- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
21st November 2020
Filing petitions under Article 32 of the Constitution.
A Supreme Court bench headed by Chief Justice of India S A Bobde observed that it is “trying to discourage” individuals from filing petitions under Article 32 of the Constitution.
- Article 32 is one of the fundamental rights listed in the Constitution that each citizen is entitled.
- Article 32 deals with the ‘Right to Constitutional Remedies’, or affirms the right to move the Supreme Court by appropriate proceedings for the enforcement of the rights conferred in Part III of the Constitution.
- Only if fundamental rights is violated can a person can approach the Supreme Court directly under Article 32.

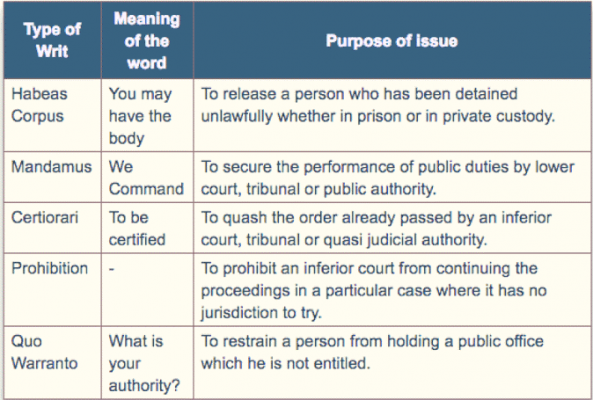
- Both the High Courts and the Supreme Court can be approached for violation or enactment of fundamental rights through five kinds of writs:
- Habeas corpus – related to personal liberty in cases of illegal detentions and wrongful arrests
- Mandamus — directing public officials, governments, courts to perform a statutory duty;
- Quo warranto — to show by what a warrant is a person holding public office;
- Prohibition — directing judicial or quasi-judicial authorities to stop proceedings which it has no jurisdiction for; and
- Certiorari — a re-examination of an order given by judicial, quasi-judicial or administrative authorities.
- When it comes to the violation of fundamental rights, an individual can approach the High Court under Article 226 or the Supreme Court directly under Article 32.
- Article 226, however, is not a fundamental right like Article 32.
Article 217 (1)
- Every Judge of a High Court shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal after consultation with the Chief Justice of India, the Governor of the State, and, in the case of appointment of a Judge other than the chief Justice, the chief Justice of the High court.
- Every Judge of a High Court shall hold office, in the case of an additional or acting Judge, as provided in Article 224, and in any other case, until he attains the age of sixty two years Provided that
- a Judge may, by writing under his hand addressed to the President, resign his office;
- a Judge may be removed from his office by the President in the manner provided in clause ( 4 ) of Article 124 for the removal of a Judge of the Supreme Court;
- the office of a Judge shall be vacated by his being appointed by the President to be a Judge of the Supreme Court or by his being transferred by the President to any other High Court within the territory of India.
- Under the MoU, EESL and DNRE will carry-out the feasibility studies and subsequent implementation of decentralized solar energy projects.
- EESL shall implement the solar energy projects, establishment of 100 MW of decentralized ground mounted Solar Power projects on government lands to be used for agricultural pumping, replace approximately 6,300 agricultural pumps with BEE star rated energy efficient pumps and distribute approximately 16 Lakh LED bulbs for rural domestic households.
- The MOU signed between EESL and Government of Goa today in some sense marks beginning of fresh green revolution.
- When we started the PM- KUSUM, this is what was in our mind to restart fresh green revolution in agriculture sector.
- This model is expected to be adopted by other states as this will reduces losses in terms of expenditure on water for farm sector runs into tens of thousands crore rupees in several States.
- That pre-empts state spending on health, education, and other important sectors.
- Together with new Roof Top Solar Scheme this will prove to be win win for farmers and States and help them turn into green States.
- The project will accrue savings of INR 2,574 crores to the State over the period of 25 years, while improving the health of DISCOMs and providing cleaner power.
- This project will provide clean day time electricity to farmers as well as energy efficient pump sets which would reduce the power consumption as well as T&D losses associated with transmitting power to agriculture and rural feeder networks.
- To treat women with ‘equality and fairness’ in all spheres of life, by the means of this initiative, all the stakeholders (especially the girl students) in AICTE approved institutions would get a unique opportunity.
- The opportunity is to present a solution to the prevalent issues of gender discrimination, which includes illiteracy, unemployment, economic and nutritional disparities, maternal mortality, human rights, etc.
- Also, if anyone has already made a successful effort towards making a mark in the society, in establishing women’s emancipation/ empowerment at large, she/ he can showcase their efforts/ contributions.
- Theme: Women empowerment
- Objective: To create awareness about issues like sanitation, hygiene, health, nutrition, literacy, employment, technology, credit, marketing, innovation, skill development, natural resources, and rights among women.
- Covering multidisciplinary areas: Women's health, self-defense, sanitation, literacy, entrepreneurship, and legal awareness
- Significance: The program is expected to ensure the participation of women and enable them to hold higher positions in educational institutions.
- The five-nation grouping BRICS has adopted a new counter-terrorism strategy to effectively deal with terrorism.
- The objective of BRICS counter-terrorism cooperation is to complement and strengthen the existing bilateral and multilateral ties among the BRICS countries, and to make a meaningful contribution to the global efforts of preventing and combating the threat of terrorism.
- BRICS is the acronym coined to associate five major emerging national economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- The BRICS countries reaffirmed that terrorism in all its forms and manifestations constitutes one of the most serious threats to international peace and security and that any act of terrorism committed is a crime and has no justification.
- The BRICS countries also recognized that the international community should take the necessary steps to enhance cooperation to prevent and combat terrorism, including cross-border movement of terrorists.
Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile System
- The second flight test of Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile System (QRSAM) was successfully conducted from the Integrated Test Range, Chandipur, off the coast of Odisha.
- The first in the series test of QRSAM took place on 13th of this month.
- The system is capable of detecting and tracking targets on the move and engaging targets with short halts. It is designed to give air defense coverage for strike columns of the Indian Army,
- Propelled by a single-stage solid propellant rocket motor, the sophisticated missile used all indigenous subsystems.
- The missile is cannisterised for transportation and launch using a mobile launcher which is capable of carrying six canisterised missiles.
- First launch test on 13th November proved the Radar and Missile capabilities with direct hit while today’s test demonstrated the warhead performance on proximity detection.
- Japan and Australia have signed a landmark defence deal in a bid to counter China’s growing influence in the South China Sea and over the Pacific island nations.
- The Reciprocal Access Agreement (RAA) comes weeks after foreign ministers of the Quad alliance, which includes the US and India, met in Tokyo.
- The pact allows Japanese and Australian troops to visit each other’s countries and conduct training and joint operations.
- Australian Prime Minister said that the treaty will strengthen their security ties and facilitate cooperation between defence forces.
- The two sides also agreed on the need for a framework to allow Japanese military to protect Australian forces if needed.
- With 1,084 females born per thousand males, Arunachal Pradesh recorded the best sex ratio in the country, followed by Nagaland at 965 females and Mizoram at 964.
- The three north-eastern states top the 2018 report on “Vital statistics of India based on the Civil Registration System (CRS)”.
- Manipur, on the other hand, featured at the bottom of the list.
- The sex ratio (number of females per thousand males) is an important indicator to map the gender gap of a population.
- Highest Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) based on registered events has been reported by Arunachal Pradesh (1,084), followed by Nagaland (965), Mizoram (964) and Kerala (963).
- Meanwhile, lowest SRB has been reported by Manipur (757), Lakshadweep (839) and Daman & Diu (877), followed by Punjab (896),” the report, prepared by the Registrar General & Census Commissioner of India, read.
- Assam recorded a sex ratio of 904, Meghalaya 942 and Tripura 945.
- Karnataka Forest Minister Anand Singh announced in the Assembly that the state government would soon declassify 6.64 lakh hectares of the 9.94 lakh hectares of deemed forests in the state (nearly 67%) and hand it over to Revenue authorities.
- The move has been taken after a study of the actual extent of deemed forest areas by local committees headed by officials from the Revenue, Forest and Land Records Departments in every district.
- While the concept of deemed forests has not been clearly defined in any law including the Forest Conservation Act of 1980, the Supreme Court in the case of T N Godavarman Thirumalpad (1996) accepted a wide definition of forests under the Act.
- “The word ‘forest’ must be understood according to its dictionary meaning. This description covers all statutorily recognised forests, whether designated as reserved, protected or otherwise for the purpose of Section 2 (1) of the Forest Conservation Act,” the Supreme Court said in its December 12, 1996 order.
- “The term ‘forest land’ occurring in Section 2 will not only include ‘forest’ as understood in the dictionary sense, but also any areas recorded as forest in the government record irrespective of the ownership. The provisions enacted in the Forest Conservation Act 1980 for the conservation of forest and the matters connected therewith must apply clearly to all forest so understood irrespective of the ownership or classification thereof,” the court said.
- An expert committee constituted by the Karnataka government after the Supreme Court order identified ‘deemed forests’ as “land having the characteristic of forests irrespective of the ownership’”.
- Thickly wooded areas of the Revenue Department not handed over to the Forest Department; thickly wooded areas recommended to be handed over to the Forest Department; thickly wooded land distributed to grantees but not cultivated; and thickly wooded plantations of the Forest Department could all be ‘deemed forests’, the committee said in a report in 2002.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies