Quantum Key Distribution(QKD)
- Recently, a joint team of experts from the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi demonstrated the Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) link.
-
- It was done for a distance of over 100 kilometres between Prayagraj and Vindhyachal in Uttar Pradesh..
- The technological breakthrough of demonstrating a QKD Link was achieved over the commercial-grade optical fibre already available in the field.
- With this success, the country has demonstrated indigenous technology of secure key transfer for bootstrapping military-grade communication security key hierarchy.
- International standards:
- The demonstration performance parameters were closely monitored and were found to be repetitively within the reported international standards.
 Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
-
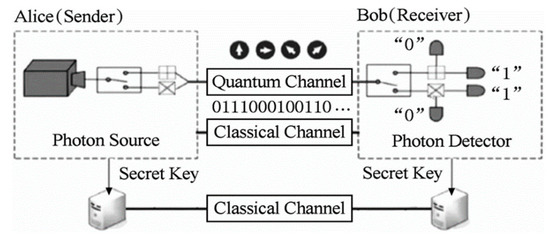
- QKD is primarily a mechanism to undertake secure communication, which utilises a cryptographic protocol involving various components of quantum mechanics.
- Process:
- The technology enables two communicating sides to come up with random secret keys shared by both of them and known exclusively to them, so only they can use it to encrypt and decrypt messages, thus achieving a very highly-secure communication.
- Key sharing:
- The distribution of encryption keys is the crucial factor for this. Sharing of keys over the air or wired links requires encryption, which in turn requires encryption keys to be pre-shared.
- Quantum-based communication offers a robust solution to sharing the keys securely.
- Use:
- Secure communications are vital not just for the defence and strategic agencies across the globe but also for various civilian applications.
- Indian agencies:
- DRDO has undertaken multiple projects for the development of this technology.
Significance
- This technology will enable security agencies to plan a suitable quantum communication network with indigenous technology backbone.
- Highly secured military grade communications could occur now.
Other achievements by DRDO
- Shorter distance feat:
- A similar demonstration was held over a shorter distance in December 2020, when the technology was tested for communication between two DRDO facilities in Hyderabad—the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) and Research Centre Imarat (RCI)—over a distance of 12 km.
- Quantum Random Number Generation (QRNG):
- DRDO Young Scientist Laboratory for Quantum Technologies (DYSL-QT), a DRDO facility based in Mumbai, developed a Quantum Random Number Generation (QRNG).
- It has the ability to detect random quantum events and convert those into a stream of binary digits.
- The QRNG system developed by DYSL-QT passed the global randomness testing standards of NIST and Die-harder Statistical Test Suites at the speed of around 150 kbps after post-processing.
- The generated random numbers were also evaluated and verified using DRDO’s indigenously developed Randomness Testing Statistical Test Suite of Scientific Analysis Group.
- With this development, India has entered the club of countries that have the technology to achieve the generation of random numbers based on the Quantum Phenomenon.
Global and domestic footing
- Global:
- Most of the large economies and defence powers across the world are in the process of formulating dedicated plans for the development of quantum technologies.
- These countries include the US, Canada, several European countries, China, Japan and South Korea.
- International symposium on Quantum Information Technology:
- It was held in Pune in 2019 and saw participation of key defence, civilian and academic and strategic entities of the country.
- India:
- India has seen significant policy decisions and budget allocation for the sector.
- China’s angle:
- Developments in India need to be seen especially in the context of several claims made by China. China has said that it has achieved multiple breakthroughs in the quantum technology domain that included:
- The world’s first quantum satellite,
- The world’s first optical quantum computing machine prototype and
- A 2000 km long quantum communication link between Beijing and Shanghai.
- China’s 13th and 14th five-year plans give high priority to quantum technology.
- In the context of China’s progress—or claims thereof—in quantum technology, India’s efforts, though significant, are scattered in nature.
Challenges
- China’s growth:
- China is leading the race. It established the first Quantum Satellite Network and distributed entangled photons between three terrestrial base stations separated by 1200 km.
- Quantum is at the heart of China’s 13th five-year plan.
- Chinese dominated in Quantum Computing patents in the last four years.
- Global investments in quantum computing are also growing in their favour.
- Funding in India:
- India has a mix of private and government sector investments.
- And neither is sufficient for the growth required to beat China.
- Absence of Roadmap:
- There is an absence of a quantum roadmap.
- There is no visibility in quantum efforts and successes.
- Lacking Skill Set:
- There is a lack of required skill power.
Road Ahead
- India’s Union Budget of 2020-21 saw the allocation of Rs 8,000 crore towards the National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications.
- While India has come a long way in quantum technology since 2019, more can be done to bring all the efforts together.
Next
previous
 Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies