- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
01st Oct 2021
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION-URBAN 2.0 AND AMRUT 2.0 (ATAL MISSION FOR REJUVENATION AND URBAN TRANSFORMATION) - MISSIONS DESIGNED TO MAKE TO MAKE ALL OUR CITIES ‘GARBAGE FREE’ AND ‘WATER SECURE’
The Prime Minister has launched Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 and Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation 2.0 on 1st October 2021 in New Delhi.
Highlights:




- SBM-U 2.0 and AMRUT 2.0 have been designed to make all cities ‘Garbage Free’ and ‘Water Secure’.
- It will address the challenges of urbanization and contribute towards achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals 2030.
- It envisions to make all cities ‘Garbage Free’ and ensure grey and black water management in all cities.
- To make urban local bodies as ODF+ and those with a population of less than 1 lakh as ODF++, thereby achieving the vision of safe sanitation in urban areas.
- It will focus on source segregation of solid waste, utilizing the principles of reduce, reuse, recycle,
- It focuses on scientific processing of municipal solid waste and remediation of legacy dumpsites for effective solid waste management.
- The outlay of SBM-U 2.0 is around ₹1.41 lakh crore.

- The (SBM-U), was launched on 2nd October 2014
- Aim: To make urban India free from open defecation and achieving 100% scientific management of municipal solid waste in 4,041 statutory towns in the country.
- The Scheme comes under Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Elimination of open defecation
- Eradication of Manual Scavenging
- Modern and Scientific Municipal Solid Waste Management
- To effect behavioral change regarding healthy sanitation practices
- Generate awareness about sanitation and its linkage with public health
- Participation of private sector in Capex capital expenditure, operation, and maintenance.
- Construction of 66.42 Lakh individual household toilets (IHHL).
- Construction of 2.52 lakh community toilet (CT) seats.
- Construction of 2.56 lakh public toilet (PT) seats.
- Achieving 100% door-to-door collection and scientific management of municipal solid waste.

- It aims to provide 100% coverage of water supply to all households in 4,700 urban local bodies by providing 2.68 crore tap connections.
- Focus on 100% coverage of sewerage and septage in 500 AMRUT cities by providing 2.64 crore sewer septage connections will benefit more than 10.5 crore people in urban areas.
- It will adopt the principles of circular economy and promote conservation of surface and groundwater bodies.
- Promote data led governance in water management and Technology Sub-Mission to leverage latest global technologies and skills.
- ‘Pey Jal Survekshan’ will be conducted to promote progressive competition among cities.
- The outlay of AMRUT 2.0 is around ₹2.87 lakh crore.
- The Government of India launched Mission AMRUT in 2015.
- Aim: To provide basic amenities like water supply, sewerage, urban transport, parks to improve the quality of life for the poor and the disadvantaged.
- The focus is on infrastructure creation to provide better services to the citizens.
- The Mission covers 500 cities including cities and towns with a population of one lakh with notified Municipalities.
- It is regulated by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- To ensure every household has access to a tap with assured supply of water and a sewerage connection.
- To increase the amenity value of cities by developing greenery and well-maintained open spaces.
- To reduce pollution by switching to public transport or constructing facilities for non-motorized transport.
- Digi Saksham will be implemented in the field by Aga Khan Rural Support Programme India (AKRSP-I).
- Aim: To enhance the employability of youth by imparting digital skills in the technology driven era.
- It is a joint initiative with Microsoft India.
- It will provide free training in digital skills, will be provided to more than 3 lakh youths.
- The Jobseekers can access the training through National Career Service (NCS) Portal.
- It gives priority to the job-seekers of semi urban areas belonging to disadvantaged communities including those who have lost their jobs due to Covid-19 pandemic.
- Jobseekers can access resources such as programming languages, data analytics, software development and advanced digital productivity.
- NCS was launched on 20th July, 2015.
- It provides a wide array of employment and career related services to the citizens of India.
- It works towards bridging the gap between jobseekers and employers
- Candidates can seek training, career guidance, counselling.
- Local services
- The portal brings together the households with specialized services for homes like drivers, electricians, plumbers, carpenters etc.
- It helps the small needs in the household to be addressed.
- It generates employment for people at the grassroots.
- Information for Entrepreneurs
- The self-employed workforce has a huge potential to grow and become entrepreneurs with better access to finance, technology, and open markets.
- They can provide employment opportunities to others.
- NCS brings a collation of material and helpful links to facilitate entrepreneurs for better growth.
- The assessment evaluated 707 district hospitals on 10 key performance indicators. It was based on data from 2017-18.
- District hospitals were categorised into small (up to 200 beds), medium (201-300 beds) and large (more than 300 beds).
- A district hospital had 24 beds for 100,000 people on an average.
- The World Health Organization recommends five hospital beds for every 1,000 people.
- Puducherry had the highest average beds in the country while Bihar had the lowest average of six beds per 100,000 citizens.
- Only 27% of the total 707 districts met the doctor-to-bed ratio of 29 doctors per 100 beds in a hospital.
- 88 hospitals out of 707 had the required ratio of staff nurses.
- Only 399 hospitals were found to have a ratio of paramedical staff.
- Madhya Pradesh had the highest proportion (14.8%) such hospitals, followed by Delhi (12.5%) and UP (11.4%).
- Every district hospital in India had 11 support services, compared to the required 14.
- Tamil Nadu had the highest proportion (20.2%) followed by Rajasthan (11.2%), UP (10.1%).
- Only 21 hospitals fulfilled the criteria of having all diagnostic testing services available.
- Karnataka had the highest proportion (28.6%) followed by Telangana (19%) and Gujarat (9.5%).
- Uttar Pradesh at (14.8%) had the highest proportion of hospitals with bed occupancy rate followed by Madhya Pradesh (10.9%), Maharashtra (8.2%).
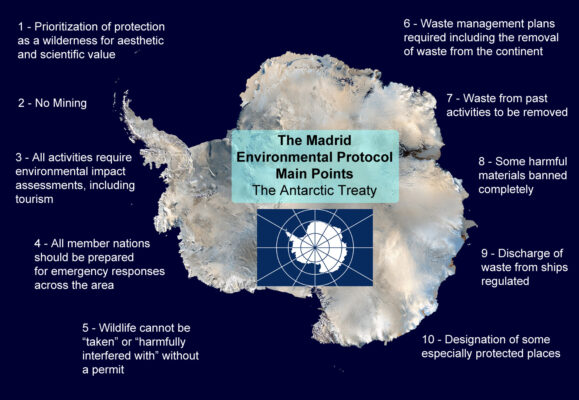
- India stood in support of sustainability in protecting the Antarctic environment.
- The two proposed MPAs are essential to regulate illegal unreported and unregulated fishing.
- India will join Australia, Norway, Uruguay, and the United Kingdom in co-sponsoring the MPA proposals by the end of October 2021.
- The support is driven by conservation and sustainable utilization principles and adhering to the global cooperation frameworks like Sustainable Development Goals, UN Decade of Oceans, Convention on Biodiversity etc.

- (MPAs) involve the protective management of natural areas according to pre-defined management objectives.
- They can be conserved for economic resources, biodiversity conservation, and species protection.
- They are created by delineating zones with permitted and non-permitted uses.
- It is vital to have in depth knowledge of the area to define ecological boundaries and set objectives for the MPA.
- It is important to have the support of the public and established techniques for surveillance and monitoring of compliance.
- IUCN engages in advocating for the expansion of the MPA network through reliable science and local stakeholders.
- (MPAAP) is a high-level venue for senior government officials from national marine protected area (MPA) agencies to discuss common issues and explore opportunities for cooperation.
- Argentina, Australia, Canada, Colombia, Finland, France, Germany, Indonesia, Italy, Malaysia, Mexico.
- New Zealand, the Philippines, the Republic of Korea, South Africa, the United Kingdom, the United States.
- The Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources came into force in 1982, as part of the Antarctic Treaty System.
- It was established in response to concerns regarding killing of fishes in the Southern Ocean and other marine life.
- To conserve and protect marine life.
- It defines a Commission and a Scientific Committee to manage marine living resources in the Southern Ocean.
- The (CCAMLR) has developed an ‘ecosystem approach’ to the regulation of fisheries.
- It has developed management approaches that assess the status of the ecosystem and its health.

- It lies between the South Shetland Islands and the continent of Antarctica.
- The sea is home to the largest number of penguin rookeries.
- It is famed for its huge ice shelves and flat-topped icebergs.
- Wildlife includes elephant seals, seabirds, and penguins.
- It was named the Weddell Sea in 1900 on a British explorer and sealer, James Weddell.

- The Ordnance Factory Board was established in 1979, comes under the Ministry of Defence.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- It supplies ammunition, and weapons used by the armed, police, and paramilitary forces.
- The products include military-grade arms and ammunition, chemicals for missile systems, explosives, propellants, armored vehicles, parachutes, troop clothing, support equipment etc.
- The decision was taken as a part of ‘Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan’.
- Government will dismantle the conglomerate into smaller companies for better autonomy, efficiency, and accountability in ordnance supplies.
- 41 factories, 9 training institutes, 4 regional controllers of safety, and 3 regional marketing centres of OFB will be restructured into 7 Defence Public Sector Units (DPSUs).
- The 7 DPSUs will be 100% state-owned.
- Gliders India Limited
- India Optel Limited
- Yantra India Limited
- Troop Comforts Limited
- Advanced Weapons and Equipment India Limited
- Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited
- Munition India Limited
- The employees across the Group A, B, & C will be transferred without any deputation allowance initially for two years from the date of appointment.
- The employees of Kolkata and New Delhi, will be transferred to the Directorate of Ordnance Factories under the Department of Defence Production for two years.
- The pay scales, allowances, medical facilities, career progression, and other services will be governed by the regulation and orders as applicable to the Central government servants.
- The pension of existing employees and retirees will be taken care by the government.

- The declaration is as per the Progress on Transboundary Water Cooperation: global status of SDG indicator 6.5.2 and acceleration needs, by UNECE and UNESCO, 2021.
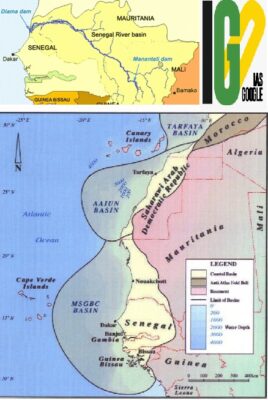
- The declaration will be first ever mechanism in West Africa and pave the way for strengthened collaboration on shared groundwater resources.
- The Senegal-Mauritanian aquifer basin is the largest basin in the Atlantic margin of north-west Africa.
- More than 24 million inhabitants of the region are dependent on it for drinking water and other needs.
- This includes the capitals of Guinea Bissau and Senegal, namely Bissau and Dakar.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies