- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
What India's new VPN rules mean for your privacy?.
Virtual private network (VPN) service providers are up in arms against a new directive of The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team or Cert-In that mandates they must maintain all customer data for five years.
What Is A VPN?
- A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure private network from a public internet connection.
- Simply put, VPNs help you hide your internet protocol (IP) address so your online actions are virtually untraceable.
- A VPN encrypts your connection to provide greater privacy as it prevents others from seeing the data you’re transferring.
- It hides you digital activity, including the search history, links you click or the files you download.
- This keeps your data secure from any spying attempts, hackers, and cybercriminals, particularly on free public Wi-Fi networks.
- A VPN encrypts your network traffic and disguises your network identity using its servers all over the world.
- This makes it almost impossible for third parties to track your online activities and steal your data.
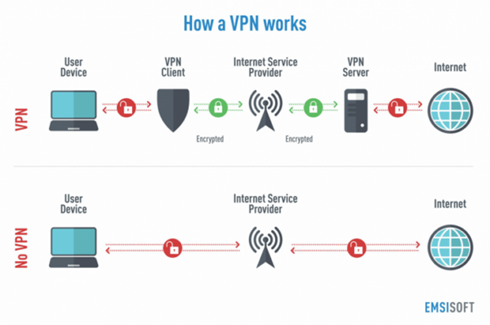
How do these networks function?
- Any and all devices connected to the internet are a part of a large network of computers, servers and other devices spread across the world.
- To identify each device connected to the internet, service providers globally assign a unique address to each such device called the internet protocol address or IP address.
- It is this IP address that helps websites, law enforcement agencies and even companies track down individual users and their accurate location.
What does the new CERT-IN directive say?
- VPN providers will need to store validated customer names, their physical addresses, email ids, phone numbers, and the reason they are using the service, along with the dates they use it and their “ownership pattern”.
- In addition, Cert is also asking VPN providers to keep a record of the IP and email addresses that the customer uses to register the service, along with the timestamp of registration.
- Most importantly, however, VPN providers will have to store all IP addresses issued to a customer and a list of IP addresses that its customers generally use.
What does this mean for VPN providers?
- VPN services are in violation of Cert’s rules by simply operating in India.
- That said, it is worth noting that ‘no logs’ does not mean zero logs.
- VPN services still need to maintain some logs to run their service efficiently.
|
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-IN)
|









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies