- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
The largest black hole ever discovered can fit 30 billion suns
Astronomers have discovered an ultramassive black hole using gravitational lensing, a phenomenon where a foreground object bends light from a distant object behind it.
Ultramassive Black Hole
- Researchers used supercomputer simulationsto simulate light from a distant galaxy travelling through the Universe, each simulation had a black hole of a different mass.
- The path taken by the light in one simulation matched the path seen in actual images captured by the Hubble Space Telescope,leading to the discovery of an ultramassive black hole in the foreground galaxy.
- The ultramassive black hole is over 30 billion timesthe mass of our Sun.
- This new approach using gravitational lensing could make it possible to study inactive black holes in distant galaxies.
- However, most black holes that are currently known are in anactive state, pulling in matter from their surroundings and releasing energy as light, X-rays and other radiation.
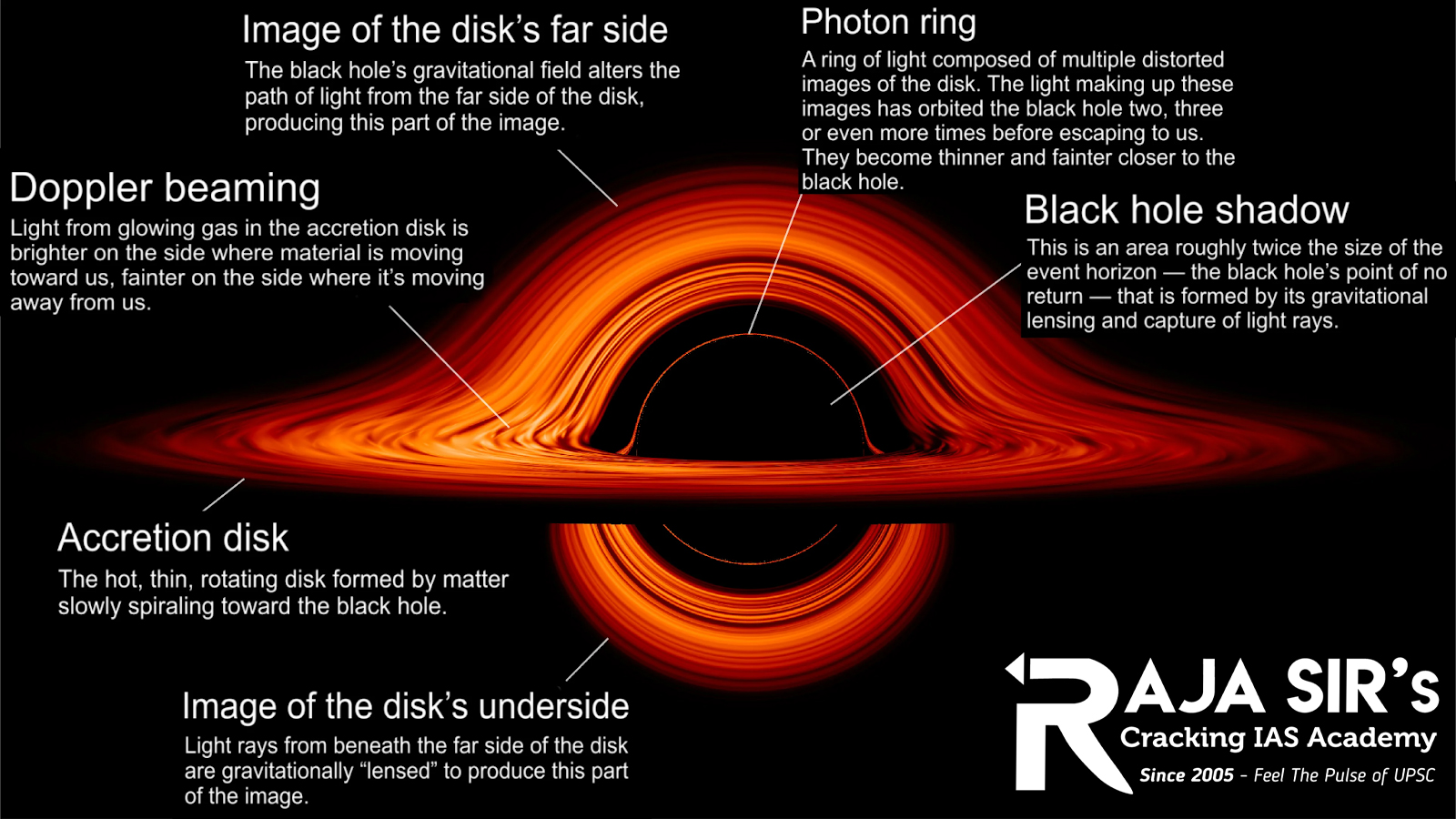
Black Hole
-
- Black holes are regions of space-time where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from them.
- They are formed when amassive star collapses in on itself at the end of its life, creating an incredibly dense object with a gravitational pull that is so strong that it warps space-time around it.
- Types of Black Holes:
- Stellar Black Hole:It is formed by the collapse of a single massive star
- Intermediate Black Hole:Their masses are between 100 and 100,000 times that of the sun.
- Supermassive Black Hole:Their masses ranging from millions to billions of times that of the sun, found at the centres of most galaxies including our own Milky Way galaxy.
- Importance:
- Black holes are important for understanding the universe and its evolution.
- They play a role in the formation and evolution of galaxiesand the distribution of matter throughout the universe.
- Studying black holes can also help us understand the fundamental properties of space, time, and gravity.
Gravitational Lensing
- Gravitational lensingis a phenomenon where the path of light from a distant object is bent by the gravitational field of a massive object, such as a galaxy or a black hole.
- This bending of light can cause distant objects to appear distorted or magnified, depending on the alignment of the massive object and the observer.
- The effect of gravitational lensing was first predicted byAlbert Einstein in his theory of general relativity, and has since been observed and studied by astronomers.
The discovery of this ultramassive black hole using gravitational lensing is an exciting development in the study of black holes. The technique used could lead to the discovery and study of more inactive black holes in distant galaxies.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies