- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Why does Russia hate NATO?.
Among the top reasons for the ongoing war in Eastern Europe is the desire of Ukraine to become part of NATO, a Western military alliance led by the United States. To President Vladimir Putin, Ukraine becoming part of NATO poses an existential threat to Russia that is serious enough for him to start a war of the scale that Europe has not seen since the end of World War II in 1945.
Collective defence
NATO, or the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, was set up in 1949 by the US, Canada, and several western European nations to ensure their collective security against the Soviet Union. It was the US’s first peacetime military alliance outside the western hemisphere.
Thirty countries are members of NATO currently. NATO is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. The headquarters of the Allied Command Operations is near Mons, also in Belgium.
Members of NATO are committed to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. Collective defence lies at the very heart of NATO, “a unique and enduring principle that binds its members together, committing them to protect each other and setting a spirit of solidarity within the Alliance”. This is laid out in Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty, the founding treaty of NATO.
Origins and rationale
At the end of WWII, as battered European nations started to rebuild their economies, the US, which believed that an economically strong, re-armed, and integrated Europe was critical to prevent the westward expansion of communist USSR, embarked on a programme to supply economic aid to the continent on a massive scale.
The European Recovery Programme, known as the Marshall Plan after President Harry S Truman’s Secretary of State George C Marshall, promoted the idea of shared interests and cooperation between the US and Europe. The USSR declined to participate in the Marshall Plan, and discouraged eastern European states in its sphere of influence from receiving American economic assistance.
In the 1946-49 Greek Civil War, the US and UK worked to thwart the Soviet-backed communist takeover of Greece. The Western nations threw their weight behind Turkey as it stood up to Soviet pressure over control of the Bosporus and Dardanelles Strait (which connect the Black Sea and Sea of Marmara and the Sea of Marmara and Aegean Sea respectively) — and in 1947-48, the US committed itself to containing the communist uprisings in Turkey and Greece.
In 1948, Stalin’s government sponsored a coup in (erstwhile) Czechoslovakia, which led to the installation of a communist regime in a country sharing borders with both Soviet-controlled East Germany and the pro-West West Germany. In 1948-49, the Soviets blockaded West Berlin to force the US, UK, and France to give up their post-war jurisdictions in the country, leading to a major crisis and an 11-month airlift of supplies by Western countries to keep their part of the city going.
All these events led the US to conclude that an American-European alliance against the USSR was necessary. The Europeans too were convinced of the need for a collective security solution, and in March 1948, the UK, France, Belgium, Netherlands and Luxembourg signed the Brussels Treaty of collective defence, which meant that if any of the signatories faced an attack, they would be defended by all the others.
The Vandenburg Resolution was the stepping stone to NATO. The US believed the treaty would be more effective if it included, apart from the signatories of the Brussels Treaty, countries of the North Atlantic — Canada, Iceland, Denmark, Norway, Ireland, and Portugal. From the American perspective, these countries were the links between the two shores of the Atlantic Ocean, and could help facilitate military action if it was needed.
The treaty was signed in Washington DC on 4 April 1949. It had 12 signatories initially: the US, UK, Canada, France, Denmark, Belgium, Norway, Portugal, the Netherlands, Italy, Iceland, and Luxembourg.
Tensions with Russia
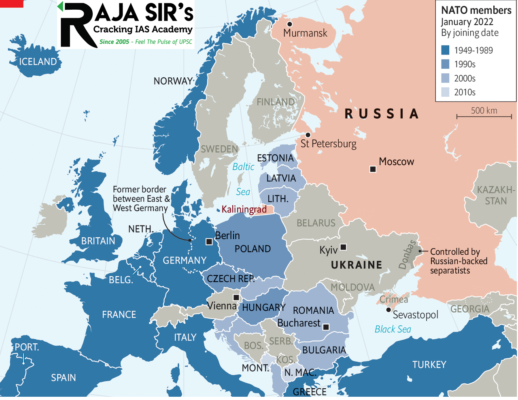 Hostility to the USSR was the reason NATO came into being, and in 1955, the Soviet Union signed its own collective defence treaty, known as the Warsaw Pact, with seven eastern European countries — Poland, Czechoslovakia, Albania, Bulgaria, East Germany, Hungary, and Romania.
The Warsaw Pact collapsed with the end of the Cold War, and was formally declared disbanded in February 1991. Among its signatories, the USSR, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany no longer exist, and the remaining five countries are part of NATO.
Barring a brief period after the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia under Putin has been suspicious and insecure about the West. The three Baltic states, now part of NATO, share borders with Russia, and only Belarus and Ukraine among the countries that were once in its sphere of influence are now outside of the western military alliance.
From the perspective of the Kremlin, keeping a buffer between NATO and Russia along its southern and western border is critical to its security. A hostile Ukraine, protected by NATO’s nuclear umbrella, could potentially have missile launchpads within a few hundred kilometres of Moscow, and cut off Russia’s access to the warm water ports of the Black Sea — it was in part to pre-empt this eventuality that Russia annexed Crimea in 2014.
Hostility to the USSR was the reason NATO came into being, and in 1955, the Soviet Union signed its own collective defence treaty, known as the Warsaw Pact, with seven eastern European countries — Poland, Czechoslovakia, Albania, Bulgaria, East Germany, Hungary, and Romania.
The Warsaw Pact collapsed with the end of the Cold War, and was formally declared disbanded in February 1991. Among its signatories, the USSR, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany no longer exist, and the remaining five countries are part of NATO.
Barring a brief period after the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia under Putin has been suspicious and insecure about the West. The three Baltic states, now part of NATO, share borders with Russia, and only Belarus and Ukraine among the countries that were once in its sphere of influence are now outside of the western military alliance.
From the perspective of the Kremlin, keeping a buffer between NATO and Russia along its southern and western border is critical to its security. A hostile Ukraine, protected by NATO’s nuclear umbrella, could potentially have missile launchpads within a few hundred kilometres of Moscow, and cut off Russia’s access to the warm water ports of the Black Sea — it was in part to pre-empt this eventuality that Russia annexed Crimea in 2014.
 Hostility to the USSR was the reason NATO came into being, and in 1955, the Soviet Union signed its own collective defence treaty, known as the Warsaw Pact, with seven eastern European countries — Poland, Czechoslovakia, Albania, Bulgaria, East Germany, Hungary, and Romania.
The Warsaw Pact collapsed with the end of the Cold War, and was formally declared disbanded in February 1991. Among its signatories, the USSR, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany no longer exist, and the remaining five countries are part of NATO.
Barring a brief period after the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia under Putin has been suspicious and insecure about the West. The three Baltic states, now part of NATO, share borders with Russia, and only Belarus and Ukraine among the countries that were once in its sphere of influence are now outside of the western military alliance.
From the perspective of the Kremlin, keeping a buffer between NATO and Russia along its southern and western border is critical to its security. A hostile Ukraine, protected by NATO’s nuclear umbrella, could potentially have missile launchpads within a few hundred kilometres of Moscow, and cut off Russia’s access to the warm water ports of the Black Sea — it was in part to pre-empt this eventuality that Russia annexed Crimea in 2014.
Hostility to the USSR was the reason NATO came into being, and in 1955, the Soviet Union signed its own collective defence treaty, known as the Warsaw Pact, with seven eastern European countries — Poland, Czechoslovakia, Albania, Bulgaria, East Germany, Hungary, and Romania.
The Warsaw Pact collapsed with the end of the Cold War, and was formally declared disbanded in February 1991. Among its signatories, the USSR, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany no longer exist, and the remaining five countries are part of NATO.
Barring a brief period after the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia under Putin has been suspicious and insecure about the West. The three Baltic states, now part of NATO, share borders with Russia, and only Belarus and Ukraine among the countries that were once in its sphere of influence are now outside of the western military alliance.
From the perspective of the Kremlin, keeping a buffer between NATO and Russia along its southern and western border is critical to its security. A hostile Ukraine, protected by NATO’s nuclear umbrella, could potentially have missile launchpads within a few hundred kilometres of Moscow, and cut off Russia’s access to the warm water ports of the Black Sea — it was in part to pre-empt this eventuality that Russia annexed Crimea in 2014.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies