- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
11th Sep 2021
PIYUSH GOYAL IS SHERPA FOR G20 SUMMIT
The government has appointed Union Minister for Commerce & Industry, as Sherpa for the G20 summit.
G20 Summit:

 Birth:
Birth:
 Profile:
Profile:

- The G20 is an annual meeting of leaders from the countries with the largest and fastest-growing economies.
- Its members account for 85% of the world’s GDP, and two-thirds of its population.
- After the Asian Financial Crisis in 1997-1998. The G7 finance ministers established the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors meeting in 1999.
- To promote of International Financial stability.
- To solve Balance of Payments problems and financial markets by improved coordination of monetary, fiscal, and financial policies.
- The G20 comprises 19 countries and the European Union.
- The 19 countries are: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany, France, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States.
- The G20 does not have a permanent secretariat or Headquarters.
- G20 Presidency rotates annually according to a system that ensures a regional balance over time.
- Every year the G20 selects a country from another group to be president.
- The president is responsible for bringing together the G20 agenda in consultation with other members and in response to developments in the global economy.
- Checking tax evasion to fight corruption, choking terror funds.
- Cutting the cost of remittances, market access for key drugs.
- Reforms in the World Trade Organisation to improve its functioning
- Full implementation of the Paris Agreement
- A Sherpa is a personal representative of the leader of a member country at an international Summit meeting such as G20.
- He engages in planning, negotiation, and implementation tasks through the Summit.
- They coordinate the agenda and participate in a series of pre-Summit consultations to help negotiate their leaders’ positions.
- Sherpas are career diplomats or senior government officials appointed by the leaders of their countries.
- Sherpas meet before the start of the Summit to point out differences on various issues.
- At the G20 Summit, work progresses through two channels: the Finance Track and Sherpas’ Track.
- Track representatives, prepare the Leaders’ “Declaration” or “Communique”, which is the outcome of the G20 Summit.
- The Sherpas’ Track involves technical and policy analyses by working groups comprising officials from each member country and international organizations.
- It focuses on development-oriented issues such as agriculture, fighting corruption, employment, etc.

- The emergency has been announced to control food prices and prevent hoarding amid shortages of some staples.
- The regulations empower authorities to provide essential food items at a concessionary rate to the public.
- This done by purchasing stocks of essential food items, including paddy, rice and sugar at government-guaranteed prices, and prevent market irregularities and hoarding.
- The law also enables authorities to detain people without warrants, seize property, enter and search any premises, suspend laws and issue orders that cannot be questioned in court.
- The opposition has said that the emergency rules can be misused to stifle critics, curb protests and other democratic action.
- Due to COVID-19 pandemic, all major sources of foreign exchange earnings — exports, worker remittances and tourism has compounded the economic stress.
- Sri Lanka’s economy contracted by 3.6% in 2020.
- The foreign reserves have decreased from $7.5 billion in November 2019 to $2.8 billion in July 2021.
- Further, it has huge foreign debt repayment, especially from China.
- Sri Lanka is home to 21 million people. The country’s is dependent on imports for essentials like petroleum, sugar, dairy products, wheat, medical supplies etc.
- Sri Lanka does not have a universal public distribution system or ration cards that can ensure essential goods reach all consumers.
- Government imposed a ban import of chemical fertilizers and adopted an organic only approach in April 2021.
- This is also being blamed by the farmers (especially paddy & tea) to around 50% drop in production.
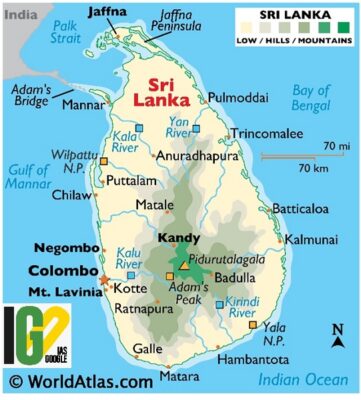
- Sri Lanka is an island country in South Asia which lies in Indian Ocean.
- It is separated from Indian subcontinent by Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait.
- Sri Lanka shares a maritime border with India and Maldives.
- Legislative Capital: Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte
- Sinhalese (buddhists) are the majority and Tamils constitute large minority group.
- It is a member of United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, G77, Non-Aligned Movement and founding member of SAARC.
- Sri Lanka is the only South Asian country with high ratings on Human Development Index.
- To empower field formations, focus on operational preparedness, promote ease of doing business and enhance jointness among the Services.
- Delegated financial powers of Vice Chiefs of the services have been increased by 10% subject to an overall ceiling of ₹500 crore.
- It empowers Field Commanders and below to procure equipment/war-like stores in a speedy manner for urgent operational necessities and meeting essential sustenance requirements.
- The critical equipment like air-to-air refuellers for Air Force can be hired for short periods as compared to buying them or a long-term lease.
- A general enhancement of up to two times has been approved for Competent Financial Authorities (CFAs).
- Financial Powers of Chief of Integrated Defence Staff to the Chairman Chiefs of Staff Committee (CISC) as CFA has been enhanced and aligned with Vice Chiefs of the Services.
- New CFAs have been added namely Deputy Chief of Army Staff, Master General Sustenance, ADG (Procurement)/DG Air Operations/DG Naval Operations etc. in service headquarters and in field formations on account of reorganisation/restructuring/functional requirements.
- Provision of Emergency Financial Powers to the Field formations below Command level for the Defence Services has been incorporated in Emergency Powers Schedule.
- The enhanced delegation of financial powers will result in:
- Overcome procedural delays
- Quicker decision-making at all levels
- Better planning and operational preparedness
- Optimum utilisation of resources
- Greater decentralisation and operational efficiency
 Birth:
Birth:
- VOC was born on 5 September 1872 in Ottapidaram, District Tirunelveli in Tamil Nadu.
- Graduated from Caldwell College, Tuticorin. Before beginning his law studies, he worked for a brief period as the taluk office clerk.
- He became a pleader in 1895 practising in Ottapidaram.
- Joined the Congress Party after the Bengal partition in 1905
- He was a follower of Bal Gangadhar Tilak.
- He was a great believer in the Swadeshi movement.
- In 1906, he decided to establish an Indian shipping company called the Swadeshi Steam Navigation Company.
- Along with Subramania Siva, he started the ‘Swadeshi Sangam’.
- Tuticorin Coral Mills strike in 1908 was the turning point in his life. The workers at the British-owned mill decided to go on a strike demanding better pay and a reduction in the number of working hours.
- He took up the workers’ cause and gave many fiery speeches which drew the people’s attention to the plight of the workers.
- V.O.C, Siva and Padmanabha Iyengar decided to hold a procession on 9 March 1908 to observe the release of national leader Bipin Chandra Pal from prison.
- On 12 March 1908, the three leaders including V.O.C, Siva and Iyengar were remanded to the district jail.
- The court sentenced V.O.C to two life imprisonments for charges of sedition.
- After he was released, he moved to Chennai with his family since he was not permitted to return to Tirunelveli.
- He was in regular correspondence with Mahatma Gandhi but later cited ideological differences with Gandhi.
- Helped in setting up labour unions in the state of Madras.
- He moved to Coimbatore later where his pleader’s license was restored by a judge. He worked as a lawyer in Kovilpatti.
- Some of his works are – Meyyaram, Meyyarivu, Autobiography, commentary on the Thirukkural, compiled works of Tolkappiyam, etc.
- A bicorne winter campaign hat is the first hat to bear the Emperor’s DNA.
- The hat was then tested extensively using various methods, including electronic microscopy.
- Two hairs when followed up, carried the DNA of Napoleon.
 Profile:
Profile:
- Napoleon was a brilliant military commander, an Emperor of France during Napoleonic Wars (1803–15), who conquered much of Europe.
- Born: August 15, 1769 France
- Died: May 5, 1821 at St. Helena, United Kingdom
- Nickname: Little Corporal
- 1785: Napoleon graduated from military academy in France.
- Commissioned as a second lieutenant of an artillery detachment in French Army.
- He rose through the ranks of military during French Revolution (1789-1799).
- Supported Jacobins, a far-left political movement and popular political club from the French Revolution.
- 1793: Fought in French Revolutionary Wars and was promoted to brigadier general.
- 1795: Suppressed a monarchy-backed uprising against the revolutionary government, and got promoted to major general.
- 1797: Negotiated Treaty of Campo Formio after victories against Austrians in northern Italy.
- 1798: Attempted to conquer Egypt but was defeated by British in the Battle of Nile.
- 1799: Coup of 18 Brumaire- Napoleon was part of a group that successfully overthrew French Directory.
- 1800: His forces defeated Austrians, driving them out of Italy in Battle of Marengo.
- 1803 to 1815- Napoleonic Wars: Series of major conflicts with various coalitions of European nations.
- 1803: To raise funds for future wars, he sold France’s Louisiana Territory in North America to United States for $15 million.
- 1804: He crowned himself emperor of France.
- 1805: British defeated Napoleon’s fleet at the Battle of Trafalgar in October.
- 1805: His army defeated Austrians and Russians at the Battle of Austerlitz in December.
- The victory resulted in dissolution of Roman Empire and creation of Confederation of Rhine.
- Continental System:
- 1806: Napoleon ordered a blockade (closing of ports) to prevent all trade and communication between Great Britain and other European nations. The Continental system hurt French more than British, weakening economy of France.
- Peninsular War:
- 1807-08: He sent an army via Spain to invade Portugal. The people in Spain rioted and started Guerrilla warfare against the French army, which continued till 1813.
- 1809: Britain also sent its troops to support the rebels.
- 1813-14: British forces, under Duke of Wellington invaded southwest France.
- Napoleon lost around 3 Lakh men in peninsular war, followed by rebellion in Germans and Italians conquered territories.
- Invasion of Russia:
- June 1812: He marched into Russia with his 4,20,000 strong Grande Armée.
- Russians burnt all grain fields and slaughtered all the livestock in Moscow, with nothing left for enemy to eat.
- October 1812: He asked his army to return back. But due to harsh climate (minus 30-degree temperature), exhaustion and hunger, his army reduced to around 30,000 soldiers.
- 1813: He was defeated in Battle of Leipzig, by coalition formed between Britain, Russia, Prussia, Sweden and Austria.
- 1814: He abdicated the throne and accepted treaty of surrender drafted by Russian emperor Alexander I.
- He was given a pension and sent to Elba, a tiny island near Italian Coast.
- 1815: Tried to comeback, but defeated in Battle of Waterloo on June 18, and exiled to St. Helena.
- 1821: He died in exile at St. Helena, United Kingdom.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies