- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
12th Nov 2021
STUDY IDENTIFIES INDIA AMONG GLOBAL FLASH DROUGHT HOTSPOTS FROM 1980-2015
Recently, a new study has identified India among global flash drought hotspots from 1980-2015.
Flash drought:






- Flash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought.
- It is set in motion by lower-than-normal rates of precipitation, accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, winds, and radiation.
- Flash droughts poses a risk to agriculture, ecosystems, and water availability.
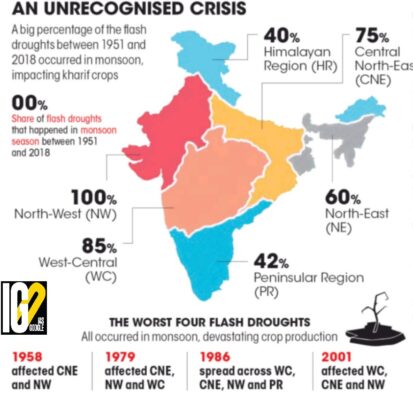
- There is a 7-8-fold increase in the frequency of flash droughts in India due to the concurrent occurrence of extremely dry and hot periods during the monsoon season and greenhouse emissions.
- The Indian summer monsoon varies across different time scales such as interannual or diurnal, but the intra seasonal variations are the most prominent and crucial ones that impact agriculture production.

- The intra seasonal variation in the monsoon along with warmer temperatures will increase the risk of flash droughts.
- An increased frequency of flash drought poses a major risk to crop production due to soil moisture depletion and intra seasonal monsoon variation.
- 10-15 %of areas under the cultivation of rice and maize were affected by flash droughts during the monsoon seasons in India between 1951 and 2018.

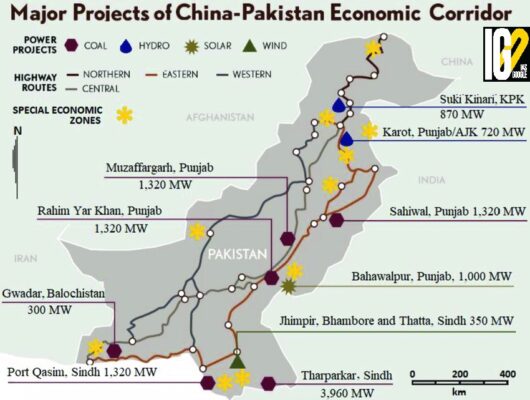
- CPEC is a flagship of the China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- It is a collection of infrastructure projects throughout Pakistan.
- CPEC runs through the entire length of Pakistan – through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) and the southern state of Balochistan.
- It reduces the distancefor Chinese goods bound for the US, Europe, Africa and the entire western world by a substantial 2,000 miles and vice versa by providing an alternate to the ‘Strait of Malacca’ route, through which most Chinese trade currently takes place.
- CPEC is intended to rapidly modernize Pakistani infrastructure and strengthen its economy by the construction of modern transportation networks, numerous energy projects and special economic zones (SEZs).
- With a USD 11 billion investment in rail and road infrastructure and USD 33 billion in energy and power generation projects, the project is largely financed by Chinese state-owned institutions.

- Considering India’s membership in Asian Investment Infrastructure Bank (AIIB), which may also ultimately fund some CPEC projects, and its involvement in Bangladesh China India Myanmar (BCIM) corridor to link Kolkata and Kunming in China via Bangladesh and Myanmar, there is a possibility that India might consider participating in CPEC corridor.
- India can join CPEC in order to gain overland access to Afghanistan and Central Asia from Pakistan, as the main purpose of CPEC would not be fulfilled without India’s participation.
- Revival of silk road near India – China border and connecting it to BRI can help develop Kashmir as the nucleus of intra-regional trade and energy cooperation between South and Central Asia.
- India shares a great deal of trust deficit with China and Pakistan and has a history of conflict with both the countries. CPEC can be a disguised political disturbance with a high-level strategic content. It brings with it many concerns and threats.
- The CPEC corridor is considered to be the alternative economic road link for the Kashmir Valley lying on the Indian side of the border.
- A well-connected Gilgit-Baltistan that attracts industrial development and foreign investment will further consolidate the region’s perception as internationally recognised Pakistani territory, diminishing India’s claim over the disputed territory of Kashmir.
- CPEC will put China in a position to offer a shorter and more economical trade route to most North and Latin American enterprises.
- This will give China the power to dictate the terms by which the international movement of goods will take place between the Atlantic and the Pacific oceans.
- Gwadar port places China in close proximity to the Iran-controlled Strait of Hormuz channel, which supplies 35% of the world’s oil requirements.
- Gwadar is located on the shores of the Arabian Sea, in Balochistan Province of Pakistan.
- Strait of Hormuz has been often used as a strategic weapon of self-defence by Iran, through a threat to choke international oil supplies.
- This means that the world will look to China to intermediate in the face of any future confrontation between Iran and Israel or the possible threat of a seizure of the canal.
- India, with over 60% of its oil supplies passing through the Strait, will be no exception.
- China has been increasing its presence in the Indian Ocean with the String of Pearls ambition.
- The String of Pearls is a geopolitical hypothesis proposed by US in 2004.
- It refers to the network of Chinese military and commercial facilities, which extend from the Chinese mainland to Port Sudan in the Horn of Africa.
- This includes Chittagong port (Bangladesh), Hambantota port (Sri Lanka), Port Sudan (Sudan), Maldives, Somalia and Seychelles.
- Development of commercial towns adjoining the corridor and better rail and road connectivity, Pakistan can emerge as a key destination for contract-manufacturing-outsourcing for the Western economies.
- This is more probable at a time when India is becoming costlier and Bangladesh has performed poorly on quality and regulatory standards.
- With the supply of raw material from China becoming easier, Pakistan will be suitably placed to become a regional market leader in these sectors – mainly at the cost of Indian export volumes.
- With US’ exit from Trans Pacific Partnership, Britain’s exit from European Union and weakened North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), can aid to China’s global leadership in trade.
- This can make a globally accepted and integrated China stronger at the United Nation further harming India’s aspirationto acquire a permanent seat at the UN Security Council.

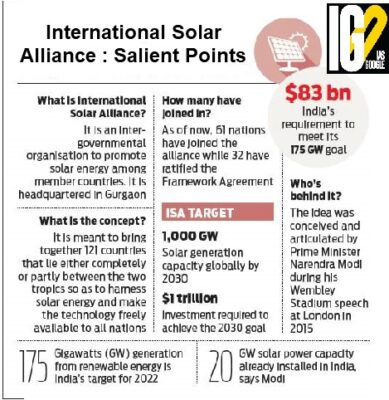
- It is an alliance of 124 countries initiated by India.
- Founded by: India and France
- Headquarters: Gurugram, Haryana, India
- Objective:
- To work for efficient consumption of solar energy to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- To bring together a group of nations to endorse clean energy, sustainable environment, public transport, and climate.
- Members: The alliance is a treaty-based inter-governmental organization.
- Countries that do not fall within the Tropics can join the alliance and enjoy all benefits as other members, except for voting rights.
- Most of the members of ISA have lots of daytime sunlight as they lie either completely or partly between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Priorities enlisted by ISA
- Assisting member countries in drafting solar policies;
- Development of standards, specifications, and test protocols for solar energy systems;
- Encouraging collaborations in solar resource mapping in member countries and the deployment of suitable technologies;
- Designing training programs for students/engineers/policymakers, etc., and organizing workshops, focused meetings, and conferences.
- Working with ISA member countries to strive for universal access to solar lighting.
- The idea behind the project is to develop solar resources in various countries to reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources.
- Countries that have come together for the project identify and address gaps in their energy requirements through a collective approach.
- ISA aims to invest $1 trillion, raised from public and private investors, for solar projects that will provide 1 TW of solar energy globally.
- India will also provide 500 training slots for ISA member countries and start a solar tech mission to lead R&D.
- The ISA is the first international body to have a secretariat in India.
- India has pledged a target of installing 175 GW of renewable energy of which 100 GW will be solar energy by 2022.
- India aims for reduction in emission intensity by 33–35% by 2030 to let solar energy reach the most unconnected villages and communities and also towards creating a clean planet.
- NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation Limited) to contribute $1 million to the Corpus fund of $15 million that India is providing to the ISA.
- India has also set aside five acres of land in Gurugram, next to the National Institute of Solar Energy to house the Headquarters of ISA.
- It is necessary to use sunrays for electricity generation, which can significantly meet the requirement of the local population which, in turn, would improve the standard of living of the population.
- It has been observed that since countries located between “Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn” have access to uninterrupted sun rays, it is necessary to tap these resources for the betterment of society.
- It is harnessed from nature free of cost and is abundantly available. This is in contrast to oil and gas-based energy.
- It is a first such meeting on Afghanistan to be chaired by India.
- The other countries who participated in the dialogue include Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
- The main aim of the dialogue is to discuss measures to promote peace in the region and address security challenges.
- The five main threats and challenges addressed in the dialogue are:
- Terrorism within Afghanistan and across its borders
- Radicalisation and extremism
- Cross-border movements
- Drug production and trafficking
- The danger posed by vast amounts of weapons and military gear left behind by US troops.

- Onake Obavva was a woman warrior who fought the forces of Hyder Ali single-handedly with a pestle in Chitradurga in the 18th century.
- Hyder Ali (1722-1782) was the Muslim ruler of Mysore princely state. He was the the father of Tipu Sultan.
- She is celebrated along with other women warriors of Karnataka state like Abbakka Rani, Keladi Chennamma and Kittur Chennamma.
- She died fighting the troops of Hyder Ali, when he invaded the Chitra Durga Fort, which was ruled by Madakari Nayaka in the 18th century.
- Chitra Durga Fort, is situated in Chitra Durga, northwest of Bengaluru.
- In 2018, the Chitradurga police started ‘Obavva Pade’, which is a squad of women police constables to protect and educate women in the district.

- Aim: To reach out 75 villages across India through the network of All India Coordinated Research Project on Women in Agriculture (AICRP-WIA).
- These 75 villages will be adopted by AICRP centres and ICAR- Central Institute for Women in Agriculture (CIWA) to develop Nutri-Smart villages.
- Promoting nutritional awareness
- Education and behavioral change in rural areas involving farm women and school children.
- Harnessing traditional knowledge to overcome malnutrition.
- Implementing nutrition-sensitive agriculture through homestead agriculture and Nutri-garden.
- Intensive awareness campaigns will be undertaken including Nutri-village / Nutri-diet etc. for strengthening the POSHAN Abhiyan.
- Awareness among the women farmers will be created about their legal rights in all walks of life.

- Project – 75 includes construction of six submarines of Scorpene design.
- INS Kalvari, commissioned in 2017
- INS Khnaderi in 2019
- INS Karanj 2021
- INS Vela in 2019
- INS Vagir (under trial)
- INS Vagsheer (under construction)
- The submarines are being constructed at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) Mumbai, under collaboration with M/s Naval Group, France.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies