- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
15th January 2021
This 45,500-year-old pig painting is the world’s oldest animal art
 Archaeologists have discovered the world’s oldest known cave art — a life-sized picture of a wild pig that was painted at least 45,500 years ago in in the limestone cave of Leang Tedongnge in South Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Archaeologists have discovered the world’s oldest known cave art — a life-sized picture of a wild pig that was painted at least 45,500 years ago in in the limestone cave of Leang Tedongnge in South Sulawesi, Indonesia.
 Lumpy skin disease (LSD) has prevailed over the village of Kammana in Kerala’s Wayanad district since the beginning of the year.
Lumpy skin disease (LSD) has prevailed over the village of Kammana in Kerala’s Wayanad district since the beginning of the year.
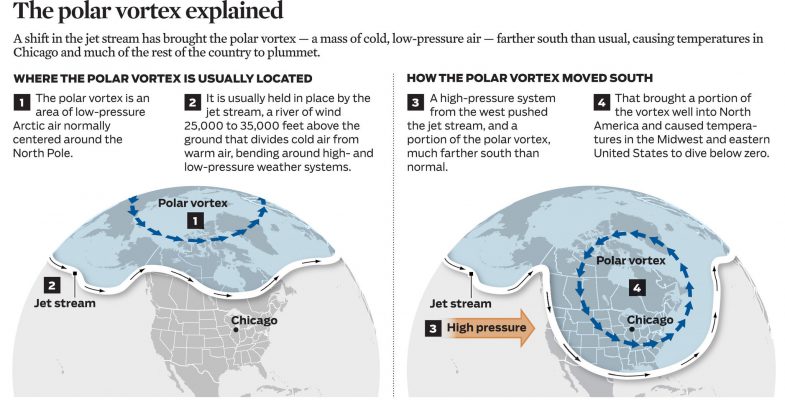 Polar vortex is splitting into two and swirling southward and this will lead to a chilling deep freeze in the US and European countries. Earlier, such vortex developed in 2014.
Polar vortex is splitting into two and swirling southward and this will lead to a chilling deep freeze in the US and European countries. Earlier, such vortex developed in 2014.
 Archaeologists have discovered the world’s oldest known cave art — a life-sized picture of a wild pig that was painted at least 45,500 years ago in in the limestone cave of Leang Tedongnge in South Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Archaeologists have discovered the world’s oldest known cave art — a life-sized picture of a wild pig that was painted at least 45,500 years ago in in the limestone cave of Leang Tedongnge in South Sulawesi, Indonesia.
- The cave painting consists of a figurative depiction of a warty pig, a wild boar that is endemic to this Indonesian island.
- The finding also represents some of the earliest archaeological evidence for modern humans in the region.
- The cave is in a valley that is enclosed by steep limestone cliffs, and is only accessible by a narrow cave passage in the dry season, as the valley floor is completely flooded in the wet season.
- It shows a pig with a short crest of upright hairs and a pair of horn-like facial warts in front of the eyes, a characteristic feature of adult male Sulawesi warty pigs.
- Painted using red ochre pigment, the pig appears to be observing a fight or social interaction between two other warty pigs.
- These pigs were the most commonly portrayed animal in the ice age rock art of the island, suggesting they have long been valued both as food and a focus of creative thinking and artistic expression.
- The previously oldest dated rock art ‘scene’ at least 43,900 years old, was a depiction of hybrid human-animal beings hunting Sulawesi warty pigs and dwarf bovids.
- It was discovered by the same research team at a nearby limestone cave site.
- Rock art produced in limestone caves can sometimes be dated using Uranium-series analysis of calcium carbonate deposits (‘cave popcorn’) that form naturally on the cave wall surface used as a ‘canvas’ for the art.
- The U.S. has punished Cuba for decades with harsh sanctions, hoping that the Castro regime would eventually collapse. But the Cuban communists survived even the fall of the Soviet Union.
- Cuba was removed from the list in 2015 by then-president US President to normalize relations with the country.
- Cuba was being blacklisted again for “repeatedly providing support for acts of international terrorism” as well as harboring US fugitives and Colombian rebel leaders.
- The U.S., the world’s largest military power that had cooperated with communist China since the early 1970s, still treats this tiny communist country that lies off the Florida coast as an enemy.
- Foreign investors will now risk US prosecution for transactions in Cuba.
- The reinstated sanctions also include major restrictions barring most travel between the US and Cuba.
- The sanctions also curb money transfers between the two countries, hitting hard the incomes of Cubans who have relatives in the US.
- Only three other countries are currently on the “state sponsor of terrorism” list, including: North Korea, Syria and Iran.
 Lumpy skin disease (LSD) has prevailed over the village of Kammana in Kerala’s Wayanad district since the beginning of the year.
Lumpy skin disease (LSD) has prevailed over the village of Kammana in Kerala’s Wayanad district since the beginning of the year.
- A viral illness that causes prolonged morbidity in cattle and buffaloes. It appears as nodules of two to five centimetre diameter all over the body, particularly around the head, neck, limbs, udder and genitals.
- The lumps gradually open up like large and deep wounds. In some cases — under 10 per cent according to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) — the infected animal succumbs to the disease.
- While the LSD virus easily spreads by blood-sucking insects like mosquitoes, flies and ticks and through saliva and contaminated water and food, no treatment is available for the disease, that is being reported for the first time in India.
- Historically, LSD has remained confined to Africa, where it was first discovered in 1929, and parts of West Asia. But in recent years, the disease has spread to territories beyond the endemic areas. In 2015, it made an incursion into the European part of Turkey and Greece.
- The next year, it created havoc in the Balkan and Caucasian countries and Russia. However, since its arrival in Bangladesh in July 2019, LSD is spreading across Asia in epidemic proportions.
- According to a risk assessment report by FAO, the disease spread to seven countries till the end of 2020 — reaching China and India in August 2019, Nepal in June 2020, Taiwan in July 2020, Bhutan and Vietnam in October 2020 and Hong Kong in November 2020.
- At least 23 countries in south Asia, east Asia and southeast Asia are now at risk of LSD, which is emerging as a trans-boundary animal disease, it says.
- In India, which has the world’s highest 303 million heads of cattle, the disease has spread to 15 states within just 16 months. In fact, in August 2019, when the first outbreak of LSD was reported from Odisha, five districts were grappling with the exotic cattle pox.
- Due to the infectious nature of LSD and its implications on the economy — decreased milk production, abortions and infertility and damaged hides due to cutaneous nodules and fibrous tissue growth cause significant economic losses to farmers — the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) declares it as a notifiable disease.
- This means a country must inform OIE about any outbreak of the disease so that it can be contained.
- Insects like ticks, biting flies, mosquitoes are anyway more prevalent in tropical climatic conditions of India. As unseasonal rains and floods become frequent, they will provide a conducive atmosphere for insect growth and multiplication and infectious disease vectors will no longer be restricted to a few months.
- This will have a devastating impact on the country, where most dairy farmers are either landless or marginal landholders and milk is among the cheapest protein source.
- 10 countries had ratified the Convention on Homework nearly 25 years since it was adopted by the International Labour Conference June 20, 1996.
- Few governments had a comprehensive policy for working from home in place. As a result, those working from home, especially in low-income countries, continued to work in poor working conditions.
- Despite contributing significantly to the economy, home-based working had remained “invisible”.
- It also noted that the propensity of women to work from home — 11.5 per cent — was much higher than that of men (5.6 per cent).
- Industrial home-based workers, who are involved in the production of goods including artisanal production, such as making of handicrafts, rolling of beedis, making of laces, etc
- Teleworkers, who use information and communication technologies to perform their work remotely
- Home-based digital platform workers, who are ‘crowdworkers’ that perform service-sector tasks as specified by employers or intermediaries
- Governments need to play a major role to protect home-workers. It strongly recommended them to adopt a national policy on home-based work.
- It called upon governments to develop and implement a gender-responsive legal and policy framework that provided equal treatment for all categories of home-based workers in relation to other wage earners.
- This included facilitating the transition of informal workers to formal employment.
- Home-based workers needed to be counted better to record their earnings, hours worked and other conditions of employment.
- The labour registries needed to be revised to incorporate “place of work” and count those home-based workers who went missing due to poor labour registries. Few countries had labour inspection schemes adapted for home-based work.
- Need for better compliance, legal protection, occupational safety and social security for industrial home-based workers.
- It can speed up transfer of quantum information and signal from one part of a device to another and increase data storage and memory.
- Due to the high mobility of the electron gas, electrons do not collide inside the medium for a long distance and hence do not lose the memory and information.
- The need for attaining new functionalities in modern electronic devices has led to the manipulation of property of an electron called spin degree of freedom along with its charge. This has given rise to an altogether new field of spin-electronics or ‘spintronics’.
- It has been realized that a phenomenon called the ‘Rashba effect’, which consists of splitting of spin-bands in an electronic system, might play a key role in spintronic devices.
 Polar vortex is splitting into two and swirling southward and this will lead to a chilling deep freeze in the US and European countries. Earlier, such vortex developed in 2014.
Polar vortex is splitting into two and swirling southward and this will lead to a chilling deep freeze in the US and European countries. Earlier, such vortex developed in 2014.
- The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding both of the Earth’s poles. It ALWAYS exists near the poles, but weakens in summer and strengthens in winter.
- The term "vortex" refers to the counter-clockwise flow of air that helps keep the colder air near the Poles.
- Many times during winter in the northern hemisphere, the polar vortex will expand, sending cold air southward with the jet stream.
- This is not confined to the United States. Portions of Europe and Asia also experience cold surges connected to the polar vortex.
- By itself, the only danger to humans is the magnitude of how cold temperatures will get when the polar vortex expands, sending Arctic air southward into areas that are not typically that cold.
- Polar vortex is losing stability and its splitting causes dramatic, extreme weather implications across the western nations like the US and Europe.
- With a ‘disrupted’ polar vortex in 2021, the colder air is expected to spill out of the Arctic and result in the onset of extremely harsh winters.
- It aims to achieve 20% blending by 2025 as well as to meet out the requirement of ethanol production capacity in the country.
- Under the scheme , Government would bear interest subvention for five years including one year moratorium against the loan availed by project proponents from banks for setting up of new distilleries or expansion of existing distilleries or converting molasses based distilleries to dual feedstock.
- Due to upcoming investment in capacity addition / new distilleries, various new employment opportunities will be created in rural areas.
- For production of ethanol, there is sufficient availability of feed stocks; & Government has also fixed remunerative prices of ethanol derived from various feed stocks.
- This scheme would not only facilitate diversion of excess sugar to ethanol but would also encourage farmers to diversify their crops to cultivate particularly maize/corn which needs lesser water compared to sugarcane and rice.
- It would enhance production of ethanol from various feed stocks thereby, facilitate in achieving blending targets of ethanol with petrol and would reduce import dependency on crude oil , thereby, realizing the goal of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- It will also enhance income of farmers as setting up of new distilleries would not only increase demand of their crops but would assure farmers of getting better price for their crops.
- Sugarcane and ethanol is produced mainly in three states viz Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Karnataka. Transporting ethanol to far flung States from these three states involves huge transportation cost. By bringing new grain based distilleries in the entire country would result in distributed production of ethanol and would save a lot of transportation cost and thus prevent delays in meeting the blending target & would benefit the farmers across the country.
- The Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation is conducting three live sessions of “Natural Capital Accounting and Valuation of Ecosystem Services” (NCAVES) India Forum 2021 are scheduled to be held on January 14, 21 and 28, 2021 in collaboration with United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), European Union and UN Environment.
- It aims to disseminate the activities taken up by the Ministry under the Project and to highlight the uses to which natural capital accounts can be put, especially in the areas of decision making and policy analysis.
- The first session of the event on 14 January 2021 was dedicated to the discussions on the efforts made by India and the international agencies in the domain of natural capital accounting and valuation of the ecosystem services.
- Through the forum, the Ministry targets to showcase Government’s efforts in making environment a key dimension in our policy paradigm and welcomes active participation of all stakeholders in the NCAVES India Forum 2021.
- In 2017, the European Union initiated a project, NCAVES in 201 7 to help nations advance the knowledge on environmental-economic accounting, in particular ecosystem accounting that can help in ensuring sustainable economic growth.
- The NCAVES Project is being implemented in five countries – India, Brazil, China, Mexico and South Africa - by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Secretariat of the Convention of Biological Diversity (CBD).
- The Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation has taken up several initiatives under the NCAVES Project during the past three years.
- The Third Phase of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY 3.0) will be launched in 600 districts across the country.
- Spearheaded by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, this phase will focus on new-age and COVID-related skills.
- Skill India Mission-PMKVY 3.0 envisages training of eight lakh candidates over a scheme period of 2020-2021 with an outlay of 948.90 crore rupees.
- The 729 Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras, empaneled non-PMKK training centres and more than 200 ITIs under Skill India will be rolling out PMKVY 3.0 training to build a robust pool of skilled professionals.
- On the basis of the learning gained from PMKVY 1.0 and PMKVY 2.0, the Ministry has improved the newer version of the scheme to match the current policy doctrine and energize the skilling ecosystem affected due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The Skill India Mission launched by Prime Minister on 15 July 2015 has gained tremendous momentum through launch of its flagship scheme PMKVY to unlock the vision of making India the Skill Capital of the world.
- CCI has started a review of all model concession agreements — the legal contract that forms the basis of the public-private partnership — across four key infrastructure sectors: airports, ports, electricity and railways.
- The goal is to ensure that competition remains “vibrant” and “there are enough players who are able to participate in the award of concessions.
- In sectors such as airports, ports and highways, and electricity, concentration of power by itself was not a concern.
- The policy of the government is to make the economy more efficient, and, in that process, what the CCI can do is look at whether the dominance is abused or not. If there is abuse of dominance, CCI can take action under Section 4 of the Competition Act.
- Section 4 bars an enterprise from abusing its dominance and defines abuse through a range of steps that include denial of access, predatory pricing, limiting goods or services in a particular market.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies