through the guide way. This power is given to the coils within the guide way, which in turn produces magnetic fields, which pulls and pushes the train through the guide way.
- The current that is given to the electric coils of the guide way will be alternating in nature. Thus the polarity of the coils will be changing in period. Thus the change causes a pull force for the train in the front and to add to this force, the magnetic field behind the train adds more forward thrust.
Advantages of MAGLEV
- The main advantage is maintenance. There is no contact between the guide way and the train which lessens the number of moving parts. Thus the components that wear out is little.
- Another advantage is the reduction in noise. As there are no wheels running along there is no wheel noise. However noise due to air disturbance will still be there.
- The next advantage is high speed. As there are no frictional contacts, the train is prone to have more speed.
- Another advantage is that the guide way can be made a lot thicker in uphill places, after stations and so on. This will help in increasing the speed of the train further.
- MAGLEV trains are more environmentally friendly than other types of trains. In terms of energy consumption maglev trains are slightly better off than conventional trains. As there is no wheel friction with the ground, the resistive force gradually increases in the air friction. Thus, the energy efficiency difference between a MAGLEV train and a conventional train is of very small margin.
Disadvantages of MAGLEV
The initial cost of MAGLEV trains are highly costly. The guide paths are also supposed to be more costly than conventional steel railways.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies