- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
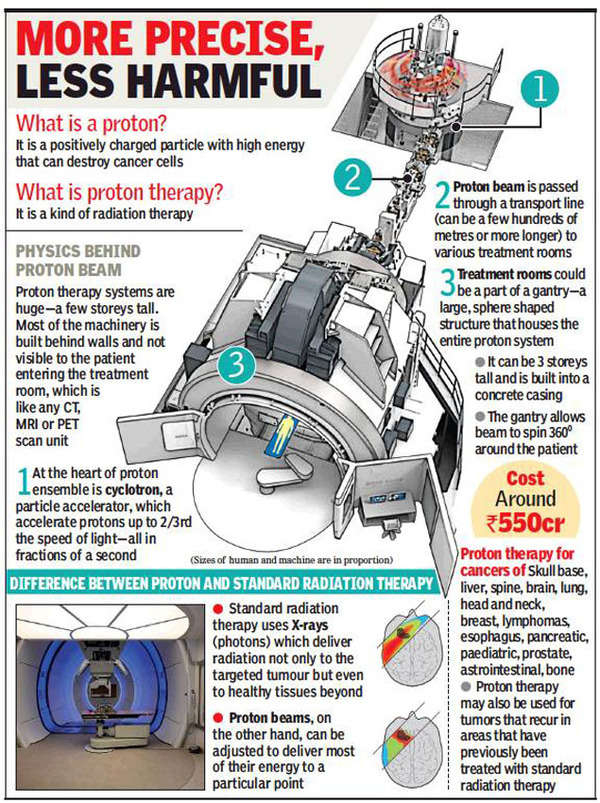
Proton Beam Therapy
Proton therapy, also called proton beam therapy, is a type of radiation therapy. It uses protons rather than x-rays to treat cancer. A proton is a positively charged particle. At high energy, protons can destroy cancer cells. Doctors may use proton therapy alone. They may also combine it with x-ray radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, and/or immunotherapy. Like x-ray radiation, proton therapy is a type of external-beam radiation therapy. It painlessly delivers radiation through the skin from a machine outside the body.
How proton therapy works
- A machine called a synchrotron or cyclotron speeds up protons. The high speed of the protons creates high energy. This energy makes the protons travel to the desired depth in the body. The protons then give the targeted radiation dose in the tumor.
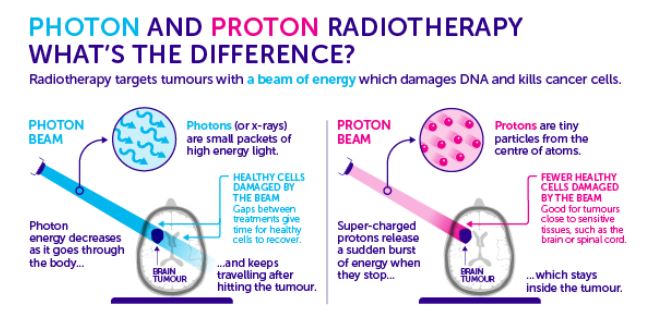
- With proton therapy, there is less radiation dose outside of the tumor. In regular radiation therapy, x-rays continue to give radiation doses as they leave the person''s body. This means that radiation damages nearby healthy tissues, possibly causing side effects.
- People usually receive proton therapy in an outpatient setting. This means they do not need to have treatment in the hospital. The number of treatment sessions depends on the type and stage of the cancer.
- Cancers treated with proton therapy Proton therapy is useful for treating tumors that have not spread and are near important parts of the body. For instance, cancers near the brain, spinal cord and eye. It is also used for treating children because it lessens the chance of harming healthy, growing tissue.
Risks and benefits
- Compared with x-ray radiation therapy, proton therapy has several benefits: Usually, up to 60% less radiation can be delivered to the healthy tissues around the tumor. This lowers the risk of radiation damage to these tissues. It may allow for a higher radiation dose to the tumor. This increases the chances that all of the tumor cells targeted by the proton therapy will be destroyed. It may cause fewer and less severe side effects such as low blood counts, fatigue, and nausea during and after treatment.
- But there are also some drawbacks to proton therapy: Because proton therapy requires highly specialized and costly equipment, it is available at just a few medical centers. Not all cancers can be treated with proton therapy.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies