- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
09th Sep 2021
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURAL PRACTICES USING MICROBIAL STRAINS FOR CROP PRODUCTION
Microbes can be used to improve crop quality and quantity, and contribute to sustainable agriculture practices.
Rhizobacteria:


 The rise in daily infections of COVID-19 among the States which have a high rate of vaccination, raise concerns in ‘breakthrough infections’.
The rise in daily infections of COVID-19 among the States which have a high rate of vaccination, raise concerns in ‘breakthrough infections’.

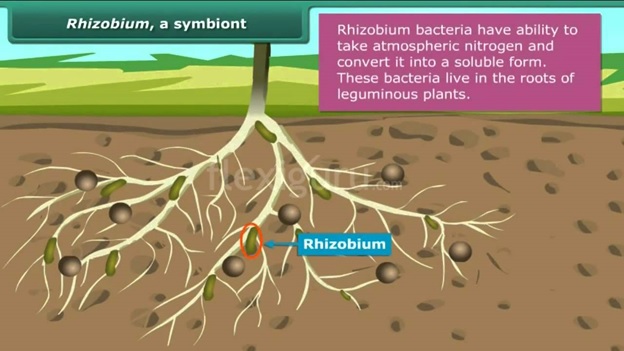
- Rhizobacteria are root-associated bacteria that form symbiotic relationships with many plants. (Rhiza in Greek means root).
- Some rhizobacteria ward off plant pathogens that cause diseases of the root, or trigger systemic resistance to a pathogen throughout the plant.
- Nitrogen fixation is one of the most beneficial processes performed by rhizobacteria.
- Nitrogen is a vital nutrient to plants. Gaseous nitrogen (N2) is not available to plants due to high energy required to break triple bonds between two Nitrogen atoms.
- Rhizobacteria through nitrogen fixation are able to convert gaseous nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) making it an available nutrient to enhance plant growth.
- The rhizobacteria require oxygen to metabolize, so oxygen is provided by a haemoglobin protein called leghaemoglobin which is produced within root nodules.
- Legumes are well-known nitrogen-fixing crops and used to maintain health of the soil.
- Mycorrhiza is a non-disease-producing association in which the fungus invades the root to absorb nutrients.
- A large number of fungi infect the roots of plants by forming an association with plants called mycorrhiza.
- About 90 percent of land plants rely on mycorrhizal fungi, especially for mineral nutrients (i.e., phosphorus), and in return the fungus receives nutrients formed by the plant.
- The trees and their seedlings can use fungal mycelium to exchange nutrients and chemical messages.
- Two breeds of buffalo– Chilika and Kalahandi, along with four breeds of cattle– Binjharpuri, Motu, Ghumusari and Khariar–and one breed of sheep, Kendrapada, have already received NBAGR recognition.

- It is found in the Eastern Ghats and plateau of Koraput region of Odisha.
- The Manda is resistant to parasitic infections, less prone to diseases and can live, produce and reproduce at low or nil input system.
- The small, sturdy buffaloes are used for ploughing in their native habitat of Koraput, Malkangiri and Nabarangpur districts.
- It has ash grey and grey coat with copper-coloured hair.
- The lower part of the legs up to elbow is light in colour with copper colour hair at the knee. Some animals are silver white in colour.
- Horns are broad and emerge slightly laterally, extending backward and inward making half circles. Jaws and nostrils are wide and prominent.
- Manda buffaloes get matured at around 3 years and drop the first calf at around 4 years. Every 1.5 to 2 years they give birth to a calf for the whole life of around 20 years.
- Average calving interval of these buffaloes is 18 months with gestation period of 307 days.
- They are moderate milk yielders having lactation milk yield of around 700 lt.
- The average milk yield of these buffaloes is 2 to 2.5 litre in single milking with more than 8% fat. However, a few of those yield up to 4 litres.
- These animals are famous for longevity, hard work and length of working life.
- The National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources and National Institute of Animal Genetics were merged in 1995 to function as a single unit in the form of National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources.
- It acts as an organization which could undertake the responsibility of evaluating, certifying and conserving the rich and varied germplasm resources available in the country and whose genetic base is shrinking fast.
- Identification, Evaluation, Characterization, Conservation and sustainable Utilization of Livestock and Poultry Genetic Resources.
- Coordination and capacity building in animal genetic resources management and policy issues.
- To conduct systematic surveys to characterise, evaluate and catalogue farm livestock and poultry genetic resources and to establish their National Data Base.
- To design methodologies for ex situ conservation and in situ management and optimal utilization of farm animal genetic resources.
- To undertake studies on genetic characterisation using modern biological techniques such as molecular cytogenetics, Immunology, DNA Fingerprinting, RFLP analysis etc.
- To conduct training programmes as related to evaluation, characterisation and utilisation of animal genetic resources.
- It is basically be a centre for information regarding the genetic resources in the country and will act as a link between ICAR Institutes, Agricultural Universities, Government or Private Agencies, national and international organizations which are concerned with livestock.
- It also supports such agencies to maintain rare species and breeds of animals which are in danger of extinction.
- Wherever information is not available or existing performance data are scanty, the Bureau will help in setting up herds and flooks for the purpose of evaluating the breeds and strains.

- National Auminium Company Ltd (NALCO) unveiled Namasya (NALCO Micro & Small enterprise Yogayog Application) for the micro & small enterprises.
- The App provides a platform and support to micro and small-scale industries to carry out their businesses.
- The App empowers MSEs with required information about vendor registration process and supports vendor development and training programmes of NALCO.
- Guinea is located in western Africa.
- Guinea is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean, Guinea-Bissau to the west, Senegal and Mali to the north, Cote d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) to the east, and Liberia and Sierra Leone to the south.
- The country has a coastline along the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest. It is located in the Northern and Western Hemispheres.
 The rise in daily infections of COVID-19 among the States which have a high rate of vaccination, raise concerns in ‘breakthrough infections’.
The rise in daily infections of COVID-19 among the States which have a high rate of vaccination, raise concerns in ‘breakthrough infections’.
- A ‘breakthrough infection’ refers to the virus being able to penetrate the protective barrier of antibodies.
- If a person gets infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus 14 days after the second shot of the vaccine, it is called a ‘breakthrough infection’.
- The two-week window is the time it takes for the body to produce necessary antibodies following a shot of the vaccine.
- It was the 28th edition of the Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX).
- Singapore India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX) is an annual bilateral naval exercise conducted by Indian Navy and Singapore Navy since 1994.
- It is Indian Navy's longest uninterrupted bilateral maritime exercise with any foreign navy.
- The Indian Navy deployed its guided-missile destroyer INS Ranvijay, anti-submarine warfare corvette INS Kiltan and guided-missile corvette INS Kora and one P8I long-range maritime patrol aircraft for the 'SIMBEX' exercise.
- The Singapore Navy was represented by formidable class frigate RSS Steadfast, victory class missile corvette RSS Vigour, one Archer class submarine and one Fokker-50 maritime patrol aircraft.
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has formed a 10-member panel led by Secretary Ajay Prakash Sawhney.
- It will formulate a process to support existing and upcoming start-up accelerators, which would then select information technology-based start-ups to scale for solving India’s problems creating positive social impact.
- The 4th edition of AUSINDEX is being held in September 2021 in North Australian exercise area.
- Includes complex surface and air operations between ships, submarines, helicopters, and Long-Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft of the participating Navies.
- Royal Australian Navy (RAN) Anzac Class Frigate, HMAS Warramunga will participate in the exercise.
- Participating Indian Naval Ships are Shivalik and Kadmatt.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies