- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
What is Biocover?
Biocovers are a type of methane oxidation system that utilizes the fine fraction material from landfill mining to effectively control methane emissions. These are porous material layers laid directly on top of a landfill which is then covered by an oxidizing layer of mature compost. It provides optimal conditions for methanotrophic (methane-utilizing) bacteria to thrive and act as biofilters, hence controlling methane emissions by converting methane to CO2.
- They reduce methane emissions from landfills and dumpsites.
- The fine fraction material recovered from landfill mining is used to construct the biocover system. This fine fraction would otherwise be difficult to repurpose due to high contaminant levels.
- By using the fine fraction in the biocover, it provides a sustainable solution for methane control, especially for smaller to medium-sized landfills and dumpsites.
- This method shows promise for application in India’s over 3,000 legacy dumpsites, which continuously generate methane and are prone to fires, making effective methane control critical for climate change mitigation.
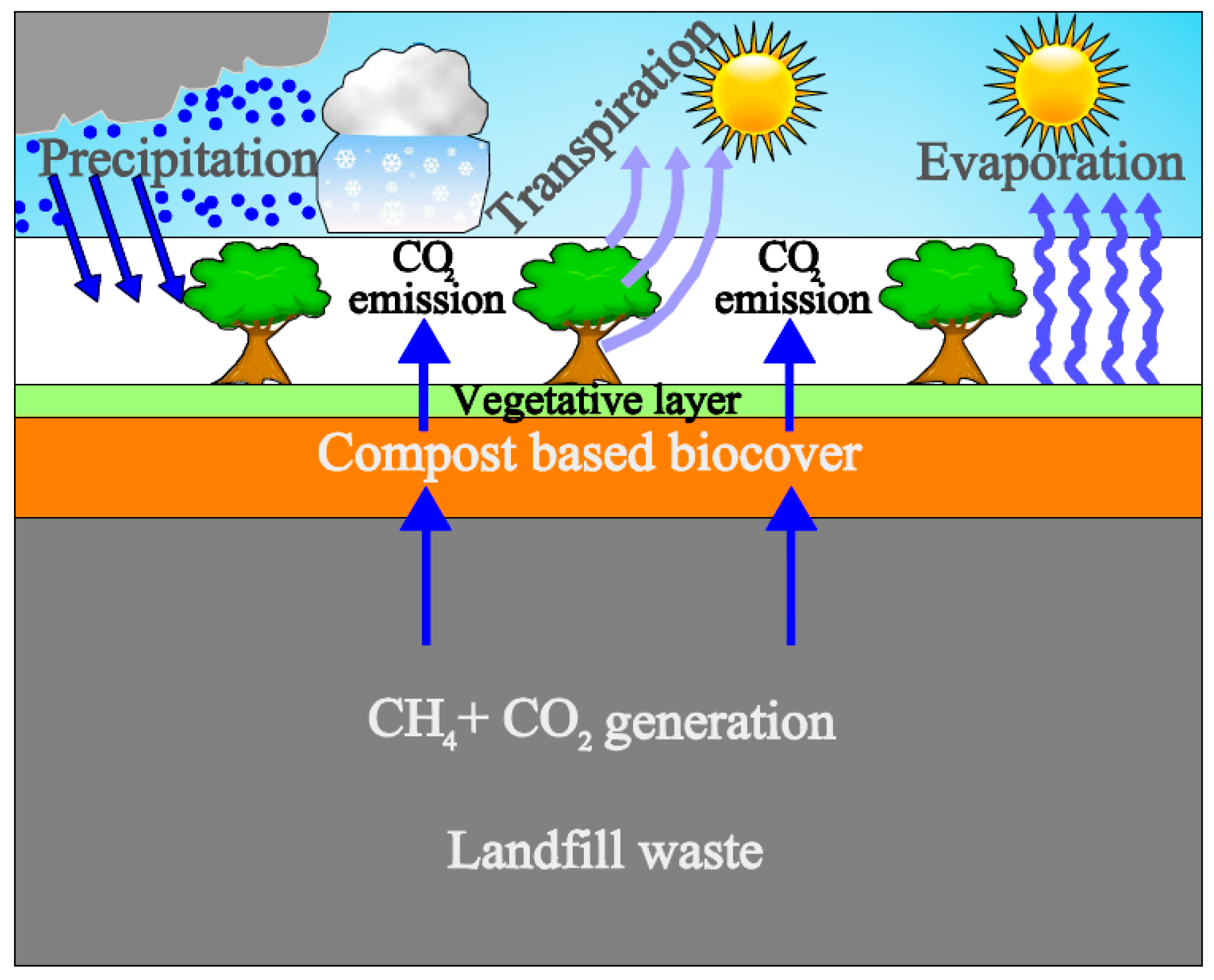
- It consists of two layers: the gas dispersion layer and the CH4 oxidation layer, where actual oxidation takes place.
- The microbial CH4 oxidation process is carried out by a group of methanotrophic bacteria present in the soil biocover.
- The CH4 oxidation layer stops a fraction of CH4 produced in landfill sites from being released into the outer atmosphere.
- Both CH4 and oxygen are required for reducing CH4 emissions using the microbial CH4 oxidation process in landfill biocover.
- The biocover layer on landfills functions as a CH4 oxidation enhancer, converting CH4 into CO2, water, and biomass.
|









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies