- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
30th Sep 2021
ANTI-DEFECTION LAW, FOR INDEPENDENT LEGISLATORS
An independent MLA from Gujarat has changed his political party and joined the Congress.




- The Tenth Schedule of the Constitution, the anti-defection law, specifies the circumstances under which changing of political parties invites action under the law.

- When a member elected on the ticket of a political party “voluntarily gives up” membership of such a party or votes in the House against the wishes of the party.
- When a legislator who has won his or her seat as an independent candidate joins a political party after the election.
- Under both Circumstances the legislator loses the seat in the legislature on changing a party.
- In case of Nominated MPs, the law gives them six months to join a political party, after being nominated.
- If they join a party after such time, they stand to lose their seat in the House.
- The power to decide the disqualification of an MP or MLA rests with the presiding officer of the legislature.
- The law does not specify a time frame in which such a decision has to be made.
- Speakers of legislatures have sometimes acted very quickly or have delayed the decision for years and have been accused of political bias in both situations.
- The data is part of Situation Assessment of Agricultural Households and Land Holdings in Rural India, 2019, by the Ministry of Programme Implementation and Statistics.

- The data shows an estimated 17.24 crore rural households.
- 44.4% were OBCs, 21.6% Scheduled Castes, 12.3% Scheduled Tribes and 21.7% other social groups.
- Of the total rural households, 54% are agricultural households.
- Highest proportion of rural OBC households is in Tamil Nadu (67.7%) and the lowest in Nagaland (0.2%).
- In Bihar (58.1%), Telangana (57.4%), Uttar Pradesh (56.3%), Kerala (55.2%), Karnataka (51.6%), Chhattisgarh (51.4%), OBC households account for more than half of the rural households.
- Rajasthan (46.8%), Andhra Pradesh (45.8%), Gujarat (45.4%) and Sikkim (45%) have a higher share of rural OBC households than the all-India figure of 44.4%.
- States like Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Manipur, Odisha, Haryana, Assam, Uttarakhand etc., have a lower share of rural OBCs households compared to the national average.
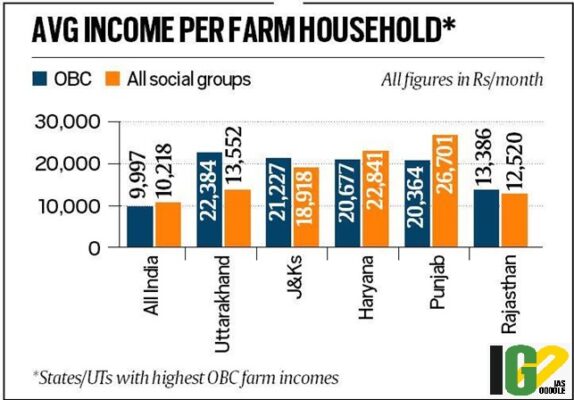
- The average monthly income of a farm household at all-India level stood at Rs 10,218 during 2018-19.
- It was lower for OBC agricultural households (Rs 9,977), SC households (Rs 8,142), ST households (Rs 8,979).
- Agricultural households of ‘Other Social Groups’, recorded an average monthly income of Rs 12,806.
- For states, the average monthly income ranged between Rs 5,009 and Rs 22,384.
- Of the 23 states, Uttarakhand recorded the highest average monthly income while Odisha was at the bottom.
- OBC category contains communities that continue to face oppression and social, economic, and educational isolation, but do not fall into the Scheduled Castes or Scheduled Tribes list.
- Article 340 gives the President the power to constitute a committee to investigate the conditions of backward classes in India
- It recommends measures for their welfare, upliftment, and development.
- The Mandal Commission was constituted in 1978, under Article 340 of the Constitution, to identify backward communities in India and recommend policy initiatives for their upliftment and welfare.
- The Commission listed 11 criteria, falling under social, economic, and educational categories, to identify and classify communities as Backward Classes.
- The National Commission for Backward Classes places Backward Classes within the expression of the term “Scheduled Castes.”
- Articles 15 and 16 of the Constitution apply to members of the Other Backward Class communities as well.
- The Mandal Commission submitted its report in 1980.
- early 52% of India’s population fell under OBC category.
- it recommended seat reservations for OBCs, in addition to the existing seat reservations for SCs and STs, in educational institutions and avenues of public employment.
- It stated that the actual number of OBC employees in government ministries, statutory bodies and departments stands at under 12 percent.
- This equates to roughly 9,040 OBC employees out of over 79,483 posts.

- The instrument representing gold will be called 'Electronic Gold Receipt, it will be notified as "securities" under Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956.
- EGRs will have the trading, clearing and settlement features akin to any other security instruments.
- Any recognized stock exchange, existing and new, can launch trading in EGRs in a separate segment.
- Trading of EGR and conversion into gold, will be decided by the recognized stock exchanges, with the approval of the market regulator.
- EGR holder can continue to hold the EGR if intended.
- At his discretion, he can withdraw the underlying gold from the vaults, upon surrender of the EGRs.
- EGRs will be made "fungible" and "inter-operability between Vault Managers" will be allowed to lower the costs associated with withdrawal of gold from the vaults.
- SSE must be Non-Profit Organization (NPO) and For-Profit Social Enterprise (FPE) with social intent and impact.
- It will engage in a social activity out of the 15 eligible activities approved by the Board.
- Eligible Non-Profit Organizations may raise funds through equity, Zero Coupon Zero Principal bonds, Mutual Funds, Social Impact Funds.
- NPOs raising funds on SSE will be required to be registered with SSE.
- Social Venture Funds will be termed as Social Impact Funds (SIFs). The corpus requirements for such funds shall be reduced from ₹ 20 crore to ₹ 5 crore.
- The concept of "muted returns" will be removed.
- Social audit will be mandated for Social Enterprises raising funds/registered on SSE.
- The Board approved an amendment to SEBI Regulations, 1996 to enable introduction of Silver Exchange Traded Funds with certain safeguards including the existing regulatory mechanism for Gold ETFs.
- The government wants India’s outsized influence in the physical market for gold to be visible in the financial market for gold as well.
- It is a way of getting people to not hoard gold, by creating an exchange that provides transparent pricing and liquidity.
- SEBI’s concept proposes, issuing an electronic gold receipt in exchange physical gold, deposited with a vault manager, and this receipt can then be traded.
- It is a basket of securities that trade on an exchange just like a stock.
- ETF share prices fluctuate all day as the ETF is bought and sold.
- It contains all types of investments including stocks, commodities, or bonds.
- They offer low expense ratios and fewer broker commissions than buying the stocks individually does.

- The first Landsat satellite was launched in 1972.
- The satellites have collected images of Earth and helped understand how land usage has changed over the decades.
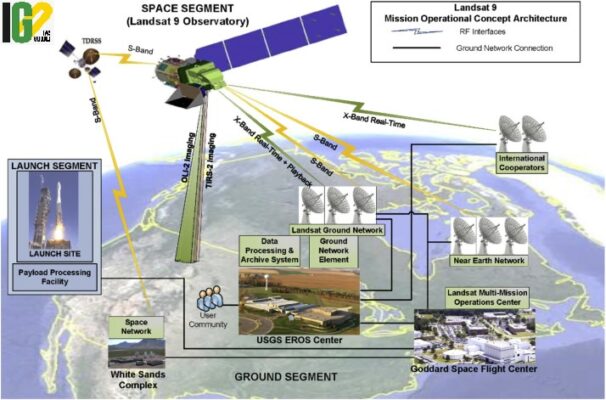
- The earth monitoring satellite, Landsat 9, is a joint mission of NASA and the US Geological Survey (USGS).
- The images have been used to study the health of forests, coral reefs, monitor water quality and melting glaciers.
- The Landsat 9 joins Landsat 8 that was launched in 2013 and the satellites will collect images of Earth’s surface.
- The satellite can see more color shades with greater depths than the previous satellites.
- The satellite has Operational Land Imager 2 (OLI-2) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2).
- OLI-2 will capture sunlight, reflected off Earth’s surface and studies the visible, near-infrared, and short-wave infrared portions of the spectrum.
- TIRS-2 will capture thermal radiation and help to study the Earth’s surface temperature.
- The Landsat will capture images if a forest is affected by drought, it will help to decode the areas at risk.
- During wildfire, the images will capture the plumes of smoke and help to study the extent of a burning.
- It can identify water bodies affected by harmful algal blooms.
- The images helped in the study of melting ice sheets of the Antarctic and Arctic regions.
- It can track cracks in the glaciers, movement of glaciers, and decode how further global warming will impact them.
- It will help the city in better urban governance, upgradation of infrastructure, disaster management, etc.
- The BMC completed 3D mapping of G-south ward, one of the administrative wards in Mumbai. It covers areas like Worli, Mahalaxmi, Elphinstone Road.
- Information regarding the population, civic facilities, houses are available in 3D and can be used in planning of development works.
- The map will be accessible to different departments of the corporation on web application.
- It is the process of preparing a map of the city’s natural areas like water bodies, open spaces, trees and map of man-made features like roads, buildings, and infrastructure facilities in digital format.
- Geospatial Technology was used which is a combination of Global Positioning System (GPS), Geographic Information System (GIS) and Remote Sensing (RS).
- Mobile street imagery vehicles mounted with Light Detection & Ranging (LiDAR) sensors were part of the virtual model.
- The technology will further help in analysis, simulation, visualization, and modelling.
- It will help in development plan, detection of unauthorized changes, building plan approval system.
- It will help in infrastructure planning of roads, bridges, flyover, and urban flood modelling.
- It can assist city planners in reaching local climate resilience, economic development, and housing goals.

- It will identify 75 Start-Up Innovations in Telemedicine, Digital Health, Block Chain, mHealth with BIG Data, Artificial intelligence, and other technologies.
- Launch of Grand Challenge coincides with the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- 75 Chosen Start-ups will be an asset for India to lead it in the next 25 years.
- It was organised by Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) in New Delhi.
- Theme- “Vigyan se Vikash”.
- The minister directed the BIRAC to reach out to Young Start-ups for their help and support.
- Young Innovations will get priority with respect to help, support and hand-holding than the established industrial hubs.
- Bio-Economy in India is on way to achieve 150-billion-dollar target.
- Sunshine Biotech Sector is set to become more than double from 70 billion dollar to 150 billion dollar by 2025.
- BIRAC has established 60 world class Bio-incubators in India.
- It engages with more than 5000 Start-ups and young entrepreneurs.

- The scheme will provide seed capital assistance to members of urban Self-Help Groups working in the food processing sector in India.
- Seed capital is the money raised to begin developing an idea for a business or a new product.
- SHGs will be sensitized and motivated about the Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro food processing Enterprise scheme to avail the benefits of seed capital for purchasing small tools and working capital.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme launched under the Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan
- Aim: To enhance the competitiveness and promote formalization of the unorganized micro—food processing enterprises in India.
- It will provide financial, technical, and business support to 2,00,000 micro food processing units.
- Seed capital support of Rs.40,000 per SHG member.
- Credit linked subsidy for capital investment up to 35% with a ceiling of Rs. 10 lakhs.
- Credit linked grant support up to 35% for establishing common infrastructure.
- Capacity building and training support.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies