- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
22nd Oct 2021
NSE, BENGALURU BLOCKCHAIN START-UP LAUNCH 'NSE-SHINE' FOR BULLION TRADE
National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) in collaboration with Bengaluru-based startup Chainflux has launched NSE-Shine, a blockchain platform for gold bullion trade.
Highlights:

 Ego4D:
Ego4D:



- The platform is developed by The India Gold Policy Centre (IGPC) at the Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad (IIM-A) and the Indian Bullion and Jewellers’ Association (IBJA) with the NSE and Chainflux.
- The platform will be launched in November 2021. NSE-approved refiners will be able to use the system to record details of their produced bullion.
- It will provide a data framework for bullion bar integrity for settlement of gold derivatives contracts.
- It will create a bullion repository for all bullion bars produced by NSE-approved refiners as per the NSE Refiner Standards (NRS).

- In 2019, the ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources came across plants of this onion species, which they have named Allium negianum, in the border area of Chamoli district of Uttarakhand.
- It grows at 3,000 to 4,800 m above sea level and can be found;
-
- In open grassy meadows, sandy soils along rivers.
- Streams forming in snow pasture lands, where the melting snow helps carry its seeds to more favourable areas.
- In open grassy meadows, sandy soils along rivers.
- With a narrow distribution, the species is restricted to the region of western Himalayas.
- Buddhist circuit is one the thematic circuit under Swadesh Darshan scheme of central government. The Buddhist Circuits are the places of holy sites of Buddhism.
- Kushinagar is a Buddhist Pilgrimage Centre, where Lord Gautam Buddha delivered his last sermon and attained Mahaparinirvan.
- Kushinagar is considered to be the center of the Buddhist circuit consisting pilgrimage sites of Lumbini, Sarnath and Gaya.
- The birthplace of Lord Buddha, is located in the Terai plains of southern Nepal.
- The area includes sandstone Ashoka pillar with its Pali inscription in Brahmi script, along with remains of Buddhists viharas and stupas.
- Sarnath is a place located 10 kilometers north-east of Varanasi near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pradesh.
- Buddha gave his first sermon and set the wheel of dharma in motion at Sarnath. It is also the place of birth for the Sangha (the religious followers of Buddha).
- Bodh Gaya is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Gaya district in Bihar.
- It is the place where Gautama Buddha is said to have attained Enlightenment (Pali: bodhi) under what became known as the Bodhi Tree.
 Ego4D:
Ego4D:
- Facebook has announced a research project in which it collected 2,200 hours of first-person footage from around the world to train next-generation AI models.
- The research project is called Ego4D (Egocentric 4D Live Perception).
- The Project could prove to be crucial to Facebook’s Reality Labs division, which is working on smart glasses, augmented reality and virtual reality projects.

- Valneva vaccine is developed by Valneva SE, which is a French vaccine company.
- VLA2001(Valneva) is an inactivated, adjuvanted vaccine.
- This means that it delivers the whole Sars-CoV-2 virus in an inactivated form.
- The virus is killed using chemicals, heat, or radiation. The dead virus cannot infect us but can still trigger an immune response.
- India’s Covaxin is also an example of inactivated vaccine.
- The Valneva jab is stable when stored in a standard refrigerator.
- Valneva is easier to distribute than the Covid vaccines, which require shipping and storage at ultra-low temperatures.
- The efficiency of the Valneva vaccine can be elaborated by the following points:
- The phase 3 trial of the vaccine was conducted in more than 1000 participants.
- The results showed that two weeks after vaccination, in adults aged 30 and older, the vaccine was able to trigger high levels of neutralizing antibodies compared to the Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccine.
- It was noticed that the vaccine was able to induce broad T-cell responses.
- This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give the cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the COVID-19 virus.
- After vaccination, the immune cells begin making the S protein pieces (harmless protein) and displaying them on cell surfaces.
- This causes the body to create antibodies. If a person later becomes infected with the COVID-19 virus, these antibodies will fight the virus.
- The mRNA is immediately broken down. It never enters the nucleus of the cells, where the DNA is kept.
- Example of mRNA vaccine: Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna
- In this type of vaccine, genetic material from the COVID-19 virus is placed in a modified version of a different virus other than the COVID-19 virus (viral vector).
- When the viral vector gets into the cells, it delivers genetic material from the COVID-19 virus that gives body cells instructions to make copies of the S protein.
- Once the cells display the S proteins on their surfaces, the body's immune system responds by creating antibodies and defensive white blood cells.
- If the body becomes infected later with the COVID-19 virus, the antibodies will fight the virus.
- Viral vector vaccines can't cause body to become infected with the COVID-19 virus or the viral vector virus. The genetic material that's delivered doesn't become part of the DNA.
- Example: The Janssen/Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine, AstraZeneca
- These vaccines include only the parts of a virus that best stimulate the immune system.
- The subunit vaccine contains harmless S proteins. Once the immune system recognizes the S proteins, it creates antibodies and defensive white blood cells.
- If the body becomes infected later with the COVID-19 virus, the antibodies will fight the virus.
- Novavax is working on a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine.
- It is known as the third-generation vaccine. DNA-based vaccines use engineered DNA to induce a response against the virus.
- It has a new radical new approach that offers several advantages over traditional vaccines, which include:
- Improved vaccine stability
- Absence of any infectious agent
- Relative ease of large-scale manufacture
- It is a 'plasmid DNA' vaccine that uses a non-replicating version of a DNA molecule called a plasmid.
- It helps to prepare a harmless version of the spike protein present on the SARS-COV-2 membrane.
- Example: ZyCoV-D vaccine of India

- To encourage attention to agricultural food production and to stimulate national, bilateral, multilateral, and non-governmental efforts to this end.
- To encourage economic and technical cooperation among developing countries and promote the transfer of technologies.
- To encourage the participation of rural people, particularly women and the least privileged categories, in decisions and activities influencing their living conditions.
- To heighten public awareness of the problem of hunger in the world.
- To strengthen international and national solidarity in the struggle against hunger, malnutrition, and poverty and draw attention to achievements in food and agricultural development.
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations marks the World Food Day each year on 16 October.
- It was the day on which the FAO was founded in 1945. World Food Day was first held on 16 Oct 1981.
- World food day is also observed by organizations like World Food Programme and International Fund for Agricultural Development.
- Theme 2021: Our actions are our future- better production, better nutrition, a better environment, and a better life.

- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- Headquarters: Rome, Italy. It maintains regional and field offices around the world, operating in over 130 countries.
- The FAO is composed of 197 member states.
- It helps governments and development agencies coordinate their activities to improve and develop agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and land and water resources.
- It also conducts research, provides technical assistance to projects, operates educational and training programs, and collects data on agricultural output, production, and development.
- The FAO is governed by a biennial conference representing each member country and the European Union, which elects a 49-member executive council.
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) has enjoyed a valuable partnership with India since it began operations in 1948.
- It continues playing a catalytic role in India’s progress in the areas of crops, livestock, fisheries, food security, and management of natural resources.
- The priorities set in the NITI Aayog’s seven-year National Development Agenda and the medium-term Three-Year Action Agenda as well as the Union Budget represent the key overarching framework for the agriculture sector.
- The main objective of the government is to double farmers’ income by solving the twin problems of maximizing efficiency and ensuring equity sustainably.
- Sustainable and improved agricultural productivity and increased farm incomes.
- FAO will facilitate the adaptation of Farmers Water School (FWS) in Uttar Pradesh on groundwater management to surface irrigation practices to increase crop productivity and improve water-use efficiency.
- Stronger food and nutrition security systems.
- FAO’s technical assistance will focus on providing technical assistance that drives the “Zero Hunger” initiative of FAO.
- Effective natural resource management, community development.
- FAO will implement the GEF-funded Green Agriculture project that will provide models for successful landscape approaches to address the interface of biodiversity conservation in and around key protected areas.
- Enhanced social inclusion, improved skills, and employment opportunity in the agriculture sector.
- FAO will focus on the building capacities and skills of the poor for gainful and sustainable livelihoods through employment-generating agribusiness and enterprise clusters.

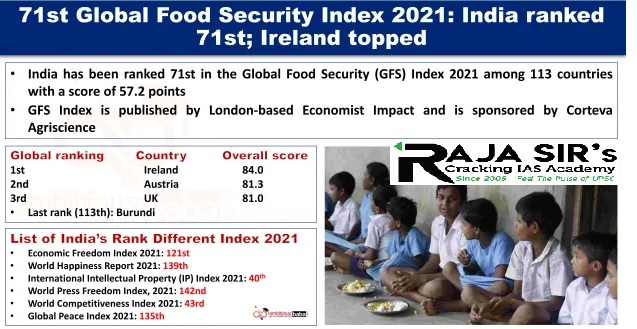
- Developed by: London-based Economist Impact sponsored by Corteva Agriscience.
- Measures the underlying drivers of food security in 113 countries, based on the following factors:
- Affordability
- Availability
- Quality and safety
- Natural resources and resilience
- The report uses 58 unique food security indicators including income and economy.
- Objective: Calling attention to systemic gaps and actions needed to accelerate progress toward United Nations Sustainable Development Goal of Zero Hunger by 2030.
- Top Rankers: Ireland, Australia, the UK, Finland, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Canada, Japan, France and the US with the overall GFS score in the range of 77.8 and 80.
- China’s score improved by 9.6 points to 71.3 in 2021 from 61.7 in 2012.
- Global food security has decreased for the second year in a row after seven years of progress towards the Sustainable Development Goal of achieving zero hunger by 2030.
- Food systems remain vulnerable to economic, climatic, and geopolitical shocks.
- India has an overall score of 57.2 points.
- In the food affordability category, Pakistan and Sri Lanka scored better than India.
- In case of availability of food, quality and safety as well as protecting natural resources for food production, India scored better than Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
- India’s incremental gains in overall food security score were lagging behind that of Pakistan, Nepal and Bangladesh as seen in the last 10 years.
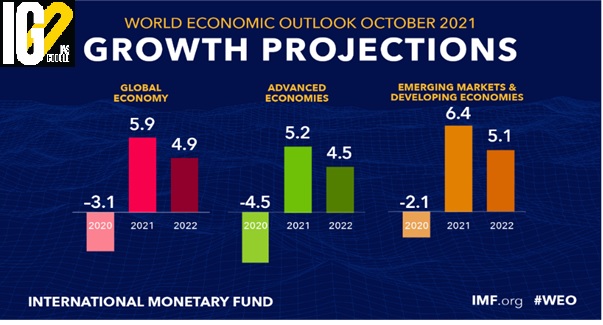
- The IMF comes out with the report twice every year in the month of April and October.

- The divergence in economic prospects among nations is a matter of major concern.
- Aggregate output for the advanced economy group will regain its pre-pandemic path in 2022 and exceed it by 0.9 per cent in 2024.
- The output for the emerging market and developing economy group will remain 5.5 per cent below the pre-pandemic forecast in 2024.
- Resulting in a larger setback to improvements in their living standards.
- Reasons for the economic divergence are: large disparities in vaccine access, and differences in policy support.

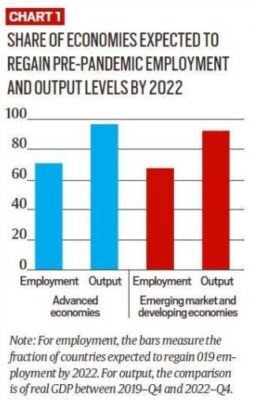
- The employment growth is likely to lag the output recovery.
- Employment around the world remains below its pre-pandemic levels, reflecting a mix of negative output gaps.
- Worker fears of on-the-job infection in contact-intensive occupations, childcare constraints.
- Labor demand changes as automation picks up in some sectors.
- Unemployment benefits helping to overcome income losses, and frictions in job searches.
- The gap between recovery in output and employment is likely to be larger in developing economies than in advanced economies.
- Young and low-skilled workers are likely to be worse off than prime-age and high-skilled workers, respectively.
- As per the IMF; the recovery in unemployment is lagging the recovery in output in India.
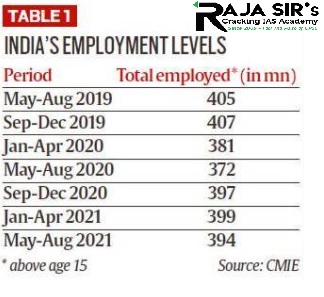
- According to the data of Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), the total number of employed people in the Indian economy as of May-August 2021 was 394 million.
- In May-August 2016 the number of employed people was 408 million.
- India is already facing a deep employment crisis before the Covid, and it became much worse after it.

- K-shaped recovery:
- India is witnessing a K-shaped recovery. That means different sectors are recovering at significantly different rates.
- Sectors like the IT-services have been practically unaffected by Covid.
- Many contact-based services, which can create many more jobs, are not seeing a similar bounce-back.
- Listed firms have recovered much better than unlisted firms.
- Unorganised sectors:
- The bulk of India’s employment is in the informal or unorganised sectors.
- The informal worker is defined as “a worker with no written contract, paid leave, health benefits or social security”.
- A weak recovery implies a drag on the economy’s ability to create new jobs or revive old ones.
- The share of different sectors of the economy in the overall Gross Value Added
- GVA is a measure of overall output from the supply side
- The share of informal/unorganised sector GVA is more than 50% at the all-India level, and is even higher in certain sectors.
- That create low-skilled jobs like construction and trade, repair, accommodation, and food services.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies