- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
April 16, 2024 Current Affairs
Government to operationalize gas-based power plant to meet high electricity demand during summer.
Steps taken by the government:
- To ensure maximum power generation from Gas-Based Generating Stations, the Government has issued directions to all Gas-Based Generating Stations under Section 11 of the Electricity Act, 2003.
- Section 11 of the Electricity Act, 2003, allows the government to direct a generating company to operate and maintain a generating station in extraordinary circumstances.
Implementation Framework:
- GRID-INDIA will inform Gas-Based Generating Stations in advance of the days when gas-based power is required.
- GRID-INDIA, a division of the Ministry of Power, Government of India, is responsible for the round-the-clock integrated operation of the Indian Power System.
- Stations holding Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) must offer their power to PPA holders first, with any surplus offered in the power market.
- Stations without PPAs must directly offer their generation in the power market.
- A high-level committee led by the Chairperson of the Central Electricity Authority will oversee the implementation of these directives.
Other Measures Undertaken:
- Planned maintenance of power plants will be deferred to the monsoon season.
- New capacity additions will be expedited to augment power supply.
- Partial outages of thermal power plants will be minimized.
- Surplus power from Captive Generating Stations will be utilized, and excess power will be offered for sale in the Energy Exchange.
- The government is promoting a gas-based economy for energy security.
Gas-based economy:
- A gas-based economy is one where gas is the primary source of commercial energy, and natural gas is a major component.
- In 2016, the Government of India (GOI) announced that India would increase the percentage of natural gas in its primary energy basket from 6.14% to 15% by 2030, and become a "gas-based economy".
Significance:
- International commitments: India is moving towards a gas-based economy to meet climate action commitments, including achieving net zero by 2070, reducing emissions intensity by 45%, and reducing total carbon emissions by 1 billion metric tonnes by 2030.
- Cost-effective: Natural gas is more cost-effective than petrol and diesel, and has a higher energy output than other fossil fuels.
- Reduce pollution: Natural gas is cleaner and safer than coal and liquid fuels, contributing to improved air quality.
- When burned for power generation, it emits almost 50% less carbon dioxide than other forms like coal.
- Logistics: Natural gas can be easily stored and delivered through pipelines or liquefied and transported by ship.
- Backup to renewables: Natural gas plants can quickly start up and fill the electricity grid gap when renewables aren''t producing enough, serving as a backup to renewables.
- International geopolitics: Trading in natural gas can provide India with more flexibility in international geopolitics.
Challenges:
- Non-renewable resource: Natural gas is a non-renewable resource that can only be obtained through costly and potentially dangerous drilling.
- Infrastructure: India has inadequate infrastructure to meet its growing energy needs, and the transmission and distribution networks are often ineffective.
- Import dependency: India imports around 45% of its gas, and more than half of its natural gas-based power capacity is idle due to a lack of domestic gas supply.
- High subsidies: The fertilizer sector has the largest share in the overall consumption of natural gas which is highly subsidized.
- Government initiatives to promote gas-based economy:
- City gas distribution (CGD) infrastructure: The GOI is developing networks to deliver Piped Natural Gas (PNG) to homes and businesses, and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for use in vehicles.
- Unified gas pipeline tariffs: In 2023, the GOI implemented unified gas pipeline tariffs to simplify gas pricing and encourage downstream demand.
- National Gas Grid: It is a long-distance pipeline network that aims to ensure equitable distribution of natural gas across India.
- Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT): It is an initiative by the Indian government that encourages entrepreneurs to set up Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) plants.
Union government has recently launched an investigation into organ transplants, focusing on violations of the Transplantation of Human Organs.
Organ transplantation in India:
- Transplantation of Human Organs & Tissues Act THOTA, 1994 is designed to regulate the removal, storage, and transplantation of human organs and tissues exclusively for therapeutic purposes and to curb commercial transactions involving them.
- However, it does not cover artificial organs.
- THOTA was updated in 2011, changing its name from "Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act, 1994" to its current name and it now acknowledges Brain Stem death as a legal form of death, which facilitates more organ and tissue transplants compared to natural cardiac death.
- The National Organ & Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO), a national-level entity under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, coordinates and networks the procurement and distribution of organs and tissues across the country.
Data unavailability
- Despite the Union Heath Ministry writing letters to States time and again for sharing of data related to organ donation and transplantation with NOTTO, complete data were still not being received, the DGHS underscored the need to ensure regular collection and sharing of data of all transplant cases, including those of foreigners, with NOTTO on monthly basis.
Tiny biodegradable straw forts could protect new coral from fish who snack on it ‘like popcorn’
- South Florida researchers trying to prevent predatory fish from devouring laboratory-grown coral are grasping at biodegradable straws in an effort to restore what some call the rainforest of the sea.
- Marine researcher Kyle Pisano and his partner, Kirk Dotson, have developed the Coral Fort—a biodegradable cage crafted partly from drinking straws—to enhance the survival rate of transplanted coral.
- Predators like parrot fish pose a significant threat to newly transplanted coral, often causing survival rates to plummet below 40%.
Coral Fort ( A biodegradable Cage ):
- The cage comprises a limestone disc encircled by eight vertical drinking straws made from a biodegradable material called polyhydroxyalkanoate ( a biopolymer derived from canola oil).
- These straws, initially designed for boba drinks, provide adequate protection for the coral before harmlessly dissolving in the ocean.
- The Coral Fort, designed to dissolve over time, eliminates the need for maintenance or removal.
Significance :
- It helps in reducing the labor-intensive process of protecting and maintaining coral.
- This innovative solution not only enhances the survival of transplanted coral but also streamlines restoration efforts crucial for preserving oceanic biodiversity and coastal resilience against natural disasters like hurricanes.
Parrot Fish relationship with Corals :
- Named for their bright colors and beak-like mouths, Parrotfish are large herbivores that graze on the algae growing atop hard corals.
- They digest the algae and excrete the coral as fine sand.
- Coral sand found on our reefs and even helps to form reef islands.
- It’s estimated a single parrotfish could produce up to 90 kilograms of sand each year.
- In the process of feeding on coral polyps, parrotfish may actually help spread the beneficial zooxanthellae algae that corals cultivate.
- This sort of cross-pollination results in more genetically diverse and resilient reefs.
- An even more important benefit of all this chewing on the reef is the removal of light-leaching algae from the surfaces of corals.
Corals :
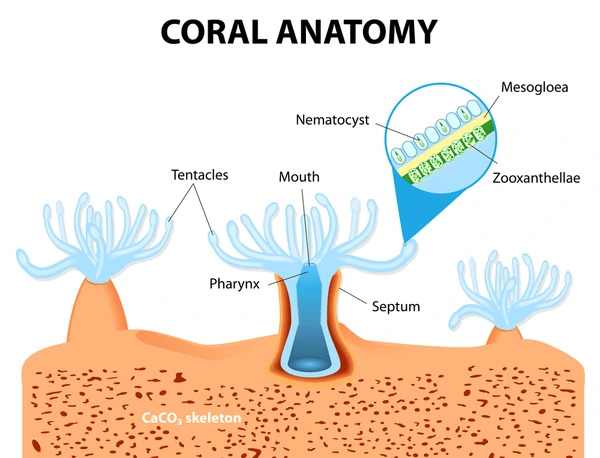
- Corals are colonial marine invertebrates of the phylum Cnidaria.
- Polyp: An individual coral is known as a polyp.
- A polyp is a sac-like animal,excretes an exoskeleton near the base.
- Polyps form a symbiotic relationship with plant-like cells called zooxanthellae (unicellular dinoflagellates).
- Symbiotic Relationship: Coral Polyp can ingest tiny organisms called plankton & other small creatures but still majority of their energy and nutrients they get from the zooxanthellae living within their tissues which also is responsible for giving the corals its color. In return corals provide the zooxanthellae with shelter and protection.
Coral Reefs :
- Coral reefs are formed when thousands of polyps living together in a coral colony secretes calcium carbonate exoskeleton beneath it. Over time, the skeletons of many coral colonies add up to build the structure of a coral reef.
- Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforest of the sea,” are crucial ecosystems supporting over 25% of marine species. However, the decline of coral populations due to various factors, including rising ocean temperatures, has prompted urgent conservation measures.
Significance of coral reef ecosystems:
- Coral reefs protect coastlines from harsh ocean storms and floods.
- They serve as nurseries, and breeding and feeding grounds for marine wildlife.
- They provide livelihood opportunities through tourism and fishery for coastal communities. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), about 500 million people worldwide are dependent on coral reefs for livelihood.
The Indian Army contingent departed recently for the 5th edition of India- Uzbekistan joint military Exercise DUSTLIK.
Exercise Dustlik:
- It is an annual joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Uzbekistan Army.
- It is conducted alternately in India and Uzbekistan.
- The first edition of the exercise was held in Uzbekistan in November 2019.
- The last edition was conducted in Pithoragarh in February 2023.
Dustlik-2024:
- It is the fifth edition of the joint exercise.
- The exercise will be conducted at Termez in Uzbekistan.
- The Indian Armed Forces contingent, comprising 60 personnel, is being represented by 45 personnel from the Indian Army, primarily from a battalion of the JAT Regiment, and 15 personnel from the Indian Air Force.
- The Uzbekistan contingent, comprising approximately 100 personnel, from the Uzbekistan Army and Air Force, will be represented by personnel from Southern Operational Command, part of the South-West Military District.
- The aim of Exercise DUSTLIK is to foster military cooperation and enhance combined capabilities to execute joint operations in mountainous as well as semi urban terrain.
- It would focus on a high degree of physical fitness, joint planning, joint tactical drills, and the basics of special arms skills.
- The complexity of this edition of Exercise DUSTLIK has been enhanced with the conduct of multi domain operations, as the contingent comprises personnel from combat support arms and services besides infantry.
World's First Orbiter that allows Smartphones to make direct Satellite Calls.
- Chinese engineers have developed the world’s first satellite series (Tiantong-1) allowing direct calls from smartphones without the need for ground-based infrastructure using Base Transceiver Station (BTS) or cellular towers.
Chinese Satellite Communication Technology (SCT):
- The satellite is part of the Tiantong Project, initiated after the 2008 Sichuan earthquake to enhance communication resilience.
- Named after the term "connecting with heaven", the project aims to provide universal communication access, unaffected by socio-economic status.
- The satellite system, Tiantong-1 series, consists of three satellites placed in geosynchronous orbit at 36,000 kilometers altitude, covering the Asia-Pacific region from the Middle East to the Pacific Ocean. This orbit allows the satellites to keep pace with the rotation of the Earth.
- Huawei Technologies introduced the world’s first smartphone capable of making satellite calls in September 2023, compatible with Tiantong satellites, followed by other Chinese brands like Xiaomi, Honor, and Oppo.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies