- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
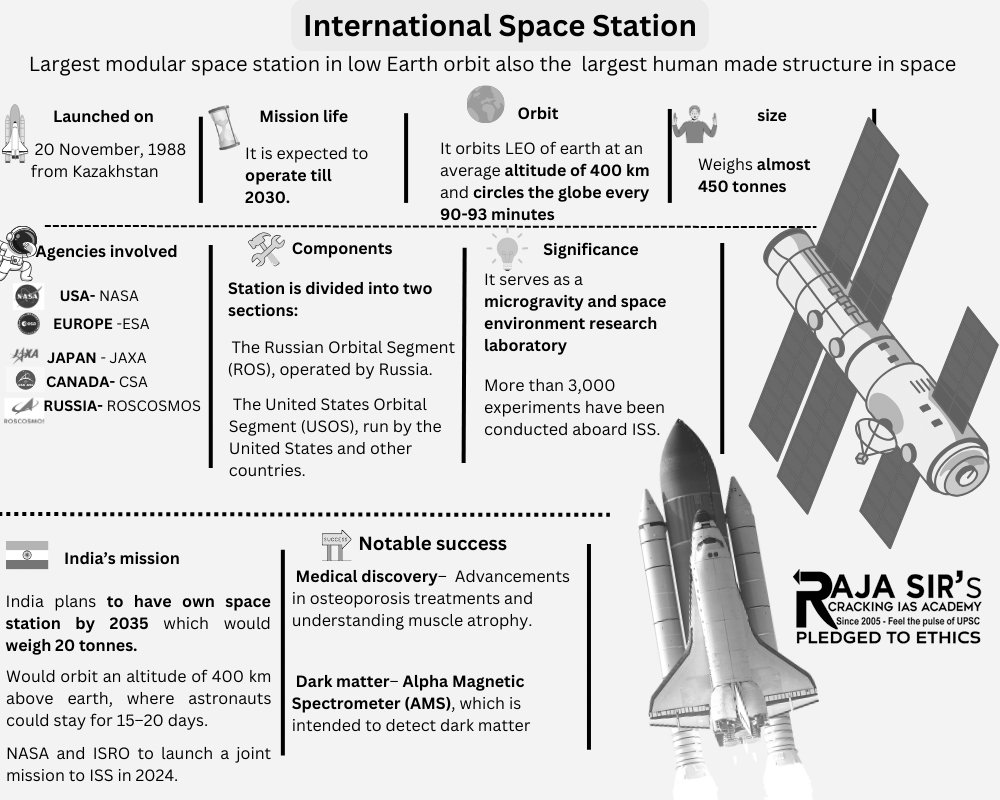
ABC of International Space Station
- It is a habitable artificial satellite, in low Earth orbit (at an altitude of between 370–460 km).
- Key partners for ISS:
- European countries (represented by European Space Agency)
- United States (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
- Japan (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency)
- Canada (Canadian Space Agency) and
- Russia (Roscosmos)
- Its first component was launched into orbit in 1998 and new modules were added as recently as 2021.
- It will continue to be a working laboratory and outpost in orbit until at least 2030.
- ISS was taken into space piece-by-piece and gradually built in orbit, with its assembly requiring more than 40 missions.
Significance of ISS
- Research and Science: It provides opportunities to conduct meaningful studies on topics such as DNA sequencing, robotics, and satellites in microgravity environment which is not possible on Earth.
- Research also includes studying effects of long-term space radiation exposure on the human body.
- International Cooperation: International partnership of space agencies has led to global collaboration in developing space facilities; communications networks, and scientific research.
- Human health: Research is being carried out to study disease formation, testing drugs and diagnostic tools, and examining the inner workings of the human body.
- Low Earth Orbit Economy: ISS is used by small businesses and entrepreneurs to test their technology in space.
- It supports development of new and improved products, and provides growth for commercial ventures.
- Long duration Spaceflight and human habitation: It serves as a testing ground to study how to keep astronauts safe and healthy on long-duration missions.
|
Other Space stations
|
Bharatiya Antariksha Station: India’s own Space Station
|









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies