- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
April 11, 2024 Current Affairs
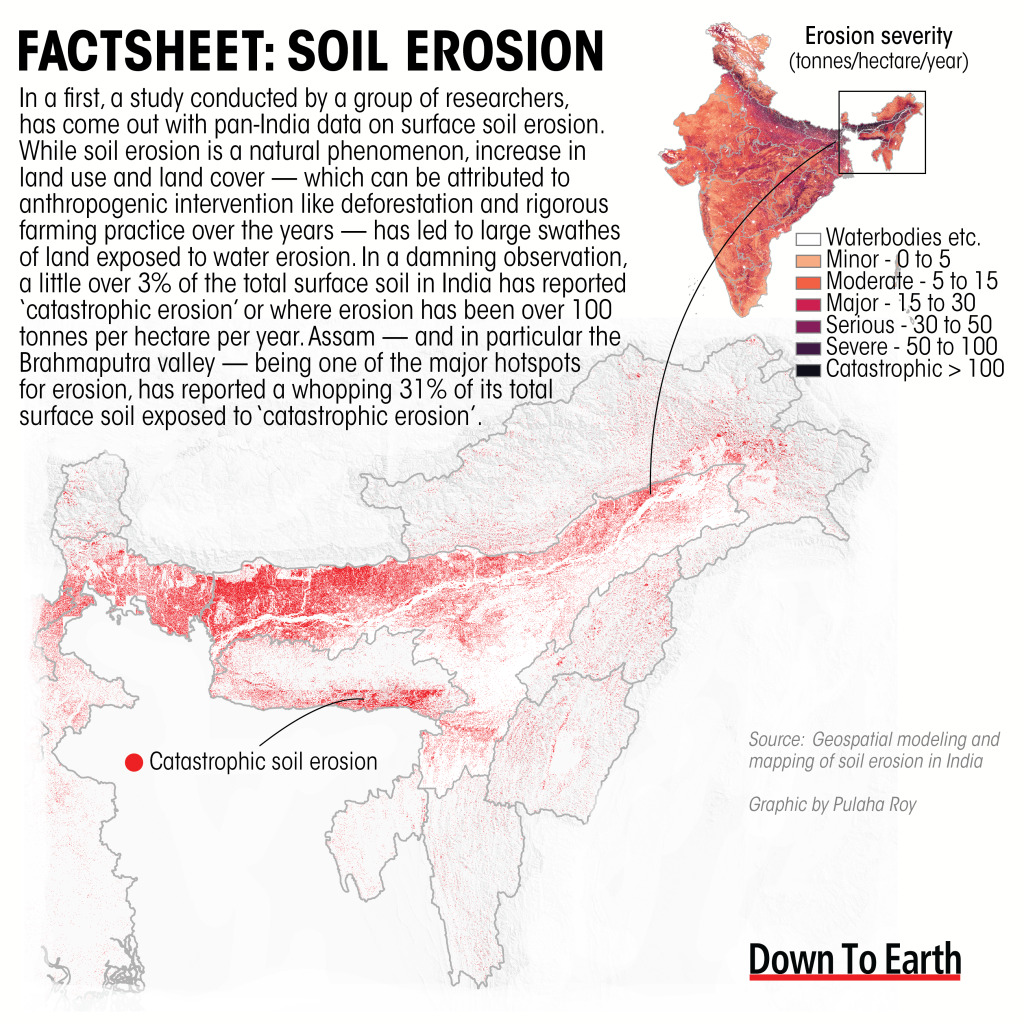
First comprehensive national-scale assessment of soil erosion and sediment yield mapping across India
- The study titled “Geospatial Modeling and Mapping of Soil Erosion in India,” conducted by IIT-Delhi, offers a comprehensive national-scale assessment of soil erosion and sediment yield mapping to facilitate the planning and implementation of soil conservation strategies.
Key highlights of the study:
- Soil erosion, described as the gradual removal of the topmost soil layer by water, wind, and mass movement, leads to long-term soil deterioration and is exacerbated by unsustainable human activities.
- It results in reduced agricultural productivity, sedimentation of water bodies, flooding, landslides, and desertification.
- The study''s key findings include an annual potential soil loss of 21 tonnes/ha/yr in India, with rainfall intensity and topographic factors being the primary contributors to this erosion.
- Over 78 million hectares of farmland suffer from a loss of productivity by an average of 8% annually.
- Approximately 5% of India''s geographical area falls into the catastrophic erosion category, threatening infrastructure like roads and buildings with deep gullies, especially in parts of Assam, Meghalaya, and Himachal Pradesh.
- The Brahmaputra basin faces the maximum potential soil erosion, followed by the Mahanadi and Ganga basins.
Initiatives in India to address soil erosion:
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) aimed at restoring ecological balance by conserving and developing degraded natural resources.
- The Integrated Wasteland Development Programme (IWDP) for improving productivity of waste and degraded lands.
- Participation in the Bonn Challenge under UNCCD, committing to restore 26 million hectares of degraded and deforested land by 2030.
Hurun Global Unicorn Index 2024
Unicorn Company:
- A unicorn company is a privately held startup company that has a valuation of over $1 billion and is not listed on the stock market.
- The term was first popularized by venture capitalist Aileen Lee in 2013, who chose the mythical animal to represent the statistical rarity of such successful ventures.
Key findings of the Index:
- India in 2023 had 67 unicorns, which is one less than 68 such startups in 2022, yet it retains its status as the world''s third-largest hub for unicorns.
- The US led the list with 703 unicorns, up 37 from 2022, and China ranked second with 340 unicorns.
- UK and EU ranked No 4 and No 5 in the list, respectively.
- The total value of the world''s unicorns have reached US$5 trillion, equivalent to year 2022''s GDP of Japan.
- The global count of unicorns surged by 171 over the past year, reaching a total of 1,453, marking a 7% increase and setting a new world record.
- The United States alone added 70 new unicorns, while China added 56.
- However, both countries also experienced the highest number of dropouts, with 21 and 11 companies respectively ceasing to be unicorns.
Declining trends:
- Indian founders are establishing more unicorns abroad than at home.
- The country produced more offshore unicorns than any other country, co-founding 109 unicorns outside of India compared to 67 in India.
- Slowdown of India''s startup ecosystem, which is mainly attributed to a lack of investment in startups.
- Failure to take prudent measures to ensure business sustainability has resulted in uncontrolled growth, marked by rapid depletion of cash reserves.
Initiatives taken by India to promote start-ups:
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): The scheme, launched by the government in 2016, aims to foster innovation by introducing new programs and policies to support startup development across various economic sectors.
- Multiplier Grant Scheme (MGS): The Department of Electronics and Information Technology initiated the Multiplier Grant Scheme (MGS) to empower collaborative research and development among industries for the growth of goods and services.
- Startup India: A program that provides venture capital funds to startups, credit guarantees for loans, and an AI-based matchmaking platform to connect startups with investors.
- SIDBI Fund of Funds: A fund that provides capital to startups and encourages private investments.
- Tax incentives: Tax exemption on capital gains invested in the Fund of Funds, and a 100% deduction of profits and gains from eligible businesses for three consecutive assessment years.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme: The Government of India introduced this scheme in January 2021 to support early-stage startups.
- National Start-up Award: It aims to recognize, promote, and provide exclusive handholding support to a diverse range of startups.
India''s startup ecosystem:
- As of 2023, India has the third largest startup ecosystem in the world, with over 1,12,718 startups recognized by DPIIT across 763 districts.
- The startup ecosystem has experienced exponential growth over the past decade, with a 15% year-on-year growth rate in 2018.
- In 2020, over 16,000 new tech companies were added, and in 2023, investment firms provided a total of $8.4 billion in funding.
- The startup ecosystem has witnessed a 15-fold increase in total funding, a nine-fold increase in the number of investors, and a seven-fold increase in the number of incubators.
C-Dome Defence System of Israel
C-Dome:
- It is the naval version of Israel’s Iron Dome missile defence system, designed to counter aerial threats.
- It was first deployed to respond to a hostile aircraft near Eilat.
Key Features of C-Dome:
- Operates similarly to the Iron Dome, using radar to detect and neutralize threats with missiles.
- Unlike Iron Dome, which is land-based, C-Dome is mounted on ships, specifically on Sa’ar 6-class corvettes, enhancing maritime security.
- Provides 360-degree protection against maritime and coastal threats.
- Uses TAMIR interceptors and a modular Vertical-Launch Unit (VLU) for threat interception.
- Integrated with the ship’s radar system for detecting and tracking threats.
Development and Operational Status:
- Unveiled in 2014 and declared operational in November 2022.
- Tested on German-made Sa’ar 6-class corvettes used by the Israeli Navy.
- Shares technology with the Iron Dome, which has been operational since 2011 with a 90% effectiveness rate.
Strategic Importance
- Ensures high kill probability against modern maritime and coastal threats.
-
C-Dome enhances the defensive capabilities of Israel’s naval forces, providing a robust shield against aerial attacks.
Higgs Boson : God’s Particle
Higgs bosons:
- The Higgs boson, a type of boson, is a force-carrying subatomic particle.
- It carries the force that a particle experiences when traversing the Higgs field(a universal energy field),which is responsible for granting fundamental particles their mass.
- A particle’s mass is directly correlated with its interaction strength with the Higgs boson.
- Therefore, Electrons possess a specific mass, while protons have more, and neutrons slightly surpass protons.
- A Higgs boson can also interact with another Higgs boson — this is how we know that its mass is greater than that of protons or neutrons.
Features:
- The Higgs Boson has a mass of 125 billion electron volts, approximately 130 times more massive than protons.
- It is also chargeless with zero spin,a quantum mechanical equivalent to angular momentum.
- It is only elementary particles with no spin.
Significance of Higgs Boson Study : Researchers aspire to employ the Higgs Boson as a mechanism for learning deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including the enigma of dark matter.
What is a Boson?
- A boson is a “force carrier” particle that comes into play when particles interact with each other, with a boson exchanged during this interaction.
- For example, when two electrons interact they exchange a photon — the force-carrying particle of electromagnetic fields.
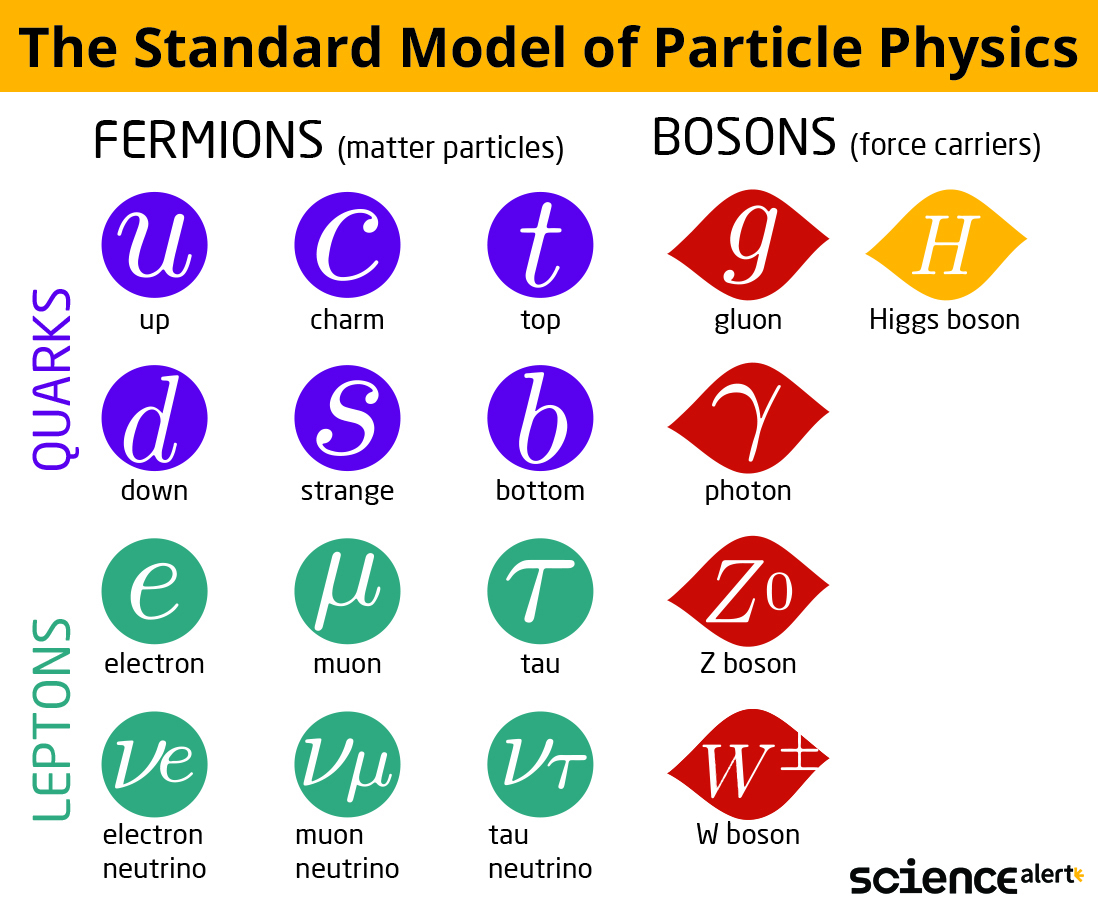
The Standard Model of Particle:
- The Standard Model of Particle Physics is scientists’ current best theory to describe the most basic building blocks of the universe.
- It explains how particles called quarks (which make up protons and neutrons) and leptons (which include electrons) make up all known matter.
- It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons.
- The Standard Model explains three of the four fundamental forces that govern the universe: electromagnetism, the strong force, and the weak force.
- Electromagnetism is carried by photons and involves the interaction of electric fields and magnetic fields.
- The strong force, which is carried by gluons, binds together atomic nuclei to make them stable.
- The weak force, carried by W and Z bosons, causes nuclear reactions that have powered our Sun and other stars for billions of years.
- The fourth fundamental force is gravity, which is not adequately explained by the Standard Model.
Experiments in Large Hadron Collider (LHC) :
- LHC generated a Higgs boson by colliding together billions of high-energy protons which resulted in a release of immense energy that forms various particles.
- Being heavy, the Higgs boson is unstable and breaks down into lighter particles.
- It can decay into a lepton pair and a photon in three different ways.
- Recent evidence indicates Higgs Boson Decay : It says that a Higgs boson will decay to a Z boson and a photon 0.1% of the time.
- This means the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) needed to have created at least 1,000 Higgs bosons to have been able to spot one of them decaying to a Z boson and a photon.
CERN (European Council for Nuclear Research) :
- Aim: To study the basic constituents of matter ie. fundamental particles and to advance the boundaries of human knowledge by delving into the smallest building blocks of our universe.
- Founded in : 1954.
- Location : at Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, Switzerland.
- Member states: 23 members with India being the associate member.
Indian government has introduced a new platform called CDP-SURAKSHA for disbursing subsidies to horticulture farmers under the Cluster Development Programme (CDP)
CDP-SURAKSHA:
- A Digital Platform: The CDP-SURAKSHA is essentially a digital platform that will allow an instant disbursal of subsidies to farmers in their bank account by utilizing the e-RUPI voucher from the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- Access Allowed: It allows access to farmers, vendors, implementing agencies (IA), and cluster development agencies (CDAs), and officials of the National Horticulture Board (NHB).
- Characteristic Features: The CDP-SURAKSHA has features such as database integration with PM-KISAN, cloud-based server space from NIC, UIDAI validation, eRUPI integration, local government directory (LGD), content management system, geotagging, and geo-fencing.
- Aim: To push the growth of India’s horticulture sector, which contributes nearly one-third to the agriculture gross value addition (GVA).
- The total production of horticulture crops has also spiked in recent years. While in 2010-11, it stood at 240.53 million tonnes, the number rose to 334.60 million tonnes in 2020-21.
Significance of the Platform:
- Upfront Subsidies: The CDP-SURAKSHA platform will provide subsidies to farmers upfront, at the time of purchasing the planting material. Vendors, who will supply planting materials to farmers, will receive their payment only after farmers verify the delivery of their orders.
- In the old system, a farmer had to buy planting materials on their own. They would then have to approach the officials concerned for the release of the subsidy.
- The e-RUPI Voucher: The voucher is a one-time payment mechanism that can be redeemed without a card, digital payments app or internet banking access, at the merchants accepting e-RUPI.
- According to the NPCI, the e-RUPI can be shared with the beneficiaries for a specific purpose or activity by organisations or government via SMS or QR code.
About Cluster Development Program (CDP):
- Launched by: The CDP is a component of the central sector scheme of National Horticulture Board (NHB) that was launched by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (MoA&FW) in 2021.
- Aim: It is aimed at leveraging “the geographical specialization of horticulture clusters and promoting integrated and market-led development of pre-production, production, post-harvest, logistics, branding, and marketing activities.”
- So far, 55 horticulture clusters have been identified, out of which 12 have been selected for the pilot. Each cluster will have an implementing agency and a cluster development agency (CDA).
Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI)
Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI)
- About: DESI is a unique piece of equipment that, oncefitted over a telescope, can capture light from 5,000 galaxies at the same time. It is mounted over the Mayall 4-Meter Telescope in Arizona, United States.
- Scheduled Operation: It is scheduled to run for five years. On March 31, DESI completed three years of operations.
- Joint Collaboration: DESI is acollaboration of more than 900 researchers in institutions across the world. From India, TIFR is the only participating institution.
- Preparation of Detailed Map of Universe: Using DESI, researchers have been able to measure light from six million galaxies to prepare the most detailed map of the universe yet with very precise information about the distances between these galaxies.
- The distances between these galaxies have been measured with a very high degree of accuracy. Thus, it is called a three-dimensional map.
- Knowing the precise distances of the galaxies is crucial because that allows us to calculate the expansion rate of the universe.
First year observations of DESI:
- Mapping of the Distribution and Movement of these Galaxies: The precise distances calculated have resulted in the mapping of the distribution and movement of these galaxies over time.
- This has been done by comparing the data with similar data for some of the galaxies obtained through other experiments.
- Measurement of the Expansion Rate of the Universe: The DESI collaboration has measured that the expansion rate of the universe was increasing by 68.5 km per second after every 3.26 million light years of distance, defined as megaparsec.
- Through these precise measurements, the scientists have found that some of the calculated values are not consistent with current well-established theoretical models, which otherwise describe the universe very well.
- Change in Energy Density: The results from DESI suggest that there are changes in energy density in contrast to the theoretical models.
- The theoretical models suggest that the energy density of dark energy, or the amount of dark energy contained in any volume of space, remains constant even under expansion.
- In these theoretical models, a change in energy density would make the universe unstable.
- Significance: Scientists expect that this could reveal some clues about dark energy.
Hypothesis of Dark Energy:
- Dark energy is the mysterious force that is believed to be causing the universe to expand uncontrollably.
- Expanding Universe: The hypothesis comes mainly from the observed phenomenon of the universe expanding at a rapid rate.
- The vast empty spaces between stars and galaxieshave been measured to be expanding at an accelerating pace, despite the countervailing force of gravitation that has the effect of pulling things together.
- Scientists have been unable to find any explanation for this rapid expansion, and have been forced to hypothesize that there must be some “dark” energy causing this expansion.
- Significance: Understanding the nature of dark energy can offer key insights into the origin and evolution of the universe, as well as its eventual fate.
- It can reveal new fundamental forces at work, and could unravel our entire knowledge of the physical world.
Dark energy Vs Dark matter
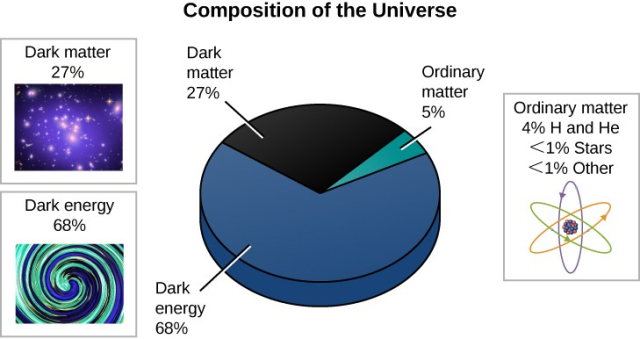
- Composition of the Universe: Dark energy accounts for roughly 68 percent of the universe’s total mass and energy. Dark matter makes up 27 percent.
- The rest i.e., around5 percent is all the regular matter we see and interact with every day.
- Dark matter: It makes up most of the mass of galaxies and galaxy clusters, and is responsible for the way galaxies are organized on grand scales.
- Dark energy: It is the mysterious influence driving the accelerated expansion of the universe.
- Whiledark matter attracts and holds galaxies together, dark energy repels and causes the expansion of our universe.
- Interaction with Gravity: Dark matter does interact with gravity, but it doesn’t reflect, absorb, or emit light. On the other hand, dark energy is a repulsive force — a sort of anti-gravity that drives the universe’s ever-accelerating expansion.
Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) has deployed its sub-metre resolution optical satellite, TSAT-1A
TSAT-1A:
- It is SpaceX’s first dedicated rideshare mission launched into a mid-inclination orbit.
- Other Mission: Alongside TSAT-1A, the Bandwagon-1 mission had 11 other spacecraft.
- These are Korea’s 425Sat, HawkEye 360’s Clusters 8 & 9, Tyvak International’s CENTAURI-6, iQPS’s QPS-SAR-7 TSUKUYOMI-II, and Capella Space’s Capella-14.
- TSAT-1A is a sub-metre resolution optical satellite.
- Developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in collaboration with Satellogic.
- It has been successfully deployed into space by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket as part of the Bandwagon-1 mission.
- It was launched from Kennedy Space centre, Florida.
- It was assembled at TASL’s Assembly, Integration, and Testing plant located at its Vemagal facility in Karnataka, India.
Features
- High-Resolution Optical Images
- Sub-meter resolution for capturing detailed imagery of Earth’s surface.
- Enhanced collection capacity for gathering more data.
- Wider dynamic range for capturing details in both bright and dark areas.
- Low-latency delivery for faster access to captured images.
- TSAT-1A has multispectral and hyperspectral capabilities.
- It is helpful in enhancing its earth observation functionalities.
- Its remote sensing offers information about minerals or vegetation of the surfaces on the Earth.
TSAT-1A Specifications:
Weight and Orbit: It weighs less than 50 kg and is positioned in a low-earth orbit.
Inclined Orbit Benefits: Its inclined orbit configuration enables more frequent revisits to specific areas compared to the Sun Synchronous Polar Orbit (SSPO).
Rs 5-trillion domestic fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) market still faces hurdles on its path to complete recovery from the current slowdown
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG):
- FMCG, or Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG), are products sold quickly and at a relatively low cost.
- The FMCG industry is characterized by high-volume sales, quick inventory turnover, and various products catering to consumer needs.
- These goods include essential everyday items such as food and beverages, toiletries, cleaning supplies, and other low-cost household items.
- FMCGs have a short shelf life because of high consumer demand (e.g., soft drinks and confections) or because they are perishable (e.g., meat, dairy products, and baked goods).
- FMCG Industry in India:
- The FMCG sector is the fourth-largest sector in the Indian economy.
- In 2022, the urban sector accounted for 65% of the overall annual FMCG sales, while rural India contributed over 35%.
- Household and personal care products make up 50% of the industry’s sales, healthcare claims 31-32%, and food and beverage products account for the remaining 18-19%.
- It provides employment to around 3 million people, accounting for approximately 5% of the total factory employment in India.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies